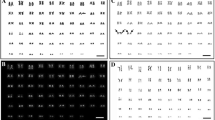
Abstract
Asellus aquaticus is an isopod crustacean whose chromosomes cannot be differentiated by G- or R-banding techniques. In this work, we have obtained a longitudinal differentiation of these chromosomes by in situ nick translation using restriction enzymes (HaeIII, DraI and BamHI) and DNase I digestions. The four nucleases, with different efficiencies, have produced similar labelling patterns. Staining with DAPI, Giemsa and chromomycin A3 reveals that the DNA of the nick-translated regions is generally more resistant to extraction from the chromosome. The results obtained on the heteromorphic sex chromosome pair observed in about a quarter of the males of a natural population allow several hypotheses to be advanced on the nature and origin of chromosome dimorphism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barzotti R, Pelliccia F, Rocchi A (1996) Heterochromatin and ribosomal genes in Asellus aquaticus (Crust. Isop.). Chrom Res 4: 177–181.
de la Torre J, Sumner AT (1994) Analysis of chromosomes with restriction endonucleases and DNase hypersensitivity. In: Gosden JR, ed. Chromosome Analysis Protocols. New Jersey: Humana Press, pp. 123–139.
de la Torre J, Herrero P, Garcia de la Vega C, Sumner AT, Gosálvez J (1996) Patterns of DNase I sensitivity in the chromosomes of the grasshopper Chortippus parallelus (Orthoptera). Chrom Res 4: 56–60.
Gazit B, Cedar H, Lerer I, Voss R (1982) Active genes are sensitive to deoxyribonuclease I during metaphase. Science 217: 648–650.
Greilhuber J (1977) Why plant chromosomes do not show Gbands. Theor Appl Genet 50: 121–124.
Herrero P, de la Torre J, Arano B, Gosálvez J, Sumner AT (1995) Patterns of DNase sensitivity in the chromosomes of Rana perezi (Amphibia: Anura). Genome 38: 339–343.
Holmquist GP (1992) Chromosome bands, their chromatin flavours and their functional features. Am J Hum Genet 51: 17–37.
Kerem B, Goitein R, Diamond G, Cedar H, Marcus M (1984) Mapping of DNase I sensitive regions on mitotic chromosomes. Cell 38: 493–499.
Rocchi A, Prantera G, Di Castro M (1980) A study of the heterochromatin of Asellus aquaticus (Crust. Isop.). Caryologia 3: 401–409.
Rocchi A, Prantera G, Lanza V, Di Castro M (1984) Incipient sex chromosome differentiation in an isopod crustacean species, Asellus aquaticus. Chromosoma 89: 193–196.
Saitoh Y, Laemmli UK (1994) Metaphase chromosome structure: bands arise from a differential folding path of the highly AT-rich scaffold. Cell 76: 609–622.
Schmid M, Guttenbach M (1988) Evolutionary diversity of reverse (R) fluorescent chromosome bands in vertebrates. Chromosoma 97: 101–114.
Sumner AT, Taggart MH, Mezzanotte R, Ferrucci L (1990) Patterns of digestion of human chromosomes by restriction endonucleases demonstrated by in situ nick translation. Histochem J 22: 639–652.
Volpi EV, Pelliccia F, Lanza V, Di Castro M, Rocchi A (1992) Morphological differentiation of a sex chromosome and ribosomal genes in Asellus aquaticus (Crust. Isop.). Heredity 69: 478–482.
Volpi EV, Pelliccia F, Lanza V, Barzotti R, Rocchi A (1995) Simple DNA repeats and sex chromosome differentiation in Asellus aquaticus (Cristacea, Isopoda). Heredity 75: 267–272.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barzotti, R., Pelliccia, F. & Rocchi, A. Longitudinal differentiation of chromosomes of Asellus aquaticus (Crust. Isop.) by in situ nick translation using restriction enzymes and DNase I. Chromosome Res 5, 521–526 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018437618242
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018437618242