Abstract
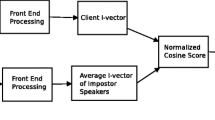
This paper presents the use of distance normalization techniques in order to improve speaker verification system performance. These techniques provide a dynamic threshold that compensates for the trial-to-trial variations and replaces the fixed threshold used in the classical speaker verification approach. Two methods are described: the cohort model normalization and a new and original hybrid cohort-world model normalization. These methods are compared from the point of view of storage space requirements and computational effort. Two algorithms are proposed: one uses existing user models, and the other creates new models. The algorithms were evaluated using the YOHO database and a proprietary database. The results showed that using these methods, the errors of false rejection are significantly reduced for a constant false acceptance error, when the cohort size is increasing. The algorithms also involve fewer computational resources than other algorithms, making them more suitable for commercial application.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beigi, H., Maes, S., and Sorensen, J. (1998). A distance measure between collections of distributions and its application to speaker recognition. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ICASSP'98 Proceedings, vol. 2, pp. 753–756.
Besacier, L. and Bonastre, J.F. (1998). Frame pruning for speaker recognition. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP'98 Proceedings, pp. 211–214.
Bryan, L.P. and Hansen, J.H.L. (1999). An experimental study of speaker verification sensitivity to computer voice-altered imposters. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP'99 Proceedings, vol. 2, pp. 833–836.
Campbell, W.M. (2001). A sequence kernel and its application to speaker recognition. Neural Information Processing System, NIPS 2001 Proceedings, Vancouver, Canada.
Carey, M.J. and Parris, E.S. (1992). Speaker verification using connected words. Proc. Institute of Acoustics, vol. 14, part 6, pp. 95–100.
Che, C.W., Lin, Q., and Yuk, D.-S. (1996). AHMMapproach to textprompted speaker verification. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP'96 Proceedings, vol. 2, pp. 673–676.
Furui, S. (1994). An overview of speaker recognition technology. Workshop on Automatic Speaker Recognition, Identification and Verification, ESCA'94 Proceedings, pp. 1–9.
Isobe, T. and Takahashi, J. (1999). A new cohort normalization using local acoustic information for speaker verification. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP'99 Proceedings, vol. 2, pp. 841–844.
James, D., Hutter, H.P., and Bimbot, F. (1997). The CAVE speaker verification project-Experiments on the YOHO and SESP Corpora. International Conference on Audio-and Video-Based Biometric Personal Authenticatio, AVBPA'97 Proceedings, Crans-Montana, Switzerland.
Liu, C.-S., Wang, H.-C., and Lee, C. (1996). Speaker verification using normalized log-likelihood score. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 4(1):56–64.
Nakagawa, S. and Markov, K.P. (1997). Speaker verification using frame and utterance level likelihood normalization. SPCHL'97 Proceedings, vol. 2, pp. 1087–1091.
Rosenberg, A.E., DeLong, J., Lee, C.-H., Juang, B.-H., and Soong, F.-K. (1992). The use of cohort normalized scores for speaker verification. International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, ICSLP'92 Proceedings, pp. 599–602.
Rosenberg, A.E. and Parthasarathy, S. (1996). Speaker background models for connected digit password speaker verification. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP'96 Proceedings, pp. 81–84.
Sonmez, K., Heck, L., and Weintraub, M. (2000). Multiple speaker tracking and detection: Handset normalization and duration scoring. Digital Signal Processing, 10(1-3):133–143.
Thyes, O., Kuhn, R., Nguyen, P., and Junqua, J.-C. (2000). Speaker identification and verification using eigenvoices. International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, ICSLP 2000 Proceedings, Beijing.
Yu, G. and Gish, H. (1993). Identification of speakers engaged in dialog. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, ICASSP'93 Proceedings, vol. II, pp. 383–386.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burileanu, C., Moraru, D., Bojan, L. et al. On Performance Improvement of a Speaker Verification System Using Vector Quantization, Cohorts and Hybrid Cohort-World Models. International Journal of Speech Technology 5, 247–257 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020244924468
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020244924468