Abstract
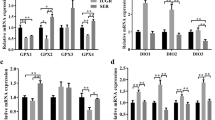
When rat L8 muscle cells were cultured to examine the effects of serum and selenium concentration on selenoprotein W levels and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) activities, no significant differences (P > 0.05) were found in selenoprotein W levels and GPX activities during differentiation. With three different forms of selenium, selenoprotein W levels and GPX activities were shown to increase in L8 myotubes cultured in media with these selenocompounds. Selenite was utilized more efficiently than selenocysteine for both selenoprotein W and GPX activity, but selenium as selenomethionine was less available. Both the protein content and mRNA levels for selenoprotein W were affected by the selenium content of the media. Northern blot data indicated that the expression of selenoprotein W mRNA increased significantly when L8 myotubes were cultured with selenium (P > 0.05). L8 myotubes cultured in 10% calf serum (CS) versus 2% CS with or without addition of 10 m selenium indicated that the increase of selenoprotein W level in L8 myotubes cultured with higher serum concentration (10% CS) is due to the higher selenium concentration in media rather than serum itself.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur JR, Nicol F, Beckett GJ. 1990 Hepatic iodothyronine 5'-deiodinase. Biochem J 272, 537–540.
Behne D, Hilmert H, Scheid S, Gessner H, Elger W. 1988 Evidence for specific selenium target tissues and new biologically important selenoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 966, 12–21.
Beilstein MA, Whanger PD. 1987 Metabolism of selenomethionine and effects of interacting compounds by mammalian cells in culture. J Inorgan Biochem 29, 137–152.
Beilstein MA, Whanger PD. 1992 Selenium metabolism and glutathione peroxidase activity in cultured human lymphoblasts. Biol Trace Elem Res 35, 105–118.
Beilstein MA, Whanger PD, Wong L. 1987 Selenium requirement and metabolism by mammalian cells in vitro. In: Combs GF, Spallholz JE, Levander OA, Oldfield JE, eds. Selenium and Biology and Medicine. New York: AVI/Van Nostrand Reinhold; 197–212.
Berry MJ, Banu L, Chen Y, et al. 1991 Recognition of UGA as a selenocysteine codon in type I deiodinase in the 3'?untranslated region. Nature 353, 273–276.
Bradford MM. 1976 A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye-binding. Anal Biochem 72, 248–254.
Brown MR, Cohen JJ, Lyons JM, et al. 1986 Proximal muscle weakness and selenium deficiency associated with long term parenteral nutrition. Amer J Nutr 43, 549–554.
Brown MW, Watkinson JH. 1977 An automated fluorimetric method for the determination of nanogram quantities of selenium. Anal Chin Acta 89, 29–35.
Chen XS, Yang GQ, Chen JS, et al. 1980 Studies on the relations of selenium and Keshen disease. Biol Trace Elem Res 2, 91.
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. 1987 Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidium thiocyanatephenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162, 156–159.
Chu F-F, Doroshow JH, Esworthy RS. 1993 Expression, characterization and tissue distribution of a new cellular selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase, GSHPx-GI. J Biol Chem 268, 2571–2576.
Croteau W, Whittemore SL, Schneider MJ, Germains DL. 1995 Cloning and expression of a cDNA for a mammalian type III iodothyronine deiodinase. J Biol Chem 270, 16569–16575.
Davey JC, Becker KB, Schneider MJ, St. Germain DL, Galton VA. 1995 Cloning of a cDNA for the type II iodothyroine. J Biol Chem 270, 26786–26789.
Giovannoni SJ 1991 The polymerase chain reaction. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M, eds. Sequencing and Hybrid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 176–201.
Gross M, Oertel M, Kohrle J. 1995 Differential selenium-dependent expression of type I 5'-deiodinase and glutathione peroxidase in the porcine epithelial kidney cell line LLC-PK1. Biochem J 306, 851–856.
Hawkes WC, Wilhelmsen EC, Tappel AL. 1985 Abundance and tissue distribution of selenocysteine-containing proteins in the rat. J Inorg Biochem 23, 77–92.
Hill KE, Lloyd RS, Yang J-G, Read R, Burk RF. 1991 The cDNA for rat selenoprotein P contains 10 TGA codons in the open reading frame. J Biol Chem 266, 10050–10053.
Kalcklosch M, Kyriakopoulos A, Hammel C, Behne D. 1995 A new selenoprotein found in the glandular epithelial cells of the rat prostate. Biochem Biophys Research Commun 217, 162–170.
Karle JA, Kull FJ, Shrift A. 1983 Uptake of selenium-75 by PHA-stimulated lymphocytes: Effect on glutathione peroxidase. Biol Trace Elem Res 5, 17–24.
Laemmli UK. 1970 Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685.
Paglia DE, Valentine WN. 1967 Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70, 158–169.
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, et al. 1973 Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 179, 588–590.
Schubert JR, Muth OH, Oldfield JE, Remmert LF. 1961 Experimental results with selenium in white muscle disease of lambs and calves. Fed Proc 10, 689–692.
Steel RGD, Torrie LH. 1980 Principles and Procedures of Statistics. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Takahashi K, Avissar N, Whitin J, Cohen H. 1987 Purification and characterization of human plasma glutathione peroxidase: a selenoglycoprotein distinct from the known cellular enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys 256, 677–686.
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J. 1979 Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamine gels to nitro-cellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76, 4350–4354.
Ursini F, Maiorino M, Gregolin C. 1985 The selenoen-zyme phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxi-dase. Biochim Biophys Acta 839, 62–70.
Vendeland SC, Beilstein MA, Chen CL, et al. 1993 Purification and properties of selenoprotein W from rat muscle. J Biol Chem 268, 17103–17107.
Vendeland SC, Beilstein MA, Yeh J-Y, Ream W, Whanger PD. 1995 Rat skeletal muscle selenoprotein W: cDNA clone and mRNA modulation by dietary selenium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92, 8749–8753.
White CL, Hoekstra WG 1979 The metabolism of selenite and selenomethionine by mouse fibroblasts grown in tissue culture. Biol Trace Elem Res 1, 253–257.
Yaffe D. 1968 Retention of differentiation potentialities during prolonged cultivation of myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 61, 477–483.
Yeh J-Y, Beilstein MA, Andrews J-S, Whanger PD. 1995 Tissue distribution and influence of selenium status on levels of selenoprotein W. The FASEB J 9, 392–396.
Yeh J-Y, Gu Q, Beilstein MA, Forsberg NE, Whanger PD. 1996 Selenium supplementation results in increased levels of selenoprotein W in sheep tissues. J Nutr (submitted).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, JY., Ou, BR., Forsberg, N.E. et al. Effects of selenium and serum on selenoprotein W in cultured L8 muscle cells. Biometals 10, 11–22 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018306502157
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018306502157