Abstract
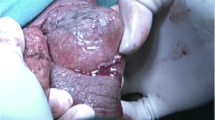
Fournier's gangrene (FG) is a rapidly progressive, fulminant infection of the scrotum, perineum and the abdominal wall. FG is caused by synergic aerobic and anaerobic organisms. Modern surgical series report mortality of up to 67% [2, 3]. This originally rare disease has become more frequent. Aggressive treatment including antibiotics, antigangrenous serum, and treatment of all accompanied diseases and disorders can be successful. Treatment also includes debridement and plastic corrections. Authors describe management of 8 patients with FG. Treatment of FG and all accompanied diseases was in all cases successful. Treatment costs of this kind of patients were approximately 20 times higher than treatment of patients with other urologic diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JA, Culkin DJ, Mata JA et al. Fournier's gangrene in children. Urology 1990; 35: 439
Addison W, Livengood C, Hill G. Necrtotising fascilitis of vulval origin in diabetic patients. Obstet Gynaecol 1984; 63: 473
Andersen R, Wegner HE. Fournier's gangrene: viability monitoring of subcutaneusly. Transported testis following extensive debridement by color-coded duplex sonography and nuclear magnetic resonance. Urol Int 1998; 6: 130
Corman IM, Moody JA, Aronson WJ. Fournier's gangrene in a modern surgical setting: improved survival with aggressive management. BJU: International 1999; 84: 85
Fournier JA. Gangrene Foudroyante de la verge. Medicin Practique 1883; 4: 589
Gerdes B, Winter KJ, Heuler R. Fournier's gangrene. Chir Praxis 1997; 52: 221
Hollabaugh RS Jr, Domochouski RR, Hickerson WL, Cox CE. Fournier's gangrene: therapeutic impact of hyperbaric oxygen. Plast Reconstr Surg 1998; 101: 94
Laucks SS. Fournier's gangrene. Surg Clin North Am 1994; 74: 1339
Maren¡ cak J, Náter S. Fournierova gangréna. Urológia 1995; 1: 23
Mazzaferri FS, Fadiliturralde JL, Provenzal O et al. Fournier's gangrene. Our 10 years experiences. Revision of the literature. Arch Esp de Urol 1999; 52: 721
Pathy R, Smith AD. Gangrene and Fournier's gangrene. Urol Clin North Am 1992; 19: 149
Pavlica P, Barozzi L. Imaging of acute scrotum. Eur Radiol 2001; 11: 220
Smith GL, Bunker CB, Dinneen MD. Fournier's gangrene. Brit J Urol 1998; 8: 348
Weis CH, Reimund KP, Bruckner R. Fournieriche gangrän. Chir Praxis 1991; 43: 463
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fillo, J., Çervenakov, I., Labas, P. et al. Fournier's gangrene: Can aggressive treatment save life?. Int Urol Nephrol 33, 533–536 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019554327341
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019554327341