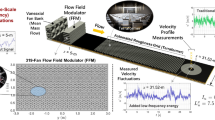
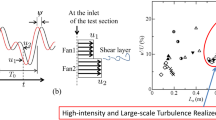
Abstract
An actively controlled wind tunnel equipped with multiple fansand airfoils has been developed, mainly for the purpose of reproducing the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) for wind engineering applications. Various fluctuating flows can be achieved in this wind tunnel by altering the input data of the fans and airfoils through computer control. In this study, the ABL is physically simulated in this wind tunnel, and particular attention ispaid to the simulation of the profile of Reynolds stress. The method of generating the fluctuating flow and the experimental results of reproducing the ABL are presented. As the results show, the spatial distribution of Reynolds stress is satisfactorily simulated, and the profiles of other statisticalturbulent parameters, such as mean velocity, turbulent intensity, integral scale and power spectrum are successfully reproduced simultaneously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cermak, J. E. and Cochran, L. S.: 1992, ‘Physical Modeling of the Atmospheric Surface Layer’ J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 41-44, 935-946.
Kikugawa et al.: 1996, ‘Development of Actively Controlled Turbulent Wind Tunnel, Part 2, Turbulence Control by Time-Lag Correction’ in 14th National Symposium onWind Engineering, Japan Association of Wind Engineering, 5-16-9 Hon Komagome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, pp. 151-156.
Kobayashi, H. and Hatanaka, A.: 1992, ‘Active Generation of Wind Gust in Two Dimensional Wind Tunnel’ J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 41-44, 959-970.
Lu, S. S. and Willmarth, W. W.: 1973, ‘Measurements of the Structure of the Reynolds Stress in a Turbulent Boundary Layer’ J. Fluid Mech. 60, 481-511.
Nishi, A. and Miyagi, H.: 1993, ‘Computer Controlled Wind Tunnel’ J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 46/47, 837-846.
Nishi, A. and Miyagi, H.: 1995, ‘Computer Controlled Wind Tunnel for Wind-Engineering Applications’ J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 54/55, 493-504.
Nishi, A. et al. 1997, ‘Turbulence Control in Multiple-FanWind Tunnel’ J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 67/68, 861-872.
Nishi, A. et al.: 1999, ‘Active Control of Turbulence for an Atmospheric Boundary Layer Model in a Wind Tunnel’ J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 83, 409-419.
Teunissen, H.W.: 1970, ‘Characteristic of the MeanWind and Turbulence in the Planetary Boundary Layer’ in UTIAS Review, University of Toronto, Canada, pp. 22-23.
Teunissen, H.W.: 1975, ‘Simulation of the Planetary Boundary Layer in a Multiple-JetWind Tunnel’ Atmos. Environ. 9, 145.
Tutu Narinder, K. and Chevray, R.: 1975, ‘Cross-Wire Anemometer in High Intensity Turbulence’ J. Fluid Mech. 71, 785-800.
Willmarth, W. W. and Lu, S. S: 1972, ‘Structure of Reynolds Stress near the Wall’ J. Fluid Mech. 65, 65-92.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shuyang, C., Nishi, A., Hirano, K. et al. An Actively Controlled Wind Tunnel And Its Application To The Reproduction Of The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 101, 61–76 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019288828837
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019288828837