Abstract
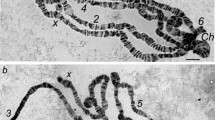
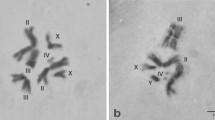
We have adapted the primed in situ labelling (PRINS) protocol for gene mapping in polytene chromosomes of two dipteran species. The method was used to localize the genes for the Balbiani ring (BR) 2.1 and the iron-regulatory protein 1A (IRP1A) in polytene salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus tentans, and Drosophila melanogaster respectively. Two oligonucleotides, correspondin g to the BR 2.1 and IRP1A genes, were used as primers and the whole procedure was performed within 3–4 h. The strong labelling with low background revealed the localization of the BR 2.1 gene in polytene chromosome IV of C. tentans and the IRP1A gene in polytene chromosome 3R83 of D. melanogaster. The results demonstrated that PRINS is a fast, sensitive and suitable approach for physical gene mapping in polytene chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beerman W (1952) Chromomerenhonstung und spezitische modifikationen der chromosomenstruktur in der endwicklung und organdifferenzievung von Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma 5: 189–198.
Bridges CB (1935) Salivary chromosome maps with a key to the banding of the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. J Hered 26: 60–64.
Coignet L, Girardet A, Andréo B, Charlieu JP, Pellestor F (1996) Double and triple in situ chromosomal labeling of human spermatozoa by PRINS. Cytogenet Cell Genet 73: 300–303.
Gu F, Hindkjær J (1996) Primed in situ labelling (PRINS) detection of the telomeric (CCCTTA)n sequences in chromosomes of domestic animals. Mamm Genome 7: 231–232.
Gu F, Hindkjær J, Gustavsson I, Bolund L (1996) A signal of telomeric sequences on porcine chromosome 6q21-q22 detected by primed in situ labelling. Chrom Res 4: 251–252.
Gosden J, Hanratty D, Starling J, Fantes J, Mitchell A, Porteous D (1991) Oligonucleotide-primed in situ DNA synthesis (PRINS): a method for chromosome mapping, banding and investigation of sequence organozation. Cytogenet Cell Genet 57: 100–104.
Henderson BR (1996) Iron regulatory proteins 1 and 2. BioEssays 9: 739–746.
Hindkjær J, Koch J, Mogensen J et al. (1991) Primed in situ labelling of nucleic acids. Biotech Forum Eur 12: 552–556.
Hindkjær J, Koch J, Mogensen J, KØlvraa S, Bolund L (1994) Primed in situ (PRINS) labelling of DNA. In: Choo KHA ed. In Situ Hybridization Protocols. Meth Mol Biol, Totowa, New Jersey: Humana Press, pp. 95–107.
Koch J, KØlvraa S, Petersen KB, Gregersen N, Bolund L (1989a) Oligonucleotide-priming methods for the chromosome-speci-fic labelling of alpha satellite DNA in situ. Chromosoma 98: 259–265.
Koch J, Hindkjær J, Mogensen J, KØlvraa S, Bolund L (1989b) An improved method for chromosome-specific labelling of alpha satellite DNA in situ by using denatured double-stranded DNA probes as primers in primed in situ labelling (PRINS) procedure. Genet Anal Tech Appl 8: 171–178.
Koch J, Mogensen J, Petersen S et al. (1992) Fast one-step procedure for the detection of nucleic acids in situ by primer-induced sequence-specific labelling with fluorescein-12-dUTP. Cytogenet Cell Genet 60: 1–3.
Pellestor F, Quennesson I, Coignet L et al. (1996) Direct detection of disomy in human sperm by the PRINS technique. Hum Genet 97: 21–25.
Saura AO, Heino TI, Sorsa V (1994) Electron micrograph map of the Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosome 3R divisions 81 through 90. Hereditas 121: 1–20.
Silver LM, Wu CEC, Elgin SCR (1978) Immunofluorescent techniques in the analysis of chromosomal proteins. Methods Cell Biol 18: 151–167.
Thomsen PD, Hindkjær J, Christensen K (1992) Assignment of a porcine male-specific DNA repeat to Y-chromosomal heterochromatin. Cytogenet Cell Genet 61: 152–154.
Wieslander L (1994) The Balbiani ring multigene family: coding repetitive sequences and evolution of a tissue-specific cell function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 48: 308–321.
Wieslander L, Paulsson G (1992) Sequence organization of the Balbiani ring 2.1 gene in Chironomus tentans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 4578–4582.
Winterù AK, Fredholm M, Thomsen PD (1992) Variable (dG-dT)n. (dC-dA)n sequences in the porcine genome. Genomics 12: 281–288.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, H.F., Lind, M.I., Wieslander, L. et al. Using PRINS for gene mapping in polytene chromosomes. Chromosome Res 5, 463–465 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018417013699
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018417013699