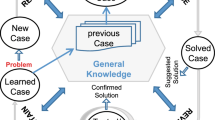
Abstract
A case-based reasoning (CBR) system supports decision makers when solving new decision problems (i.e., new cases) on the basis of past experience (i.e., previous cases). The effectiveness of a CBR system depends on its ability to retrieve useful previous cases. The usefulness of a previous case is determined by its similarity with the new case. Existing methodologies assess similarity by using a set of domain-specific production rules. However, production rules are brittle in ill-structured decision domains and their acquisition is complex and costly. We propose a framework of methodologies based on decision theory to assess the similarity of a new case with the previous case that allows amelioration of the deficiencies associated with the use of production rules. An empirical test of the framework in an ill-structured diagnostic decision environment shows that this framework significantly improves the retrieval performance of a CBR system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.P. Allen, Case based reasoning, business applications, Communications of the ACM 37(1994) 40–42.
K.D. Ashley, Assessing similarity among cases: A position paper, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1989, pp. 72–75.
K.D. Ashley and E.L. Rissland, A case-based approach to modeling legal expertise, IEEE Expert 3(1988)70–77.
K.D. Ashley and E.L. Rissland, Compare and contrast, a test of expertise, Proceedings of the 6th National Conference on AI, AAAI, Seattle, WA, 1987, pp. 273–278.
R. Bariess and J.A. King, Similarity assessment in case-based reasoning, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1989, pp. 67–71.
N.J. Belkin and W.B. Croft, Information filtering and information retrieval, two sides of the same coin?, Communications of the ACM 35(1992)29–38.
C. Bento and E. Costa, Retrieval of cases imperfectly described and explained: A quantitative approach, Case-Based Reasoning, Papers from 1993 Workshop, Technical Report WS-93-01, AAAI Press, Menlo Park, CA, 1993, p. 156.
M.H. Bickhard and L. Terveen, Foundational Issues in Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive Science: Impasse and Solution, Elsevier, New York, 1995.
F. Bolger and G. Wright, Assessing the quality of expert judgement: Issues and analysis, Decision Support Systems 11(1994).
T. Cain, M. Pazzani and G. Silverstein, Using domain knowledge to influence similarity judgments, Proceedings: Case-Based Reasoning Workshop, Washington, DC, May 1991, pp. 191–198.
Cognitive Systems, REMIND Developers Reference Manual, Boston, MA, 1992.
P.R. Cohen, Evaluation and case-based reasoning, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1989, pp. 168–172.
L. Console and P. Torasso, A multi-level architecture for diagnostic problem solving, in: Computational Intelligence, Vol. 1, A. Martelli and G. Valle, eds., Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989, pp. 101–112.
G. DeJong and R. Mooney, Explanation-based learning: An alternative view, Machine Learning 1(1986)145–176.
T.G. Dietterich and R.Z. Michalski, A comparative review of selected methods for learning from examples, in: Machine Learning: An Artificial Intelligence Approach, R.Z. Michalski, J.G. Carbonell and T.M. Mitchell, eds., MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1990, pp. 41–81.
D. Donahue, OGRE: Generic reasoning from experience, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1989, pp. 248–252.
R. Duda and P. Hart, Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis, Wiley, New York, 1973.
M.B. Eisenberg, Measuring relevance judgements, Information Processing and Management 24 (1988)373–389.
T.C. Eskeridge, Continuous analogical reasoning: A summary of current research, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1989, pp. 253–257.
L. Festinger, Conflict, Decision and Dissonance, Tavistock Publications, London, UK, 1964.
D. Gentner, Structure mapping: A theoretical framework for analogy, Cognitive Science 7(1983) 155–170.
K.M. Gupta and A.R. Montazemi, A methodology for evaluating the retrieval performance of case-based reasoning systems, Research and Working Paper Series, # 398, School of Business, McMaster University, 1994.
K.M. Gupta and A.R. Montazemi, Empirical evaluation of retrieval in case-based reasoning systems using modified cosine matching function, IEEE Transaction on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, forthcoming.
W.L. Hays, Statistics, Holt Rinehart and Wilson, New York, 1963.
T.R. Hinrichs, Problem Solving in Open Worlds: A Case Study in Design, Erlbaum, Northvale, NJ, 1992.
J. King and R. Bareiss, Similarity assessment in case-based reasoning, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1989, pp. 67–77.
D.W. King and E.C. Bryant, The Evaluation of Information Services and Products, Information Resources Press, Washington, DC, 1971.
J.L. Kolodner and R.L. Simpson, The MEDIATOR: Analysis of an early case-based problem solver, Cognitive Science 13(1989)507–549.
J.L. Kolodner, Case-Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1993.
J.L. Kolodner, Improving human decision making through case-based decision aiding, AI Magazine 12(1991)52–68.
J.L. Kolodner, Judging which is the best case for a case-based reasoner, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1989, pp. 77–81.
J.L. Kolodner and W. Mark, Case-based reasoning, IEEE Expert 7(1992)5–6.
M. Kriegsman and R. Barletta, Building a case-based help desk application, IEEE Expert 8(1993) 18–26.
D.B. Lenat, R.V. Guha, K. Pittman, D. Pratt and M. Shepherd, CYC: Toward programs with common sense, Communications of the ACM 33(1990)30–49.
S. Minton, J.G. Carbonell, C.A. Knoblock, D.R. Kuokka, O. Etzioni and Y. Gil, Explanation-based learning: A problem solving perspective, in: Machine Learning: Paradigms and Methods, J.G. Carbonell, ed., MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1990, pp. 64–118.
A.R. Montazemi and K.M. Gupta, An adaptive agent for case description in diagnostic CBR systems, Journal of Computers in Industry 29(1996)209–224.
A. Newell, Unified Theories of Cognition, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA, 1994.
E. Ozakarahan, Database Machines and Database Management, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1986.
Panel of CBR Workshop, Case-based reasoning from DARPA machine learning program, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1989, pp. 1–14.
B.W. Porter, R. Bariess and R.C. Holte, Concept learning in weak theory domains, Artificial Intelligence 45(1990)229–264.
J. Preece, Y. Rogers, H. Sharp, D. Benyon, S. Holland and T. Carey, Human-Computer Interaction, Addison-Wesley, New York, 1994.
O. Raoult, A survey of diagnosis expert systems, in: Knowledge Based Systems for Test and Diagnosis, G. Saucier, A. Ambler and M.A. Breuer, eds., Elsevier Science, New York, 1989, pp. 153–167.
J.J. Regazzi, Performance measures for information retrieval systems — an experimental approach, Journal of American Society for Information Science 39(1988)235–251.
C.K. Riesbeck and R.C. Schank, Inside Case-Based Reasoning, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillside, NJ, 1989.
G. Salton, The state of retrieval system evaluation, Information Processing and Management 28(1992)441–449.
T.L. Satty, Thoughts on decision making, ORMS Today 23(1996).
K.J. Schmucker, Fuzzy Sets, Natural Language Computations, and Risk Analysis, Computer Science Press, Rockville, MD, 1984.
H.S. Shinn, Abstractional analogy: A model of analogical reasoning, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA, 1988, pp. 370–389.
E. Simoudis and J. Miller, Validated retrieval in case-based reasoning, 8th National Conference on AI, AAAI, Vol. 1, 1990, pp. 310–315.
E. Simoudis, Using case-based retrieval for customer technical support, IEEE Expert 7(1992) 7–11.
C. Stanfill and D.L. Waltz, Memory-based reasoning paradigm, Proceedings of DARPA Workshop on Case Based Reasoning, Morgan Kaufmann, San Mateo, CA 1988, pp. 414–424.
R.J. Sternberg, Component processes in analogical reasoning, Psychological Review 84(1977) 353–378.
R.H. Stottler, CBR for cost and sales prediction, AI Expert 9(1994)25–33.
R. Sun, A connectionist model for commonsense reasoning incorporating rules and similarities, Knowledge Acquisition 4(1992)293–332.
P. Thagard, K.J. Holyoak, G. Nelson and D. Gochfeld, Analog retrieval by constraint satisfaction, Artificial Intelligence 46(1990)259–310.
C. Tsatsoulis and R.L. Kashyap, Case-based reasoning in manufacturing with TOLTEC planner, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 23(1994)1010–1023.
M. Zeleny, Multiple Criteria Decision Making, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1982.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reza Montazemi, A., Moy Gupta, K. A framework for retrieval in case-based reasoning systems. Annals of Operations Research 72, 51–73 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018960607821
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018960607821