Abstract
Objectives: The aims of this study were to compare the efficacy of a 2- versus a 3 RF lesions ablation procedure in the RA in patients with paroxysmal AF, and to map right atrial activation during AF.
Background: RF catheter-mediated ablation lines mimicking the Maze operation have been proposed as a novel curative approach for AF. The relationship between this type of ablation and right atrial mapping has not been extensively studied.
Methods: Twenty-four patients with recurrent, drug-refractory, paroxysmal AF underwent an extensive mapping of the RA before attempting linear lesion RF ablation. Patients were divided into two groups: 15 patients received two linear lesions (Group 1), 9 patients three linear lesions (Group 2).
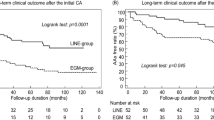
Results: One-month success rate AF did not recur in 40% of Group 1 patients (6/15) and in 66% (6/9) of Group 2 patients. 27% of patients in Group 1 and 11% of patients in Group 2 had recurrences controlled by drugs. No benefit in 33% of Group 1 patients and 22% of Group 2.
Long-term follow-up In the absence of any drug treatment, no AF recurrences were observed in 26% of Group 1 patients (FU: 23 to 47 months) and 55% of Group 2 (FU: 14 to 23 months). No complications were reported.
Conclusions: Right atrial linear ablation is safe and may be proposed for AF treatment in selected patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 1998;339:659–666.
Alessie MA, Lammers WJEP, Bonke FIM, Hollen J. Experimental evaluation of Moe's multiple wavelet hypothesis of atrial fibrillation. In: Zipes DP, Jalife J, eds. Cardiac Arrhythmias. NY: Grune & Stratton, 1985: 265–276.
Olgin JE, Kalman JM, Fitzpatrick AP, Lesh MD. Role of right atrial endocardial structures as barriers to conduction during human type I atrial flutter: activation and entrainment mapping guided by intracardiac echocardiography. Circulation 1995;92:1839–1848.
Roithinger FX, SippensGroenewegen A, Karch MR, et al. Organized activation during atrial fibrillation in man: endocardial and electrocardiographic manifestations. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 1998;9:451–456.
Cox JL, Canavan TE, Schuessler RB, et al. The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation II: Intraoperative electrophysiologic mapping and description of the electrophysiologic basis of atrial flutter and fibrillation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1991;101:406–426.
Haïssaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, et al. Right and left atrial radiofrequency catheter therapy of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 1996;7:1132–1144.
Gaita F, Riccardi R, Calo' L, et al. Atrial mapping and radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with idiopathic atrial fibrillation: electrophysiological findings and ablation results. Circulation 1998;97:2136–2145.
Adam M, Montenero AS, Fischetti D, Maseri A. A typical pattern of activation in the right atrium during paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: the washing-machine phenomenon. Cardiologia 1999;44:63–68.
Barbaro V, Bartolini P, Bernarducci R, Calcagnini G, Martelli F, Morelli S. An algorithm for the detection and the classification of atrial fibrillation from intra-atrial electrograms. Proceedings of the VIII Mediterranean on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing (MEDICON '98), 1998, acts on CD Rom.
Wells JL, Karp RB, Kouchoukos NT, et al. Characterization of atrial fibrillation in man: studies following open heart surgery. PACE 1978;1:426–438.
Jaïs P, Haïssaguerre M, Shah DC, et al. A focal source of atrial fibrillation treated by discrete radiofrequency ablation. Circulation 1997;95:572–576.
Becker AE. Atrial anatomy: relationship to atrial flutter. In: Waldo AL, Touboul P, eds. Atrial Flutter: Advances in Mechanism and Management. Armonk, New York: Futura Publishing Co., Inc., 1996:13–19.
Roithinger FX, Karch MR, Steiner PR, et al. Relationship between atrial fibrillation and typical atrial flutter in humans. Activation sequence changes during spontaneous cardioversion. Circulation 1997;96: 3484–3491.
Saffitz JE, Kanther HL, Green KG, et al. Tissuespecific determinants of anisotropic conduction velocity in canine atrial and ventricular myocardium. Circ Res 1994;74:1065–1070.
Tondo C, Scherlag BJ, Otomo K, et al. Critical atrial site for ablation of pacing-induced atrial fibrillation in the normal dog heart. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 1997;8:1255–1265.
Garg A, Finneran W, Mollerus M, et al. Right atrial compartmentalization using radiofrequency catheter ablation for management of patients with refractory atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 1999;10:763–771.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montenero, A.S., Adam, M., Franciosa, P. et al. The Linear Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation in the Right Atrium: Can the Isthmus Ablation Improve Its Efficacy?. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 6, 251–265 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019513904900
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019513904900