Abstract
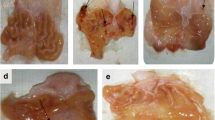
Effects of a novel zinc compound polaprezinc[N-(3-aminopropionyl)-L-histidinatozinc] and sucralfateon the mucosal ulcerogenic responses induced bymonochloramine (NH2Cl) were examined in ratstomachs. Oral administration of NH2Cl (≥60mM) produced severe lesions in unanesthetized ratstomachs, with concomitant increase of lipidperoxidation. These lesions were aggravated by sensorydeafferentation but not affected by pretreatment with indomethacinor L-NAME. The mucosal ulcerogenic response toNH2Cl was significantly inhibited by oralpretreatment with either dmPGE2 (10μg/kg), capsaicin (30 mg/kg), or NOR-3 (3 mg/kg), the NO donor. Gastriclesions induced by NH2Cl were also inhibitedby prior oral administration of polaprezinc (3-30 mg/kg)as well as sucralfate (30 and 100 mg/kg). The protectiveeffect of polaprezinc was not affected by anypretreatments such as indomethacin, L-NAME, or sensorydeafferentation, while that of sucralfate wassignificantly mitigated in the presence of eitherindomethacin or L-NAME. On the other hand, mucosal exposureto NH2OH (60 mM) caused a marked PD reductionin ex vivo stomachs made ischemic by bleeding from thecarotid artery, followed by severe gastric lesions.These ulcerogenic and PD responses caused by NH OHplus ischemia were also attenuated by prior applicationof polaprezinc, while dmPGE2 and sucralfateprevented such lesions without affecting the reduced PDresponse. These results suggest that: (1)NH2Cl generated either exogenously orendogenously damages the gastric mucosa, (2) bothpolaprezinc and sucralfate protect the stomach againstinjury caused by NH2Cl, and (3) the mechanisms underlying the protectiveaction of sucralfate may be partly mediated by bothendogenous PGs and NO but may be different from those ofpolaprezinc.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Marshall BJ, Warren JR: Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1:1273-1275, 1983
Graham DY: Campylobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology 96(suppl):615-625, 1989
Marshall BJ, Langton SR: Urea hydrolysis of patients with Campylobacter pyloridis infection. Lancet 1:965-966, 1983
Whitehead R, Truelove SC, Gear MWL: The histological diagnosis of chronic gastritis in fiberoptic gastroscope biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol 25:1-11, 1972
Badwey JA, Karnovsky ML: Active oxygen species and the functions of phagocytic leukocytes. Annu Rev Biochem 46:695-726, 1980
Klevanoff SJ: Oxygen metabolism and the toxic properties of phagocytes. Ann Intern Med 93:480-489, 1980
Grisham MB, Jefferson MM, Thomas EL: Chlorination of endogenous amines by isolated neutrophil. Ammonia-dependent bactericidal, cytotoxic, and cytolytic activities of the chloramines. J Biol Chem 259:10404-10413, 1984
Grisham MB, Hernandez LA, Granger DN: Xanthine oxidase and neutrophil infiltration in intestinal ischemia. Am J Physiol 251:G567-G574, 1986
Murakami M, Asagoe K, Dekigai H, Kusaka S, Saita H, Kita T: Products of neutrophil metabolism increase ammonia-induced gastric mucosal damage. Dig Dis Sci 40:268-273, 1995
Dekigai H, Murakami M, Kita T: Mechanism of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric mucosal injury. Dig Dis Sci 40:1332-1339, 1995
Seiki M, Ueki S, Tanaka Y, Soeda M, Hori Y, Arita H, Yoneta T, Morita H, Tagashira E, Okabe S: Studies on anti-ulcer effects of a new compound zinc L-carnosine (Z-103). Folia Pharmacol Jpn 95:257-269, 1990
Ito M, Tanaka T, Suzuki Y: Effect of N-(3-aminopropionyl)-L-histidinato zinc (Z-103) on healing and hydrocortisone-induced relapse of acetic acid ulcers in rats with limited food-intake-time. Jpn J Pharmacol 52:513-521, 1990
Arakawa T, Satoh H, Nakamura A, Fukuda T, Sakuma H, Nakamura H, Ishikawa M, Seiki M, Kobayashi K: Effect of zinc-L-carnosine on gastric mucosal and cell damage caused by ethanol in rats. Dig Dis Sci 35:559-566, 1990
Yoshikawa T, Naito Y, Tanigawa T, Yoneta T, Kondo M: The antioxidant properties of a novel zinc-carnosine chelate compound, N-(3-amino-propionyl)-L-histidinatozinc. Biochim Biophys Acta 1115:15-22, 1991
Takeuchi K, Matsumoto J, Ueshima K, Okabe S: Role of capsaicin-sensitive afferent neurons in alkaline secretory responses to luminal acid in the rat duodenum. Gastroenterology 101:954-961, 1991
Holzer P, Sametz W: Gastric mucosal protection against ulcerogenic factors in the rat mediated by capsaicin-sensitive afferent neurons. Gastroenterology 91:975-981, 1986
Ohkawa H, Ohishi Y, Yagi K: Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351-358, 1979
Takeuchi K, Ishihara Y, Okada M, Niida H, Okabe S: A continuous monitoring of mucosal integrity and secretory activity in rat stomach. A preparation using a lucite chamber. Jpn J Pharmacol 49:235-244, 1989
Tsujii M, Kawano S, Tuji S, Fusamoto H, Kamada T, Sato N: Mechanism of gastric mucosal damage induce by ammonia. Gastroenterology 102:1881-1888, 1992
Murakami M, Saita H, Teramoto S, Dekigai H, Asagoe K, Kusaka S, Kita T: Gastric ammonia has a potent ulcerogenic action on the rat stomach. Gastroenterology 105:1710-1715, 1993
Takeuchi K, Ohno T, Okabe S: Irritative and protective activity of mild irritants in rat stomach. Dig Dis Sci 32:889-896, 1987
Ivy KJ, Den Bensteubm L, Glifton JA: Effect of bile salts on ionic movement across the human gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology 59:683-690, 1970
Svanes K, Ito S, Takeuchi K, Silen W: Restitution of the surface epithelium of the in vitro frog gastric mucosa after damage with hyperosmolar sodium chloride: Morphologic and physiologic characteristics. Gastroenterology 82:1409-1426, 1982
Schiessel R, Matthews JB, Barzilai A, Merhav A, Silen W: PGE2 stimulates gastric chloride transport: Possible key to cytoprotection. Nature 283:671-673, 1980
Robert A: Role of endogenous and exogenous prostaglandins in the mucosal protection. In: Mechanisms of Mucosal Protection in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract. A Allen, G Flemstrom, A Garner, W Silen, LA Turnberg (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1984, pp 377-382
Hollander D, Tarnawski A: The protective and therapeutic mechanisms of sucralfate. Scand J Gastroenterol 173(suppl):1-5, 1990
Konturek SJ, Brzozowski T, Majka J, Czarnobilski K: Role of nitric oxide and prostaglandins in sucralfate-induced gastroprotection. Eur J Pharmacol 211:277-279, 1992
Cho CH, Luk CT, Ogle CW: The membrane-stabilizing action of zinc carnosine (Z-103) in stress-induce gastric ulceration in rats. Life Sci 49:PL189-PL194, 1991
Wong SH, Cho CH, Ogle CW: Protection by zinc sulphate against ethanol-induced ulceration: Preservation of the gastric mucosal barrier. Pharmacology 33:94-102, 1986
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kato, S., Nishiwaki, H., Konaka, A. et al. Mucosal Ulcerogenic Action of Monochloramine in Rat Stomachs (Effects of Polaprezinc and Sucralfate). Dig Dis Sci 42, 2156–2163 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018847324172
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018847324172