Abstract
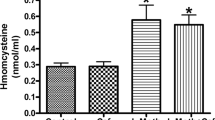
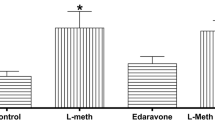
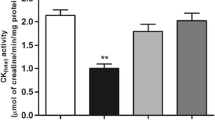
Homocystinuria is a metabolic disorder caused by deficiency of cystathione β-synthase activity leading to tissue accumulation of homocysteine (Hcy); affected patients present neurological dysfunction. Considering that Hcy induces free radical formation and that memory is impaired by oxidative stress, in the present study we investigated the effect of an acute administration of Hcy on retrieval of step-down inhibitory avoidance in adult rats. The action of vitamins E and C on the effects produced by Hcy was also tested. Adult Wistar rats were pretreated for 1 week with daily i.p. administration of saline (control group) and vitamins E and C (vitamin E 40 mg/kg and vitamin C 100 mg/kg). Hcy (11 mmol/kg) or an equivalent volume of 0.9% saline were administered 1 h before training, 1 h before testing, or immediately after training sessions. Memory was significantly impaired in Hcy-treated group, whereas the rats chronically treated with vitamins E and C had this effect prevented. Present data strongly indicate that Hcy administration impairs memory, an effect probably mediated by oxidative stress since treatment with vitamins E and C prevented amnesia. Assuming the possibility that this might occur in the human condition, reported results may be relevant to explain, at least in part, neurologic dysfunction associated with homocystinuria.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Allen, I.C., Grieve, A., and Griffiths, R. (1986). Differential changes in the content of amino acid neurotransmitters in discrete regions of the rat brain prior to the onset and during the course of homocysteine-induced seizures. J. Neurochem. 46:1582-1592.
Ames, B.N., Shigenaga, M.K., and Hagen, T.M. (1993). Oxidants, antioxidants and the degenerative diseases of aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:7915-7922.
Anderson, D.K., Waters, T.R., and Means, E.D. (1988). Pretreatment with alpha-tocopherol enhances neurologic recovery after experimental spinal cord compression injury. J. Neurotrauma 5:61-67.
Bergendi, L., Benes, L., Durackova, Z., and Ferencik, M. (1999). Chemistry, physiology and pathology of free radicals. Life Sci. 65:1865-1874.
Bickford, P.C., Gould, T., Briederick, L., Chadman, K., Pollock, A., Young, D., Shukitt-Hale, B., and Joseph, J. (2000). Antioxidant-rich diets improve cerebellar physilogy and motor learning in aged rats. Brain Res. 866:211-217.
Burton, G.W., Wronska, U., Stone, L., Foster, D.O., and Ingold, K.U. (1990). Biokinetics of dietary RRR-?-tocopherol in the male guinea-pig at three dietary levels of vitamin C and two levels of vitamin E. Lipids 25:199-210.
Cantuti-Castewlvetri, I., Shukitt-Hale, B., and Joseph, J.A. (2000). Neurobehavioral aspects of antioxidants in aging. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 18:367-381.
Carr, A., and Frei, B. (1999). Does vitamin C act as a pro-oxidant under physiological conditions? FASEB J. 13:1007-1024.
Fighera, M.R., Queiroz, C.M., Stracke, M.P., Brauer, M.L.N., González-Rodrigues, Frussa-Filho, R., Wajner, M., and Mello, C.F. (1999). Ascorbic acid and ?-tocopherol attenuate methylmalonic acid-induced convulsions. NeuroReport 10:2039-2043.
Frei, B., Stocker, R., England, L., and Ames, B.N. (1990). Ascorbate: The most effective antioxidant in the blood. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 264:155-163.
Fuchs, D., Jaeger, M., Widner, B., Wirleitner, B., Artner-Dworzak, E., and Leblhuber, F. (2001). Is hyperhomocysteinemia due to the oxidative depletion of folate rather than to insufficient dietary intake? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 39:691-694.
Halliwell, B. (1996). Free radicals, protein and DNA: Oxidative damage versus redox regulation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 24:1023-1027.
Halliwell, B., and Gutteridge, J.M.C. (1985). Oxygen radicals in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 8:22-26.
Hara, H., Kato, H., and Kogure, K. (1990). Protective effect of alpha-tocopherol on ischemic neuronal damage in the gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res. 510:335-338.
Hogg, N. (1999). The effect of cyst(e)ine on the auto-oxidation of homocysteine. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 27:28-33.
Izquerdo, I., and Medina, J.H. (1997). Memory formation: The sequence of bochemical events in the hippocampus and its connection to activity in other brain structures. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 68:285-316.
Izquierdo, I., and Medina, J.H. (1995). Retrograde messengers, long-term potentiation and memory. Brain Res. Rev. 21:185-194.
Jacobsen, D.J. (2000). Hyperhomocysteinemia and oxidative stress. Time for a reality check? Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 20:1182-1184.
Kim, W.-K., and Pae, Y.-S. (1996). Involvement of N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor and free radical in homocysteine-mediated toxicity on rat cerebellar granule cells in culture. Neurosci. Lett. 216:117-120.
Kubová, H., Folbergrová, J., and Mares, P. (1995). Seizures induced by homocysteine in rats during ontogenesis. Epilepsia 36:750-756.
Lees, G.J. (1993). Contributory mechanisms in the causation of neurodegenerative disorders. Neuroscience 54:287-322.
Malinow, M.R. (1990). Hyperhomocyst(e)inemia. A common and easily reversible risk factor for occlusive atherosclerosis. Circulation 81:2004-2006.
McCay, P.B. (1985). Vitamin E: Interactions with free radical and ascorbate. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 5:323-340.
Mudd, S.H., Levy, H.L., and Skovby, F. (2001). Disorders of transsulfuration. In (C.R. Scriver, A.L. Beaudet, W.S. Sly, and D. Valle, eds.), The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, 8th edn., McGraw-Hill, New York, pp. 1279-1327.
Netto, C.A., Dias, R.D., and Izquierdo, I. (1986). Differential effect of post-training naloxone, beta-endorphin, leu-enkephalin and ECS upon memory of an open-field habituation and of a water-finding task. Psychoneuroendocrinology 11:437-446.
Reznick, A.Z., and Packer, L. (1993). Free radicals and antioxidants in muscular neurological diseases and disorders. In (G. Poli, E. Albano, and M.U. Dianzani, eds.), Free Radicals: From Basic Science to Medicine, Basel, Birkhäuser Verlag, pp. 425-437.
Sano, M., Ernesto, C., Thomas, R.G., Klauber, M.R., Schafer, S., Grundman, M., Woodbury, P., Growdon, J., Cotman,C.W., Pfeiffer, E., Schneider, L.S., and Thal, L.J. (1997). A controlled trial of selegiline, ?-tocopherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimr's disease. New Engl. J. Med. 336:1216-1222.
Welch, G.N., Upchurch, G.R., and Loscalzo, J. (1997). Homocysteine, oxidative stress and vascular disease. Hosp. Pract. 32:81-92.
Zanatta, M.S., Quillfeldt, J.H., Schaeffer, E., Schhmitz, P.K., Quevedo, J., Medina, J.H., and Izquierdo, I. (1997). Involvement of the hippocampus, amygdala, entorhinal cortex and posterior parietal cortex in memory consolidation. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 30:235-240.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reis, E.A., Zugno, A.I., Franzon, R. et al. Pretreatment with Vitamins E and C Prevent the Impairment of Memory Caused by Homocysteine Administration in Rats. Metab Brain Dis 17, 211–217 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019982223034
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019982223034