Abstract
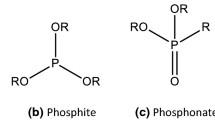
Tribochemical interactions between antiwear zinc dithiophosphate (Zndtp), friction modifier molybdenum dithiocarbamate (Modtc) and detergent overbased calcium borate (CB) lubricant additives have been investigated by coupling analytical TEM and micro‐spot XPS in the tribotester Optimol of SRV GmbH (mild wear conditions in boundary lubrication). Synergistic effects have been observed on both friction and wear data, especially in the Modtc/Zndtp combination. Results have been interpreted on the basis of a chemical hardness concept: the hard and soft acids and bases (HSAB) principle, stabilisation of hard–hard pairs and the maximum hardness principle. The performance of the Modtc/Zndtp mixture is mainly due to the generation of MoS2 single sheets and the digestion of MoO3, which is also formed, by the zinc polyphosphate glass. The final result of the tribochemical reaction is a tribofilm composed of MoS2 sheets embedded in a mixed Mo/Zn polyphosphate glass. The CB/Modtc mixture has a similar mechanism except that the oxide is not completely eliminated, due to the softer borate anion compared with the phosphate one.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Kajdas, in:Proc. ITC Yokohama Satellite Forum on Tribochemistry, Yokohama (1995) p. 31.
H. Mansuy, Ph.D. thesis, University Paris VI (1995).
M.D. Johnson, R.K. Jensen and S. Korcek, SAE Technical Paper No. 972860 (1997) 37.
R.G. Pearson, in:Chemical Hardness (Wiley/VCH, New York/Weinheim, 1996).
S. Mori, in:Proc. ITC Yokohama Satellite Forum on Tribochemistry, Yokohama (1995) pp. 37–42.
C. Grossiord, J.-M. Martin, Th. Le Mogne and Th. Palermo, Surf. Coat. Techn. 108-109 (1998) 352.
S. Fujisawa, Y. Sugawara, S. Ito, S. Mishima, T. Okada and S. Morita, Nanotechnology 4 (1993) 138.
D.A. Rigney and J.E. Hammerberg, MRS Bulletin 23 (1998) 32.
M.N. Gardos, Tribol. Lett. 4 (1998) 175.
J.-M. Martin, Th. Le Mogne, C. Grossiord and Th. Palermo, Tribol. Lett. 3 (1997) 87.
J.-M. Martin, J.-L. Lavergne, B. Vacher and K. Inoue, Microsc. Microanal. Microstruct. 6 (1995) 53.
K. Varlot, J.-M. Martin, C. Grossiord, R. Vargiolu, B. Vacher and K. Inoue, Tribol. Lett. 6 (1999) 181.
C. Grossiord, K. Varlot, J.-M. Martin, Th. Le Mogne, C. Esnouf and K. Inoue, Tribol. Int. 31 (1998) 737.
D.R Lide, ed.,Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (CRC Press, New York, 1997) pp. 4–130.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, J., Grossiord, C., Varlot, K. et al. Synergistic effects in binary systems of lubricant additives: a chemical hardness approach. Tribology Letters 8, 193–201 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019147520893
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019147520893