Abstract
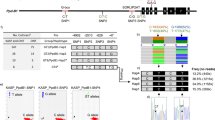
DNA amplification fingerprinting (DAF) and arbitrary signatures from amplification profiles (ASAP) were used to evaluate the genetic stability of two important bermudagrass (Cynodon) cultivars, the interspecific cross Tifgreen and its somatic mutant Tifdwarf, and study genetic diversity and origin of derived bermudagrass off-types that exhibit patches of contrasting morphology and performance. Mini-hairpin primers produced complex and reproducible DAF and ASAP profiles with high levels of polymorphic DNA, and established genetic relationships between 11 Tifgreen and 8 Tifdwarf turf plot accessions and 16 off-types. DAF analysis revealed an average 14.1 ± 5.6 (SE) polymorphic bands/primer within cultivar accessions. In contrast, the higher resolving power of ASAP detected 24.5 ± 2.1 polymorphic bands/primer. Similarly, DAF and ASAP produced 13.0 ± 5.5 (SE) and 20 ± 2.8 polymorphic bands/primer within off-types, respectively. Phenetic analysis using cluster (UPGMA) and ordination (PCO) techniques showed that both Tifdwarf and Tifgreen were genetically unstable. The analysis showed that almost all cultivar accessions and one-half of the off-types studied were genetically distinct, but very close to each other. In this case, genetic variation was probably the result of somatic mutations. The other off-types and some Tifgreen accessions represented a genetically distant and diverse bermudagrass group of interspecific hybrid (n=27) origin. Off-types were probably the result of sod contamination. Results complement a previous study that established that the interspecific Tifway bermudagrass was genetically stable whereas derived off-types were contaminants rather than somatic mutants. Tifgreen and Tifdwarf showed genetic instabilities that were readily detected by DNA amplification with mini-hairpin primers. The present study offers a direct molecular alternative capable of evaluating the genetic stability of selected cultivars.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderson, J. & W.C. Sharp, 1994. Grass varieties in the United States. Agriculture Handbook No. 170. SCS/USDA, Washington DC.
Bassam, B.J. & G. Caetano-Anollés, 1993. Silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 42: 181-188.
Bassam, B.J. & S. Bentley, 1995. Electrophoresis using polyesterbacked polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques 19: 568-573.
Bassam, B.J., G. Caetano-Anoll és & P.M. Gresshoff, 1991. Fast and sensitive silver staining of DNA in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 196: 80-83.
Beard, J.B., 1973. Turfgrass: Science and culture. Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
Burton, G.W., 1966. Tifway (Tifton 419) bermudagrass (Reg. No. 7). Crop Sci 6: 93-94.
Burton, G.W. & J.E. Elsner, 1965. Tifdwarf - A new bermudagrass for golf greens. USGA Green Section Record 2: 8-9.
Caetano-Anollés, G., 1996. Scanning of nucleic acids by in vitro amplification: new developments and applications. Nature biotechnology 14: 1668-1674.
Caetano-Anollés, G. & B.J. Bassam, 1993. DNA amplification fingerprinting using arbitrary oligonucleotide primers. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 42: 189-200.
Caetano-Anollés, G. & P.M. Gresshoff, 1994. DNA amplification fingerprinting using arbitrary minihairpin oligonucleotide primers. Bio/Technology 12: 619-623.
Caetano-Anollés, G. & P.M. Gresshoff, 1996. Generation of sequence signatures from DNA amplification fingerprints with minihairpin and microsatellite primers. Biotechniques 20: 1044- 1056.
Caetano-Anollés, G., B.J. Bassam & P.M. Gresshoff. 1991. DNA amplification fingerprinting using very short arbitrary oligonucleotide primers. Bio/Technology 9: 553-557.
Caetano-Anollés, G., L.M. Callahan, P.E. Williams, K.R. Weaver & P.M. Gresshoff, 1995. DNA amplification fingerprinting analysis of bermudagrass (Cynodon): genetic relationships between species and interspecific crosses. Theor Appl Genet 91: 228-235 (errata in 92: 498, 1996).
Caetano-Anollés, G., R.N. Trigiano & M.T. Windham, 1996. Sequence signatures from DNA amplification fingerprints reveal fine population structure of the dogwood pathogen Discula destructiva. FEMS Microbiol Lett 145: 377-383.
Caetano-Anollés, G., L.M. Callahan & P.M. Gresshoff, 1997. The origin of bermudagrass (Cynodon) offtypes inferred by DNA amplification fingerprinting. Crop Sci 37: 81-87.
Fukui, K., 1996. Plant chromosomes at mitosis. In: K. Fukui & S. Nakayama (Eds.), Plant chromosomes: laboratory methods, pp. 1-17. CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Hanna, W.W., 1986.Abermudagrass primer and the Tifton bermudagrasses. USGA Greens Section Record 24: 11-13.
Hanna, W.W, 1996. TW72: A potential new bermudagrass for golf greens. USGA Green Section Record 34: 11-12.
Hein, M.A, 1961. Registration of varieties and strains of bermudagrass. III. Tifgreen bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon(L.) Pers.]. (Reg. No. 5). Agronomy J 53: 276.
Jaccard, P., 1908. Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud Sci Nat 44: 223-270.
Juska, F.V. & A.A. Hanson, 1964. Evaluation of bermudagrass varieties for general-purpose turf. Agricultural Handbook No. 270. ARS/USDA, Washington DC.
Robinson, B.P. & J.M. Latham, 1956. Tifgreen - An improved turf bermudagrass. USGA Journal & Turf Management 9: 26-28.
Rohlf, F.J., 1992. Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System (NTSYS-pc), version 1.8. Exeter Software, Setauket, NY.
Weaver, K.R., L.M. Callahan, G. Caetano-Anollés& P.M. Gresshoff, 1995. DNA amplification fingerprinting and hybridization analysis of centipedegrass. Crop Sci 35: 881-885.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caetano-Anollés, G. Genetic instability of bermudagrass (Cynodon) cultivars 'Tifgreen' and 'Tifdwarf' detected by DAF and ASAP analysis of accessions and off-types. Euphytica 101, 165–173 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018392623408
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018392623408