Abstract
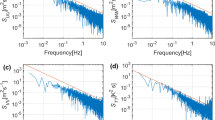
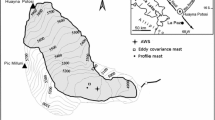
Two situations observed during the second Aerosol Characterization Experiment (ACE-2) are analysed from aircraft measurements in the broken stratocumulus (Sc)-topped marine boundary layer. The first one (26 June 1997), characterized by a non-polluted, oceanic air mass, presents a decoupling between the Sc layer (1400–1520 m) and the turbulent mixed layer, this latter extending from the surface up to 580 m. In contrast, the second case (9 July 1997), during which continental air had been advected over the experimental area, presents a well-coupled layer extending from the surface up to the top of the Sc layer(910 m). This coupling, uncommon in this area in the middle of the day, isrelated to the relative shallowness of the boundary layer. For both situations,it is shown that the turbulent fluxes can be computed with reasonably goodaccuracy (better than 10 %), taking into account both the random and thesystematic errors involved in the eddy-correlation technique. Estimationof random error is based on the computation of the integral scale of thecovariance, and systematic error is estimated from the parameterizationof Mann and Lenschow. The fluxes show that the buoyancy, as a sourceof turbulence, is due to latent heat flux rather than sensible heat flux,with values comparable to previous experiments in the Azores-Canariesbasin. In addition, we propose a method to analyse, for coupled situations,the relationship between the fractional cloudiness and the organization ofthe turbulent field below the clouds. This method is based on a conditionalsampling technique. It is shown that this organization cannot be deducedfrom the analysis of the velocity signal, which is dominated by turbulence.However, when the signals are conditionally sampled according to thepresence or absence of clouds, a weak cloud-related organization can beshown, and the cloud-related transports quantified; the values found areof the order of 10 % of the total transfers, i.e. the same order of magnitude asthe errors on the total flux computation. The method developed is thereforepromising, provided that the uncertainties can be reduced by analyzing a highamount of data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, B. A.,Bretherton, C. S.,Johnson, D.,Schubert,W. H., and Frish, A. S.: 1995, 'The Atlantic Stratocumulus Transition Experiment-ASTEX', Bull. Amer. Meteorol. Soc. 76, 889-904.
Attié, J. L.,Durand, P.,Druilhet, A., and Saï d, F.: 1997, 'Study of Exchange Processes at the Top of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer', in Proceedings of the 12th Symposium on Boundary Layers and Turbulence, AMS Ed., 28 Jul.-01 Aug., Vancouver, Canada, pp. 50-51.
Betts, A. K.,Bretherton, C. S., and Klinker, E.: 1995, 'Relation between Mean Boundary-Layer Structure and Cloudiness at the R/V Valdivia during ASTEX', J. Atmos. Sci. 52, 2752-2762.
Brenguier, J.-L.,Chuang, P. Y.,Fouquart, Y.,Johnson, D. W.,Parol, F.,Pawlowska, H.,Pelon, J.,Schüller, L.,Schröder, F., and Snider, J.: 2000, 'An Overview of the ACE-2 CLOUDYCOLUMN Closure Experiment', Tellus 52, 815-827.
Delon, C.: 1999,'Etude des échanges biosphè re atmospè re en milieu équatorial. Mesure aéroportée des flux de matiè re et d'énergie pendant la campagne EXPRESSO, Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France, 146 pp.
Durand, P.,Dupuis, H.,Lambert, D.,Bénech, B.,Druilhet, A.,Katsaros, K.,Taylor, P., and Weill, A.: 1998, 'Comparison of Sea Surface Flux Measured by Instrumented Aircraft and Ship during SOFIA and SEMAPHORE Experiments', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 25125-25136.
Garratt, J. R.: 1992, The Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Cambridge University Press, 316 pp.
Kaimal, J. C. and Finnigan, J. J.: 1994, Atmospheric Boundary Layer Flows-Their Structure and Measurement, Oxford University Press, 289 pp.
Lambert, D.: 1997, Structure moyenne et turbulente de la couche limite atmosphérique au dessus de l'océan (expérience SEMAPHORE)', Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France, 212 pp.
Lambert, D. and Durand, P.: 1998, 'Aircraft-to-Aircraft Intercomparison during SEMAPHORE', J. Geophys. Res. 103, 25109-25123.
Lambert, D. and Durand, P.: 1999, 'The Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer during SEMAPHORE. Part 1: Mean Vertical Structure and Non-axisymmetry of Turbulence', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 125, 495-512.
Lambert, D.,Durand, P.,Thoumieux, F.,Bénech, B., and Druilhet, A.: 1999, 'The Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer during SEMAPHORE. Part 2: Turbulence Profiles in the Mixed Layer', Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 125, 513-528.
Lenschow, D. H., 1986, 'Aircraft Measurements in the Boundary Layer', in D. H. Lenschow (ed.), Probing the Atmospheric Boundary Layer, Amer. Meteorol. Soc., Boston, MA., pp. 39-56.
Lenschow, D. H. and Stankov, B. B.: 1986,' Length Scales in the Convective Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 43, 1198-1209.
Lumley, J. L. and Panofsky, H. A.: 1964, The Structure of Atmospheric Turbulence, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 239 pp.
Mann, J. and Lenschow, D. H.: 1994, 'Errors in Airborne Flux Measurements', J. Geophys. Res. 99, 14,519-14,526.
Nicholls, S.: 1984, 'The Dynamics of Stratocumulus: Aircraft Observations and Comparisons with a Mixed Layer Model', Quart J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 110, 783-820.
Raes, F.,Bates, T.,McGovern, F., and Van Liedekerke, M.: 2000, 'The Second Aerosol Characterization Experiment (ACE-2): General Overview and Main Results', Tellus 52, 111-125.
Réchou, A.,Durand, P.,Druilhet, A., and Bénech, B.: 1995, 'Turbulence Structure of the Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer Observed during the SOFIA Experiment', Ann. Geophys. 13, 1075-1086.
Shaw, W. J. and Businger, J. A.: 1985, 'Intermittency and Organization of Turbulence in the Near-Neutral Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer', J. Atmos. Sci. 42, 2563-2584.
Stevens, B.,Cotton, W. R.,Feingold, G., and Moeng, C.: 1998, 'Large-Eddy Simulations of Strongly Precipitating, Shallow, Stratocumulus-Topped Boundary Layers', J. Atmos. Sci. 55, 3616-3638.
Tjernström, M. and Smedman, A.: 1993, 'The Vertical Structure of the Coastal Marine Atmospheric Boundary Layer', J. Geophys. Res. 98, 4809-4826.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durand, P., Bourcy, T. Observations Of The Turbulence Structure Within Two Stratocumulus-Topped, Marine Boundary Layers. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 99, 105–125 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018999221303
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018999221303