Abstract
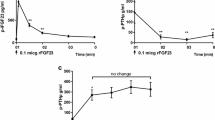
Calcium disturbances in the critically ill coincide with elevations of proinflammatory cytokines. The effects of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) on parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion were investigated. IL-6 and TNF-α had no acute effect on PTH secretion in extracellular Ca2+ concentrations of 0.5, 1.25 and 3.0 mM. In contrast to TNF-α, cultures for 24 h in the presence of l0 ng/mL of IL-6 showed decreased PTH secretion by 51% and 29% in 0.5 mM and 1.25 mMCa2+ respectively. Neither IL-6 nor TNF-α, affected cytoplasmic Ca2+ of the cells. We conclude that PTH secretion in vitro can be suppressed by IL-6 at clinically relevant concentrations. This suppression may aggravate hypocalcemia of the critically ill and attenuate the conventionally strong stimulation of the PTH release by reduction in serum calcium.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Burchard, K. W., Gann, D. S., Colliton, J., and Forster, J. (1990) Ionized calcium, parathormone, and mortality in critically ill surgical patients. Ann. Surg. 212:543-9.
Zaloga, G. P. (1992) Hypocalcemia in critically ill patients. Crit. Care Med. 20:251-62.
McKay, C., Beastall, G. H., Imrie, C. W., and Baxter, J. N. (1994) Circulating intact parathyroid hormone levels in acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg 81:357-60.
Desai, T. K., Carlson, R. W., and Geheb, M. A. (1988) Prevalence and clinical implications of hypocalcemia in acutely ill patients in a medical intensive care setting. Am. J. Med. 84:209-14.
Henderson, S. A., Graham, H. K., and Mollan, R. A. (1992) Serum and other calcium fractions in patients after severe musculoskeletal trauma. Clin. Orthop. 275:306-311.
Forman, D. T. and Lorenzo, L. (1991) Ionized calcium: its significance and clinical usefulness. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 21:297-304.
Carlstedt, F., Lind, L., Wide, L., et al. (1997) Serum levels of parathyroid hormone are related to the mortality and severity of illness in patients in the emergency department [see comments]. Eur. J. Clin. Invest 27:977-981.
Zaloga, G. P. and Chernow, B. (1987) The multifactorial basis for hypocalcemia during sepsis. Studies of the parathyroid hormone-vitamin D axis. Ann. Intern. Med. 107:36-41.
Dettelbach, M. A., Deftos, L. J., and Stewart, A. F. (1990) Intraperitoneal free fatty acids induce severe hypocalcemia in rats: a model for the hypocalcemia of pancreatitis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 5:1249-55.
Bone, R. C. (1996) Toward a theory regarding the pathogenesis of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome: what we do and do not know about cytokine regulation. Crit. Care Med. 24:163-72.
Modawer, L. L. (1994) Biology of proinflammatory cytokines and their antagonists. Crit. Care Med. 22:S3-S7.
Hotchkiss, R. S. and Karl, I. E. (1996) Calcium: a regulator of the inflammatory response in endotoxemia and sepsis. New Horiz. 4:58-71.
Damas, P., Ledoux, D., Nys, M. et al. (1992) Cytokine serum level during severe sepsis in human IL-6 as a marker of severity. Ann. Surg. 215:356-62.
Carlstedt, F., Lind, L., and Lindahl, B. (1997) Proinflammatory cytokines, measured in a mixed population on arrival in the emergency department, are related to mortality and severity of disease. J. Intern. Med. 242:361-5.
Ridefelt, P., Bjorklund, E., Akerstrom, G., Olsson, M., Rastad, J., and Gylfe, E. (1995) Ca2+-induced Ca2+ oscillations in parathyroid cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 215:903-909.
Juppner, H., Rosenblatt, M., Segre, G., and Hesch, R. (1983) Discrimination between intact and mid-C regional PTH using selective radioimmunoassay systems. Acta Endocrinol 102:543-548.
Grynkiewicz, G., Poenie, M., and Tsien, R. (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluoroscence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 260:3440-3450.
Hirano, T. (1998) Interleukin 6 and its receptor: ten years later. Int. Rev. Immunol. 16:249-284.
Ershler, W., Harman, S., and Keller, E. (1997) Immunologic aspects of osteoporosis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 21:487-499.
Gray, A., Mitnick, M., Shapses, S., Ellison, A., Gundberg, C., and Insogna, K. (1996) Circulating levels of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha are elevated in primary hyperparathyroidism and correlate with markers of bone resorption-a clinical research study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81:3450-3454.
Silverberg, S. and Bilezikian, J. (1996) Cytokines in primary hyperparathyroidism-factors that matter. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81:3448-3449.
af Ekenstam, E., Benson, L., Hallgren, R., Wide, L., and Ljunghall, S. (1990) Impaired secretion of parathyroid hormone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: relationship to inflammatory activity. Clin. Endocrinol. Oxf. 32:323-8.
Brown, E. M. (1991) Extracellular Ca2+ Sensing, Regulation of Parathyroid Cell Function, and Role of Ca2+ and Other Ions as Extracellular (First) Messengers. Phys. Rev. 71:371-411.
Vandenabeele, P., Declerq, W., Beyaert, R., and Fiers, W. (1995) Two tumour necrosis factor receptors: structure and function. Trends Cell Biol. 5:392-399.
Masumoto, N., Tasaka, K., Kasahara, K., Miyake, A., and Tanizawa, O. (1991) Purification of gonadotropes and intracellular free calcium oscillation. Effects of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and interleukin-6. J. Biol. Chem. 266:6485-6488.
Nielsen, P., Rasmussen, A., Butters, R. et al. (1997) Inhibition of PTH secretion by interleukin-1 beta in bovine parathyroid glands in vitro is associated with an up-regulation of the calcium-sensing receptor mRNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 238:880-885.
Weber, M., Michl, P., Auernhammer, C., and Engelhardt, D. (1997) Interleukin-3 and interleukin-6 stimulate cortisol secretion from adult human adrenocortical cells. Endocrinology 138:2207-2210.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carlstedt, E., Ridefelt, P., Lind, L. et al. Interleukin-6 Induced Suppression of Bovine Parathyroid Hormone Secretion. Biosci Rep 19, 35–42 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020146023812
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020146023812