Abstract
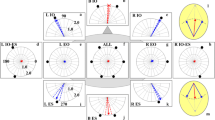
The authors studied postural responses to bilateral vibratory stimulation (70 Hz, 1 mm, 2 s) of the calf triceps proprioceptors or anterior tibial muscles. Anteroposterior body tilts evoked by vibration were recorded by stabilography. The authors compared the values of postural responses under various conditions of visual control, namely, with normal vision, eyes closed, right–left inversion of the visual space by prismatic spectacles, central vision, and diffuse light. Visual inversion influenced the subjects' proprioceptive postural responses. The amplitude of vibration-evoked shifts of the feet pressure center was minimal with eyes open and significantly increased with eyes closed and inverted vision. Postural responses with visual inversion were significantly stronger than with eyes closed. Since inversion spectacles enabled a subject to see only the central part of the visual field (20°), the reference point was the condition of central vision, i.e., spectacles with same visual angle and without prisms. Postural responses were significantly weaker under these conditions than with visual inversion and eyes closed. Visual field inversion by prismatic spectacles made it impossible to use visual information for stabilizing the human upright posture and, moreover, destabized it. True, this holds only for a randomized experimental protocol, which prevents adaptation to prisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Shumway-Cook, A. and Horak, F.B., Assessing the Influence of Sensory Interaction of Balance: Suggestion from the Field, Phys. Ther., 1986, vol. 66, no. 10, p. 1548.
Rushton, D.N., Brandt, T., Paulus, W., and Krafczyk, S., Postural Sway during Retinal Image Stabilisation, J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry, 1989, vol. 52, no. 3, p. 376.
Peterka, R.J. and Black., F.O., Age-related Changes in Human Posture Control: Sensory Organization Tests, J. Vestib. Res., 1991, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 73.
Hamid, M.A., Clinical Patterns of Dynamic Posturography, in Dizziness and Balance Disorders, Arenberg, I.K., Ed., Amsterdam; New York: Kugler, 1993, p. 377.
Soechting, J.F. and Berthoz, A., Dynamic Role of Vision in the Control of Posture in Man, Exp. Brain Res., 1979, vol. 36, no. 3, p. 551.
Ledin, T. and Odkvist, L.M., Visual Influence on Postural Responses to Sudden Antero-Posterior Support Surface Movements, Acta Otolaryngol. Stockh., 1991, vol. 111, no. 5, p. 813.
Smetanin, B.N., Popov, K.E., and Shlykov, V.Yu., Dependence of Changes in Vestibular Postural Responses on the Information Content of Visual Feedback, Neirofiziologiya, 1990, vol. 22, no. 1, p. 80.
Yardley, L., Lerwill, H., Hall, M., and Gresty, M., Visual Destabilisation of Posture in Normal Subjects, Acta Otolaryngol. Stockh., 1992, vol. 112, p. 14.
Lestienne, F., Soechting, J., and Berthoz, A., Postural Readjustments Induced by Linear Motion of Visual Scenes, Exp. Brain Res., 1977, vol. 28, no. 3-4, p. 363.
Bronstein, A.M., Suppression of Visually Evoked Postural Responses, Exp. Brain Res., 1986, vol. 63, no. 3, p. 655.
Popov, K.E., Kozhina, G.V., Smetanin, B.N., and Shlikov, V.Yu., Postural Responses to Combined Vestibular and Hip Proprioceptive Stimulation in Man, Eur. J. Neurosci., 1999, vol. 11, no. 9, p. 3307.
Gurfinkel', V.S., Kots, Ya.M., and Shik, M.L., Regulyatsiya pozy cheloveka (Human Postural Control), Moscow: Nauka, 1965.
Collins, J.J. and De Luca, C.J., The Effect of Visual Input on Open-Loop and Closed-Loop Postural Control Mechanisms, Exp. Brain Res., 1995, vol. 103, no. 1, p. 151.
Dijkstra, T.M., Schoner, G., and Gielen, C.C., Temporal Stability of Action-Perception Cycle for Postural Control in a Moving Visual Environment, Exp. Brain Res., 1994, vol. 97, no. 3, p. 477.
Gonshor, A. and Jones, G.M., Postural Adaptation to Prolonged Optical Reversal of Vision in Man, Brain Res., 1980, vol. 192, no. 1, p. 239.
Fitzpatrick, R. and McCloskey, D.I., Proprioceptive, Visual and Vestibular Thresholds for the Perception of Sway during Standing in Humans, J. Physiol. (London), 1994, vol. 478, no. 1, p. 173.
Fukuoka, Y., Tanaka, K., Ishida, A., and Minamitani, H., Characteristics of Visual Feedback in Postural Control during Standing, IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. Dec., 1999, vol. 7, no. 4, p. 427.
Nashner, L.M. and Berthoz, A., Visual Contribution to Rapid Motor responses during Postural Control, Brain Res., 1978, vol. 150, no. 2, p. 403.
Robinson, D.L. and Rugg, M.D., Latencies of Visually Responsive Neurons in Various Regions of the Rhesus Monkey Brain and Their Relation to Human Visual Responses, Biol. Psychol., 1988, vol. 26, p. 111.
Fitzpatrick, R., Burke, D., and Gandevia, S.C., Taskdependent Reflex Responses and Movement Illusions Evoked by Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation in Standing Humans, J. Physiol., 1994, vol. 478, no. 2, p. 363.
Van Asten, W.N., Gielen, C.C., and van der Gon, J.J., Postural Movements Induced by Rotations of Visual Scenes, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A., 1988, vol. 5., no. 10, p. 1781.
Maurer, C., Mergner, T., Bolha, B., and Hlavacka, F., Vestibular, Visual, and Somatosensory Contributions to Human Control of Upright Stance, Neurosci. Lett., 2000, vol. 281, no. 2-3, p. 99.
Hlavacka, F., Krizkova, M., and Horak, F.B., Modification of Human Postural Response to Leg Muscle Vibration by Electrical Vestibular Stimulation, Neurosci. Lett., 1995, vol. 189, no. 1, p. 9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smetanin, B.N., Popov, K.E. & Kozhina, G.V. Human Postural Responses to Vibratory Stimulation of Calf Muscles under Conditions of Visual Inversion. Human Physiology 28, 556–560 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020274717931
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020274717931