Abstract
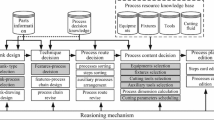
This paper describes a process-planning model using mixed-type reasoning designed for processing prismatic parts on CNC machine tools in a batch manufacturing environment. This mixed-type reasoning handles feature interactions by combining forward chaining for feature sequencing and backward chaining for the construction of a process plan. In such a model, the human problem-solving strategies are decoupled from the tools for analysis and sorting algorithms. Two databases are used to contain the results from forward and backward chaining. The process-planning algorithm combines the processes of modeling the given information in four stages: (1) defining the important information for features and feature-related concerns; (2) interpreting and rearranging the given feature according to the given constraints and sorting guideline; (3) sequencing the features; (4) attaching the needed operations to the features in machine/process/feature/set-up/tool/time/cost format.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdou, G. and Cheng, R. (1993) TVCAPP, tolerance verification in computer-aided process planning. International Journal of Production Research, 31(2), 393–411.
Buteau, B. (1990) Generic framework for distributed, cooperating blackboard systems, in Eighteenth Annual Computer Science Conference, Washington, D. C., pp. 358–365.
Corkill, D. (1990) Blackboard architectures and control applications, in Proceedings 5th IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control, Philadelphia, PA, pp. 36–38.
Engel, B., Beasley, D. and Barrett, J. (1990) Integrating expert systems with conventional problem-solving techniques using blackboard. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 4, 287–301.
Ihara, T. and Ito, Y. (1991) A new concept of CAPP based on flair of experienced engineers analyses of decision-making processes of experienced process engineers. Annals of the CIRP, 40, 437–440.
Karinthi, R., Nau, D. and Ying, Q. (1992) Handling feature interactions in process planning. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 6, 389–415.
Nau, D., Yang, Q. and Hendler, J (1989) Planning for multiple goals with limited interactions, in Fifth IEEE Conference on Artificial Intelligence Application, Miami, FL., pp. 77–84.
Willhelm, R.G. and Lu, S.C-Y. (1992) Tolerance synthesis is to support concurrent engineering. Annals of the CIRP, 41(1), 197–200.
Zhang, H. and Huq, M. (1992) Tolerancing techniques: the-state-of-the-art. International Journal of Production Research, 30, 2111–2135.
Zompi, A. and Tornincasa, S. (1991) Feature-based object oriented approach in automated manufacturing. Annals of the CIRP, 40(1), 515–518.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HWANG , JS., MILLER , W.A. Using mixed-type reasoning in computer-aided process planning for feature interactions. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 8, 297–306 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018589628373
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018589628373