Abstract
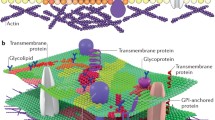
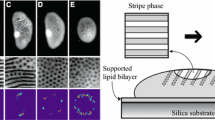
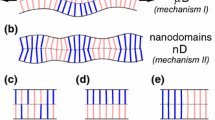
Both biomembranes and biomimetic membranes such as lipid bilayers withseveral components contain intramembrane domains and rafts.Macromolecules, which are anchored to the membrane but have no tendeney tocluster, induce curved nanodomains. Clustering of membrane componentsleads to larger domains which can grow up to a certain maximal size andthen undergo a budding process. The maximal domain size depends on theinterplay of spontaneous curvature, bending rigidity, and line tension.It is argued that this interplay governs the formation of bothclathrin-coated buds and caveolae. Finally, membrane adhesion often leadsto domain formation within the contact zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lipowsky, R.: (a) Budding of membranes induced by intramembrane domains, J. Phys. II France 2 (1992), 1825–1840; (b) Domain-induced budding of fluid membranes, Biophys. J. 64 (1993), 1133–1138.
Jülicher, F. and Lipowsky, R.: (a) Domain-induced budding of vesicles, Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 (1993), 2964–2967; (b) Shape transformations of inhomogeneous vesicles with intramembrane domains, Phys. Rev. E 53 (1996), 2670–2683.
Kumar, S., Gompper, G. and Lipowsky, R.: Budding dynamics of multicomponent membranes, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 (2001), 3911–3914.
Döbereiner, H.-G., Käs, J., Noppl, D., Sprenger, I. and Sackmann, E.: Budding and fission of vesicles, Biophys. J. 65 (1993), 1396–1403.
Bradley, A.J., Maurer-Spurej, E., Brooks, D.E. and Devine, D.V.: Unusual electrostatic effects on binding of C1q to anionic liposomes: Role of anionic phospholipid domains and their line tension, Biochemistry 38 (1999), 8112–1823.
Holopainen, J.M., Angelova, M.I. and Kinnunen, P.K.J.: Vectorial budding of vesicles by asymmetrical enzymatic formation of ceramide in giant liposomes, Biophys. J. 78 (2000), 830–838.
Schekman, R. and Orci, L.: Coat proteins and vesicle budding, Science 271 (1996), 1526–1533.
Simons, K. and Ikonen, E.: Functional rafts in cell membranes, Nature 387 (1997), 569–572.
Jacobson, K. and Dietrich, C.: Looking at lipid rafts?, Trends in Cell Biology 9 (1999), 87–91.
Huttner, W.B. and Zimmerberg, J.: Implications of lipid microdomains formembrane curvature, budding and fission, Curr. Opinion Cell Biol. 13 (2001), 478–484.
Thompson, T.E. and Tillack, T.W.: Organization of glycosphingolipids in bilayers and plasma membranes of mammalian cells, Ann. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 14 (1985), 361–386.
Sek Wen Hui: The spatial distribution of cholesterol in membranes, in: P.L. Yeagle (ed.), Biology of cholesterol, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1988.
Scheiffele, P., Rietveld, A., Wilk, T. and Simons, K.: Influenza viruses select ordered lipid domains during budding from the plasma membrane, J. Biol. Chem. 247 (1999), 2038–2044.
Lu, X. and Silver, J.: Ecotropic murine leukemia virus receptor is physically associated with caveolin and membrane rafts, Virology 276 (2000), 251–258.
Keller, S.L., Pitcher III, W.H., Huestis, W.H. and McConnell, H.M.: Red blood cell lipids form immiscible liquids, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 (1998), 5019–5022.
Dietrich, C., Bagatolli, L.A., Volovyk, Z.N., Thompson, N.L., Levi, M., Jacobson, K. and Gratton, E.: Lipid rafts reconstituted in model membranes, Biophys. J. 80 (2001), 1417–1428.
Korlach, J., Schwille, P., Webb, W.W. and Feigenson, G.W.: Characterization of lipid bilayer phases by confocal microscopy and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96 (1999), 8461–8466.
Bagatolli, L.A. and Gratton, E.: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy observation of shape changes at the phase transition in phospholipid giant unilamellar vesicles, Biophys. J. 77 (1999), 2090–2101.
Lipowsky, R.: Bending of membranes by anchored polymers, Europhys. Lett. 30 (1995), 197–202.
Hiergeist, C. and Lipowsky, R.: Elastic properties of polymer-decorated membranes, J. Phys. France 6 (1996), 1465–1481.
Breidenich, M., Netz, R. and Lipowsky, R.: The shape of polymer-decorated membranes, Europhys. Lett. 49 (2000), 431–437.
Hiergeist, C., Indrani, V.A. and Lipowsky, R.: Membranes with anchored polymers at the adsorption transition, Europhys. Lett. 36 (1996), 491–496.
Breidenich, M., Netz, R. and Lipowsky, R.: Adsorption of polymers anchored to membranes, Eur. Phys. J. E 5 (2001), 403–414.
Decher, G., Kuchinka, E., Ringsdorf, H., Venzmer, J., Bitter-Suermann, D. and Weisgerber, C.: Interaction of amphiphilic polymers with model membranes, Angew. Makromol. Chem. 166/167 (1989), 71–80.
Simon, J., Kühner, M., Ringsdorf, H. and Sackmann, E.: Polymer-induced shape changes and capping in giant liposomes, Chem. Phys. Lipids 76 (1995), 241–258.
Döbereiner, H.G., Lehmann, A., Goedel, W., Selchow, O. and Lipowsky, R.: Membrane curvature induced by sugar and polymer solutions, in: B. Mulder, C.F. Schmidt and V. Vogel (eds.), Materials Science of the Cell 489, of Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., pp. 101–106, MRS, Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 1998.
Frette, V., Tsafrir, I., Guedeau-Boudeville, M.A., Jullien, L., Kandel, D. and Stavans, J.: Coiling of cylindrical membrane stacks with anchored polymers, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 (1999), 2465–2468.
Jakobs, B., Sottmann, T., Strey, R., Allgaier, J., Willner, L. and Richter, D.: Amphiphilic block copolymers as efficiency boosters for microemulsions, Langmuir 15 (1999), 6707–6711.
Tsafrif, I., Guedeau-Boudeville, M.A., Kandel, D. and Stavans, J.: Coiling instability of multilamellar membrane tubes with anchored polymers, Phys. Rev. E 63 (2001), 031603/1–11.
Gompper, G., Edo, H., Mihailescu, M., Allgaier, J., Monkenbusch, M., Richter, D., Jakobs, B., Sottmann, T. and Strey, R.: Measuring bending rigidity and spatial renormalization in bicontinuous microemulsions, Europhys. Lett. (in press).
Dimova, R., Döbereiner, H.G. and Lipowsky, R.: In preparation.
Lipowsky, R., Döbereiner, H.G., Hiergeist, C. and Indrani, V.: Membrane curvature induced by polymers and colloids, Physica A 249 (1998), 536–543.
Duwe, H.P., Käs, J. and Sackmann, E.: Bending elastic moduli of lipid bilayers: Modulation by solutes, J. Phys. France 51 (1990), 945–962.
Benvegnu, D.J. and McConnell, H.M.: Line tension between liquid domains in lipid monolayers, J. Phys. Chem. 96 (1992), 6820–6824.
Goetz, R., Gompper, G. and Lipowsky, R.: Mobilitiy and elasticity of self-assembled membranes, Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 (1999), 221–224.
Pralle, A., Keller, P., Florin, E.L., Simons, K. and Hörber, J.K.H.: Sphingolipid-cholesterol rafts diffuse as small entities in the plasma membrane of mammalian cells, J. Cell Biol. 148 (2000), 997–1007.
Brown, D.A. and London, E.: Structure and origin of ordered lipid domains in biological membranes, J. Membrane Biol. 164 (1998), 103–114.
Harder, T., Scheiffele, P., Verkade, P. and Simons, K.: Lipid domain structure of the plasma membrane revealed by patching of membrane components, J. Cell. Biol. 141 (1998), 929–942.
Nardi, J., Feder, T., Bruinsma, R. and Sackmann, E.: Electrostatic adhesion between fluid membranes: phase separation and blistering, Europhys. Lett. 37 (1997), 371–376.
Albersdörfer, A., Feder, T. and Sackmann, E.: Adhesion-induced domain formation by interplay of long-range repulsion and short-range attraction force: A model membrane study, Biophys. J. 73 (1997), 245–257.
Braun, D. and Fromherz, P.: Fluorescence interferometry of neuronal cell adhesion on microstructured silicon, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 (1998), 5241–5244.
Lipowsky, R.: Adhesion of membranes via anchored stickers, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 (1996), 1652–1655. 210 R. LIPOWSKY
Weikl, T., Netz, R. and Lipowsky, R.: Unbinding transitions and phase separation of multicomponent membranes, Phys. Rev. E 62 (2000), R45–R48.
Bruinsma, R., Behrisch, A. and Sackmann, E.: Adhesive switching of membranes: Experiment and theory, Phys. Rev. E 61 (2000), 4253–4267.
Komura, S. and Andelman, D.: Adhesion-induced lateral phase separation in membranes, Eur. Phys. J. E 3 (2000), 259–271.
Weikl, T. and Lipowsky, R.: Adhesion-induced phase behavior of multicomponent membranes, Phys. Rev. E 64 (2001), 11903–11915.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lipowsky, R. Domains and Rafts in Membranes – Hidden Dimensions of Selforganization. Journal of Biological Physics 28, 195–210 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019994628793
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019994628793