Abstract
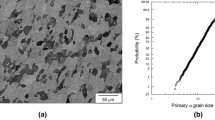
Evidence for sub-surface fatigue crack initiation is often reported for near alpha titanium alloys such as the coarse grained IMI685 and the fine duplex structured IMI834. In such materials with a typical as received hydrogen concentration of 40–60 ppm the initiation site is invariably characterized by quasi-cleavage facetting. Similar facetting is also associated with the low temperature dwell sensitive fatigue response in the same alloys. For IMI685, it is reported that this failure mechanism is replaced by α/β interface cracking when the alloy contains a relatively high concentration of interstitial hydrogen. The present paper characterises the local grain orientation and microstructural conditions associated with these various forms of failure through the use of a microtextural analysis technique based upon electron back scattered diffraction (EBSD) measurements. The observations are related to an existing model to account for facet formation based upon the pile-up of dislocations at grain-boundaries. The implications for further use of this technique with titanium alloys are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. J. EVANS and M. R. BACHE,Int. J. Fatigue 16 (1994) 443.
D. L. DAVIDSON and D. EYLON,Met. Trans. A 11A (1980) 837.
W. J. EVANS and M. R. BACHE,Scripta Met. 32 (1995) 1019.
idem in Titanium '95 Science and Technology Proc. 8th World Conf. on Titanium, 1995, Birmingham, U.K. edited by P. A. Blenkinsop, W. J. Evans and H. M. Flower (Institute of Metals, London) p 1339.
D. J. DINGLEY and V. RANDLE,J. Mater. Sci. 27 (1992) 4545.
D. EYLON,Met. Trans. A 10A (1979) 311.
M. R. BACHE and W. J. EVANS,Int. J. Fatigue 14 (1992) 331.
C. C. WOJCIK, K. S. CHAN and D. A. KOSS,Acta Met. 36 (1988) 1261.
C. SARRAZIN, R. CHIRON, S. LESTERLIN and J. PETIT,Fatigue Fract. Engng. Mater. Struct. 17 (1994) 1383.
J. LUFRANO, P. SOFRONIS and H. K. BIRNBAUM,J. Mech. Phys. Solid 44(2) (1996) 179.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BACHE, M.R., EVANS, W.J. & DAVIES, H.M. Electron back scattered diffraction (EBSD) analysis of quasi-cleavage and hydrogen induced fractures under cyclic and dwell loading in titanium alloys. Journal of Materials Science 32, 3435–3442 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018624801310
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018624801310