Abstract
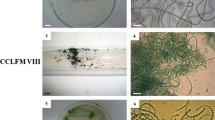
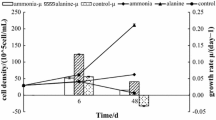
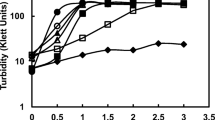
An amino acid (L-lysine) was screened against eighteen strains ofCyanophyceae, Bacillariophyceae and Chlorophyceae. OnlyMicrocystis strains (Cyanophyceae) were sensitive tolysine; other strains were not affected. Cells of sevenMicrocystis strains (106 cellsmL−1) were completely killed within 48h by lysine at concentrations between 0.6 and 5.0 mgL−1. Two Microcystis strains wereinhibited by 92 and 98 %. Similar results were obtained when lysine malonateandlysine copper were used as algicides. Microcystis specieswere killed by lysine malonate at concentrations between 0.6 and 5 mgL−1, and by lysine copper at concentrations between 0.5and 20 mg L−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahluwalia A.S. 1985. Effect of amino acids and some chemicals on cellular differentiation in Anabaena oscillarioides. Ann. Biol. 1: 137-144.
Berman T. and Chava S. 1999. Algal growth on organic compounds as nitrogen sources. J. Plankton Res. 21: 1423-1437.
Caiola M.G. and Pellegrini S. 1984. Lysis of Microcystis aeruginosa (Kütz.) by Bdellovibrio-like bacteria. J. Phycol. 20: 471-475.
Deppe T., Ockenfeld K., Meybohm A., Opitz M. and Benndorf J. 1999. Reduction of Microcystis blooms in a hypertrophic reservoir by a combined ecotechnological strategy. Hydrobiologia 408/409: 31-38.
Goluobinoff P., Brusslan J., Golden S.S., Haselkorn R. and Edelman M. 1988. Characterization of the photosystem II 32kDa protein in Synechococcus PCC7942. Pl. mol. Biol. 11: 441-447.
Kamjunke N. and Jähnichen S. 2000. Leucine incorporation by Microcystis aeruginosa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 45: 741-743.
Kaya K. and Sano T. 1996. Algicidal compounds in yeast extract as a component of microbial culture media. Phycologia 35: 117-119.
Lam A.K-Y., Prepas E.E., Spink D. and Hrudey S.E. 1995. Chemical control of hepatotoxic phytoplankton blooms: Implications for human health. Wat. Res. 29: 1845-1854.
Lindenschmidt K-E. 1999. Controlling of the growth of Microcystis using surged artificial aeration. Int. Revue Hydrobiol. 84: 243-254.
Parker D.L., Kumar H.D., Rai L.C. and Singh J.B. 1997. Potassium salts inhibit growth of the cyanobacteria Microcystis spp. in pond water and defined media: Implications for control of microcystin-producing aquatic blooms. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 63: 2324-2329.
Peterson H.G., Boutin C., Freemark K.E. and Martin P.A. 1997. Toxicity of hexazinone and diquat to green algae, diatoms, cyanobacteria and duckweed. Aquat. Toxicol. 39: 111-134.
Phlips E.J., Hansen P. and Velardi T. 1992. Effect of the herbicide diquat on the growth of microalgae and cyanobacteria. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 49: 750-756.
Reynolds C.S., Wiseman S.W. and Clarke M.J.O. 1984. Growthand loss-rate responses of phytoplankton to intermittent artificial mixing and their potential application to the control of planktonic algal biomass. J. appl. Ecol. 21: 11-39.
Ridge I., Walters J. and Street M. 1999. Algal growth control by terrestrial leaf litter: a realistic tool? Hydrobiologia 395/396: 173-180.
Ruzycki E.M., Axler R.P., Owen C.J. and Martin T.B. 1998. Response of phytoplankton photosynthesis and growth to the aquatic herbicide Hydrothol 191. Envir. Toxicol. Chem. 17: 1530-1537.
Watanabe M.M., Kawachi M., Hiroki M. and Kasai F. 2000. NIESCollection. List of strains. Sixth edition: Microalgae and Protozoa National Institute for Environmental Studies, Environment Agency, Tsukuba, Japan, 159 pp.
Yamamoto Y., Kouchiwa T., Hodoki Y., Hotta K., Uchida H. and Harada K-I. 1998. Distribution and identification of actinomycetes lysing cyanobacteria in an eutrophic lake. J. appl. Phycol. 10: 391-397.
Yasuno M., Sugaya Y., Kaya K. and Watanabe M.M. 1998. Variations in the toxicity of Microcystis species to Moina macrocopa. Phycol. Res. 46: 31-36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hehmann, A., Kaya, K. & Watanabe, M.M. Selective control of Microcystis using an amino acid – a laboratory assay. Journal of Applied Phycology 14, 85–89 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019546829940
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019546829940