Abstract
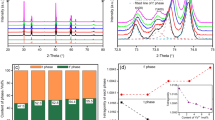
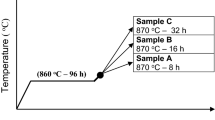
The evolution of crystallization and porosity changes with firing temperature were studied in ZnO–B2O3–SiO2–MgO glasses. Those glasses presintered at 610 °C to a low porosity were crystallized in the temperature range of 690–870 °C. The glasses were crystallized by a surface crystallization mechanism. The porosity increased with the crystallization temperature. In the temperature range of 710–790 °C, several crystalline phases, such as 3ZnO–B2O3, willemite (2ZnO–SiO2), 5ZnO–2B2O3, and another form of zinc silicate (2ZnO–SiO2), produced at relatively low temperatures, were produced, while above 800 °C only the 2ZnO–SiO2 phase co-existed with a glass phase. Only an observed density difference between the glass and the crystallized glass cannot be attributed to the void formation during the crystallization reaction. Due to the crystallization the composition of the remaining glass around the crystalline phases is expected to change. The depletion of a certain component in the remaining glass, probably the SiO2 due to the production of the 2ZnO–SiO2 phase, might result in the increase in the vapour pressure of the remaining glass and lead to the observed increase in porosity. Below 800 °C, at which temperature the crystallization rate is fast and only a small amount of the glass phase remained, the porosity remained constant after the completion of the crystallization. Contrarily at 860 °C the porosity continuously increased with firing time.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Y. MISAWA, H. HACHINO, S. HARA and M. HANAZONO,J. Electrochem. Soc.: Solid-State Sci. and Tech. 131 (1984) 359.
Y. MISAWA,ibid. 131 (1984) 2618.
S. MURAKAMI, K. MIYATA, M. TSURUOKA and Y. KOBAYASHI,ibid. 134 (1987) 2293.
R. MORELL,Proc. Br. Ceram. Soc. 28 (1979) 53.
T. J. CLARK and J. S. REED,J. Amer Ceram. Soc. 69 (1986) 837.
E. M. RABINOVICH,J. Mater. Sci. 20 (1985) 4259.
A. WATANABE, Y. IMADA and S. KIHARA,ibid. 69 (1986) c31.
A. WATANABE, M. MITSUDOU, S. KIHARA and Y. ABE,ibid. 72 (1989) 1499.
J.-J. KIM, B.-K. KIM, B.-M. SONG and D. Y. KIM,ibid. 70 (1987) 734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KIM, J.S., CHEON, C.I. Crystallization and void formation in ZnO–B2O3–SiO2–MgO sintered solder glasses. Journal of Materials Science 32, 1575–1579 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018534824257
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018534824257