Abstract
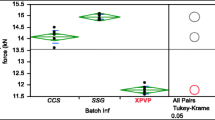
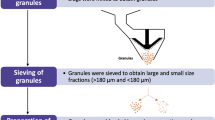
The mechanism and the extent of sorption of water molecules by tablets containing superdisintegrants and microcrystalline cellulose, following the aqueous film coating of formulated tablets, were investigated. The penetration of water from the coating solution into the tablet matrix resulted in significant changes in physical properties of the coated tablet cores, such as residual moisture content, tensile strength, and pore-size distribution. The swelling and the morphological characteristics of each individual disintegrant compound and microcrystalline cellulose were found to have important implications on the extent of penetration of water from the aqueous film coating solution. A hypothesis concerning the interaction between microcrystalline cellulose and the superdisintegrant particles present in the tablet matrix is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. M. Franz, and G. Doonan. Measuring the surface temperature of tablet beds using infrared thermometry. Pharm. Tech. March:55–67 (1983).
L. K. Mathur, S. J. Forbes, and M. Yelvigi. Characterization techniques for the aqueous coating process. Pharm. Tech. October: 42–56 (1984).
G. J. Alcorn, G. H. Closs, R. J. Tinko, A. A. Rosenberg, J. Hall, and J. Shotwell. Comparison of coating efficiency between a Vector Hi-Coater and a Manesty Accela-Cota. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 14 (2):1699–1711 (1988).
G. C. Ebey. A thermodynamic model for aqueous film coating. Pharm. Tech. April:40–50 (1982).
G. Stetsko. Process Analysis and Mathematical Modeling of Aqueous Tablet Film Coating in Production Scale Equipment; Ph.D. thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, 1984, p. 56.
N. Pourkavoos and G. E. Peck. Evaluation of moisture sorption by tablet cores containing superdisintegrants during the aqueous film coating process. Pharm. Res. 10:1212–1218 (1993).
D. Ganderton. The effect of distribution of magnesium stearate on the penetration of a tablet by water. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 21:9S–18S (1969).
L. S. C. Wan and Y. L. Choong. The effect of excipients on the penetration of liquid into tablets. Pharm. Acta Helv. 61:150–156 (1986).
L. S. C. Wan and P. W. S. Heng. Technique of measuring rapid water penetration rate into tablets. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 35:1615–1618 (1987).
L. S. C. Wan and K. P. Prasad. Uptake of water into tablets with low-substituted carboxymethyl cellulose sodium as disintegrant. Int. J. Pharm. 55:115–121 (1989).
J. E. Botzolakis and L. L. Augsburger. Disintegrating agents in hard gelatin capsules. Swelling efficiency. Drug. Dev. Ind. Pharm. 14:1235–1248 (1988).
J. C. Callahan, G. W. Cleary, M. Elefant, R. A. Nash, and L. Kaplan. Equilibrium moisture of content of pharmaceutical excipients. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 8 (3):355–369 (1982).
F. Y. Nakai, S. Nakagima, and J. Hasegawa. Crystallinity and physical characteristics of microcrystalline cellulose. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 25:96–101 (1977).
Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, American Pharmaceutical Association, Washington, DC, and Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain, London, 1986.
R. Shangraw, A. Mitrevej, and M. Shah. A new era of tablet disintegrants. Pharm. Tech. October:49–57 (1980).
Ac-Di-Sol, Modified Cellulose Gum, Bulletin SD-2, Technical Literature, FMC Corp., Philadelphia, PA.
L. Van Campen. Hygroscopicity, Proceedings of the Seventh Wisconsin Update Conference, Madison, WI, April 11–13 1988, p. 7.
G. Zografi. States of Water Associated with Solids, Proceedings of Seventh Wisconsin Update Conference, Madison, WI, April 11–13 1988, pp. 19–41.
Primojel, a Disintegrant in Pharmaceutical Tablets, Technical literature, Avebe American Inc., Hopelawn, NJ.
A. M. Guyot-Hermann and J. Ringard. Disintegration mechanisms of tablets containing starches. Hypothesis about the particle-particle repulsive force. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 7 (2):155–177 (1981).
GAF Corporation. Insoluble Polymers of Vinylpyrrolidone and Process for Producing Same, U.S. patent, 2,038,017, May (1960).
GAF Corporation. Methods of Polymerizing N-Vinyl Lactams with a Metal Oxide or Hydroxide and Water Catalyst. U.S. patent, 3,277.066, October (1966).
GAF Corporation. Polymerization of N-Vinyl Lactams Using Plural Stage Heating in the Presence of Catalyst Compositions of Hydrides or Borohydrides of Alkali Metals and Water. U.S. patent, 3,306,886, February (1967).
Polyplasdone-XL, Crospovidone NF, Technical literature, GAF Corporation, Wayne, NJ.
F. Carli, I. Colombo, L. Magarotto, A. Motta, and C. Torricelli. Influence of polymer characteristics on drug loading into Crospovidone. Int. J. Pharm. 33:115–124 (1986).
P. Molyneux. Synthetic polymers. In F. Franks (ed.), Water: A Comprehensive Treatise, Vol. 4, Plenum Press, London and New York, 1975, pp. 569–731.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourkavoos, N., Peck, G.E. The Effect of Swelling Characteristics of Superdisintegrants on the Aqueous Coating Solution Penetration into the Tablet Matrix During the Film Coating Process. Pharm Res 10, 1363–1371 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018938301252
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018938301252