Abstract
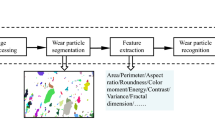
Although the study of wear debris can yield much information on the wear processes operating in machinery, the method has not been widely applied in industry. The main reason is that the technique is currently time consuming and costly due to the lack of automatic wear particle analysis and identification techniques. In this paper, six common types of metallic wear particles have been investigated by studying three‐dimensional images obtained from laser scanning confocal microscopy. Using selected numerical parameters, which can characterise boundary morphology and surface topology of the wear particles, two neural network systems, i.e., a fuzzy Kohonen neural network and a multi‐layer perceptron with backpropagation learning rule, have been trained to classify the wear particles. The study has shown that neural networks have the potential for dealing with classification tasks and can perform wear‐particle classification satisfactorily.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Naval Air Engineering Center, Wear Particle Atlas, Report NAEC–92–163 (1982).
J.C. Russ, Computer-Assisted Microscopy: The Measurement and Analysis of Images (Plenum Press, New York, 1990).
R.V. Anamalay, T.B. Kirk and D. Panzera, Wear 181–183 (1995) 771.
Z. Peng, T.B. Kirk and Z.L. Xu, Wear 203–204 (1997) 418.
Z. Peng and T.B. Kirk, Wear, submitted (1997).
D. Scott, W.W. Seifert and V.C. Westcott, Scientific American 230(5) (1973) 88.
J.S. Stecki and M.L.S. Anderson, Bulletin of the CMCM, Monash University 3(1) (1991) 9.1.
A.D.H. Thomas, T. Davies and A.R. Luxmoore, Wear 142 (1991) 213.
J.B. Beddow, Particle Characterization in Technology, Vol. II, Morphological Analysis (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1984).
Z. Peng and T.B. Kirk, Tribology International 30 (1997) 583.
N.K. Myshkin, O.K. Kwan, A.Y. Grigoriev, H.S. Ahn and H. Kong, Wear 203–204 (1997) 658.
K. Xu and A.R. Luxmoore, Wear 208 (1997) 184.
B. Kosko, Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1992).
A. Nigrin, Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1993.
E.C. Tsao, J.C. Bezdek and N.R. Pal, Pattern Recognition 27 (1994) 754.
B.H. Chowdhury and K. Wang, in: Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Systems to Power Systems, ISAP, IEEE, 1996, pp. 194–198.
R.J. Hathaway and J.C. Bezdek, Pattern Recognition 27 (1994) 429.
L.G. Allred and G.E. Kelly, in: Proceedings of Int. Joint Conf. on Neural Networks, 1990, pp. 721–728.
W. Fakhr and M.I. Elmasry, in: IJCNN, International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, IEEE, 1990, pp. 257–262.
D.R. Hush and B.G. Horne, IEEE Signal Processing Magazine (January 1993) 8.
W.P. Dong and K.J. Stout, Proceedings Instn. Mech. Engrs. 209 (1995) 381.
D.C. He and L. Wang, IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 28 (1990) 509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Z., Kirk, T. Automatic wear‐particle classification using neural networks. Tribology Letters 5, 249–257 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019126732337
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019126732337