Abstract
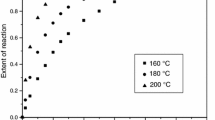
The influence of curing time and curing temperature for a commercially available ethylcellulose latex coating dispersion (Aquacoat®) were evaluated using response surface methodology. Levels for the factor curing time ranged from 30 to 300 minutes while levels for curing temperature ranged from 45° to 75°C. Responses, A, κ, and γ, were derived from regression analysis of the dissolution profiles and correspond to the maximum amount of drug released over the 12 hour sampling period, the rate of release, and the inflection point of the dissolution profile, respectively. The nature of the response surface was dramatically influenced by the plasticizer incorporated into the coating formula. When dibutyl sebacate was employed as the plasticizer, faster release resulted (higher A and κ values, lower γ values) when samples were exposed to higher curing temperatures or were stored for longer periods of time. Paradoxically, when tributyl citrate was used as the plasticizer, slower release resulted when samples were exposed to more rigorous conditions. Overall, curing temperature had a more dramatic effect than curing time.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J.N. Yoo, L.H. Sperling, C.J. Glinka and A. Klein. Characterization of film formation from polystyrene latex particles via SANS. 1. Moderate molecular weight. Macromolecules. 23: 3926–3967 (1990).
Aquacoat Handbook, FMC Corporation, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 1982.
M.R. Harris, I. Ghebre-Sellassie, and R.U. Nesbitt. A water-based coating process for sustained release. Pharm. Tech. 10: 102–107 (1986).
N.H. Parikh, S.C. Porter, and B.D. Rohera. Aqueous ethylcellulose dispersion of ethylcellulose I. Evaluation of coating process variables. Pharm. Res. 10: 525–534 (1993).
F.W. Goodhart, M.R. Harris, K.S. Murthy, and R. U. Nesbitt. An evaluation of aqueous film-forming dispersions for controlled release. Pharm. Tech. 8: 64–71 (1984).
B.H. Lippold, B.K. Sutter, and B.C. Lippold. Parameters controlling drug release from pellets coated with aqueous ethyl cellulose dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 54: 15–25 (1989).
C. Zhao, Y. Wang, Z. Hruska, and M.A. Winnik. Molecular aspects of latex film formation: An energy-transfer study. Macromolecules. 23: 4082–4087 (1990).
R.M. Franz, J.E. Browne, and A.R. Lewis. Experimental design, modeling, and optimization strategies for product and process development. In H.A. Lieberman, M.M. Rieger, and G.S. Banker (eds.), Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Disperse Systems (Volume I), Marcel Dekker, New York, 1988, pp. 427–514.
D.M. Lipps. Application of response surface methodology to wet granulation in tablet technology. Doctor of Philosophy dissertation, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio, 1991.
M. Turkoglu and A. Sakr. Mathematical modelling and optimization of rotary fluidized-bed coating process. Int. J. Pharm. 88: 75–87 (1992).
S. Bolton. Pharmaceutical Statistics. Marcel Dekker, New York, 1990.
A.I. Khuri and J.A. Cornell. Response Surfaces. Marcel Dekker, New York, 1987.
G.A.F. Seber and C.J. Wild. Nonlinear Regression. Wiley & Sons, New York, 1989, pp. 328–331.
A.G. Ozturk, S.S. Ozturk, B.O. Palsson, T.A. Wheatley, and J.B. Dressman. J. Controlled Release. 14: 203–213 (1990).
A.F.M. Barton. CRC handbook of solubility parameters and other cohesion parameters. CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1983.
D.W. Van Krevelen and P.J. Hoftyzer. Properties of polymers: their estimation and correlation with chemical structure. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1976.
R. Chang, C.H. Hsiao, and J.R. Robinson. A review of aqueous coating techniques and preliminary data on release from a theophylline product. Pharm. Tech. 11: 56–68 (1987).
D. Hutchings, S. Clarson, and A. Sakr, Studies of free films prepared using and ethylcellulose latex coating system. Int. J. Pharm. accepted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hutchings, D., Kuzmak, B. & Sakr, A. Processing Considerations for an EC Latex Coating System: Influence of Curing Time and Temperature. Pharm Res 11, 1474–1478 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018960310144
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018960310144