Abstract
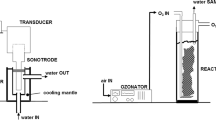
A new type of electrochemical reactor for use in electrochemical water disinfection was tested. To solve the problem of the formation of calcium carbonate scales on the cathode surface a cathode which simultaneously acts as a sonotrode was used. This sonotrode is an efficient means for in situ cleaning the cathode surface from calcareous deposits formed during hydrogen evolution from potable water. The production rate of active chlorine from potable water in the new reactor in dependence on current, ultrasound intensity, and flow-through velocity was measured. The production of active chlorine is not significantly changed by the effect of ultrasound.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.E. Stoner, G.L. Cahen, Jr., M. Sachyani and E. Gileadi, Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 9 (1982) 229.
G. Patermarakis and E. Fountoukidis, Wat. Res. 24 (1990) 1491.
A. Kraft, M. Stadelmann, M. Blaschke, D. Kreysig, B. Sandt, F. Schröder and J. Rennau, J. Appl. Electrochem. 29 (1999) 861.
A. Kraft, M. Blaschke, D. Kreysig, B. Sandt, F. Schröder and J. Rennau, J. Appl. Electrochem. 29 (1999) 895.
J. Miller, US Patent 4 048 030 (1977).
F. Stummer and J. Miller, US Patent 4 169 035 (1979).
D. Colvin and V.A. Schultz, US Patent 3 378 479 (1968).
M. Blaschke, A. Kraft, H. Petzer and M. Suchi, German Patent Appl., 19 836 431 (1998).
M.A. Silveri, US Patent 5 885 426 (1999).
D.J. Walton, L.D. Burke and M.M. Murphy, Electrochim. Acta 41 (1996) 2747.
R.G. Compton, J.C. Eklund and F. Marken, Electroanalysis. 9 (1997) 509.
R.G. Compton, J.C. Eklund, F. Marken, T.O. Rebbit, R.P. Akkermans and D.N. Waller, Electrochim. Acta 19 (1997) 2919.
P.W. Davies, S.H. Greenhaigh, J.K. Donnelly and E.I. Stentiford, UK Patent Appl., 2 265 615 (1993)
S.A. Masri, US Patent 4 961 860 (1990).
I. Hua and J.E. Thompson, Wat. Res. 34 (2000) 3888.
I.E.C. Mott, D.J. Stickler, W.T. Coakley and T.R. Bott, J. Appl.Microbiol. 84 (1998) 509.
American Public Health Association, 'Standard Methods for the Examination ofWater and Wastewater', 18th edn, American Public Health Association APHA, Washington DC (1992), p. 4–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kraft, A., Blaschke, M. & Kreysig, D. Electrochemical water disinfection Part III: Hypochlorite production from potable water with ultrasound assisted cathode cleaning. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry 32, 597–601 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020199313115
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020199313115