Abstract
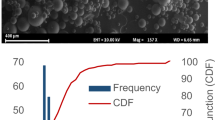
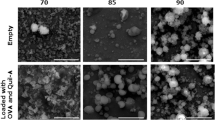
Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLG) microparticles with entrapped antigens have recently been investigated as controlled-release vaccines. This paper describes the preparation of PLG microparticles with an entrapped model antigen, ovalbumin (OVA), using a (water-in-oil)-in-water emulsion solvent evaporation technique. In a series of experiments, the effects of process parameters on particle size and OVA entrapment were investigated. It was found that smooth, spherical microparticles 1–2 µm in diameter containing up to 10% (w/w) OVA could be produced using a small volume of external aqueous phase containing a high concentration of emulsion stabilizer and a 1:5 antigen:polymer ratio. PAGE analysis, isoelectric focusing, and Western blotting of OVA released from the microparticles in vitro confirmed that the molecular weight and antigenicity of the protein remained largely unaltered by the entrapment procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. T. O'Hagan. Novel non-replicating antigen delivery systems. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 3:393–401 (1990).
D. T. O'Hagan, D. Rahman, J. P. McGee, H. Jeffery, M. C. Davies, P. Williams, S. S. Davis, and S. J. Challacombe. Biodegradable microparticles as controlled release antigen delivery systems. Immunology 73:239–242 (1991).
B. R. Bloom. Vaccines for the Third World. Nature 342:115–120 (1989).
D. E. Cutright, E. Perry, J. D. Beasley, W. J. Larson, and W. R. Perry. Degradation of poly(lactic acid) polymer and copolymer of poly(glycolic acid). J. Oral. Surg. 37:142–152 (1974).
F. G. Hutchinson and B. J. A. Furr. Biodegradable polymers in sustained release of polypeptides. In S. S. Davis, L. Illum, and E. Tomlinson (eds.), Delivery Systems for Peptide Drugs, Plenum Press, New York, 1986, pp. 115–124.
D. T. O'Hagan, H. Jeffery, M. J. J. Roberts, J. P. McGee, and S. S. Davis. Controlled release microparticles for vaccine development. Vaccine 9:768–771 (1991).
Y. Tabata and Y. Ikada. Effect of the size and surface charge of polymer microspheres on their phagocytosis by macrophage. Biomaterials 9:356–362 (1988).
D. T. O'Hagan. Intestinal translocation of particulates—implications for drug and antigen delivery. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 5:265–285 (1990).
D. T. O'Hagan, K. Palin, S. S. Davis, P. Artusson, and I. Sjoholm. Microparticles as potentially orally active immunological adjuvants. Vaccine 7:421–424 (1989).
S. J. Challacombe, D. Rahman, H. Jeffery, S. S. Davis, and D. T. O'Hagan. Enhanced secretory IgA and systemic IgG antibody responses after oral immunisation with biodegradable microparticles containing antigen. Immunology 76:164–168 (1992).
P. Jani, W. Halbert, J. Landridge, and A. T. Florence. The uptake and translocation of latex nanospheres and microspheres after oral administration to rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 41:809–812 (1989).
H. Jeffery, S. S. Davis, and D. T. O'Hagan. The preparation and characterisation of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles 1: Oil-in-water emulsion solvent evaporation. Int. J. Pharm. 77:169–175 (1991).
J. W. Fong, J. P. Nazareno, J. Pearson, and H. V. Maulding. Evaluation of biodegradable microcapsules prepared by solvent evaporation process using sodium oleate as emulsifier. J. Control. Release 3:119–130 (1986).
R. Bodmeier and J. W. McGinity. The preparation and evaluation of drug containing poly(D,L-lactide) microspheres formed by solvent evaporation. Pharm. Res. 4:465–471 (1987).
Y. Ogawa, M. Yamamoto, H. Okada, T. Yashiki, and T. Shimamoto. A new technique to efficiently entrap leuprolide acetate into microcapsules of copoly(lactic/glycolic acid). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 36:1095–1103 (1988).
M. S. Hora, R. K. Rana, J. H. Nunberg, T. R. Tice, R. M. Gilley, and M. E. Hudson. Release of human serum albumin from poly (lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres. Pharm. Res. 7:1190–1194 (1990).
B. Lugtenberg, J. Meijers, R. Peters, P. Van der Hoek, and L. Alphen. Electrophoretic resolutions of the “major outer membrane protein” of Escherichia coli K12 into four bands. FEBS Lett. 58:254–258 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeffery, H., Davis, S.S. & O'Hagan, D.T. The Preparation and Characterization of Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) Microparticles. II. The Entrapment of a Model Protein Using a (Water-in-Oil)-in-Water Emulsion Solvent Evaporation Technique. Pharm Res 10, 362–368 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018980020506
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018980020506