Abstract
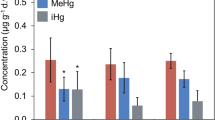
A field experiment was conducted to determine the degree to which fish accumulated methylmercury (MeHg) via their food or via passive uptake from water through the gills. Finescale dace (Phoxinus neogaeus) were held in 2000 L enclosed pens floating in an undisturbed, oligotrophic lake in northwestern Ontario. Fish were exposed to water containing either low (0.10–0.40 ng L-1), intermediate (0.45–1.30 ng L-1), or high (0.80–2.1 ng L-1) concentrations of MeHg. Zooplankton with either low (0.16–0.18 µg g-1 d.w.) or high (0.28–0.76 µg g-1 d.w.) concentrations of MeHg were added daily to each pen. Fish fed zooplankton with high concentrations of MeHg had significantly higher concentrations of mercury in muscle after 32 days than fish fed zooplankton with low concentrations of MeHg (ANCOVA, P<0.0001). Fish feeding on zooplankton with low concentrations of MeHg had the same amount of Hg in their tissues as fish at the start of the experiment. Uptake from water was at most 15%. This is the first experiment to confirm that food is the dominant pathway of MeHg bioaccumulation in fish at natural levels of MeHg.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, F. A. J. and Uthe, J. F.: 1971, At. Absorpt. Newsl. 10, 101.
Bloom, N. S., Horvat, M. and Watras, C. J.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 80, 1257.
Bloom, N. S.: 1989, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 46, 1131.
Bodaly, R. A., Hecky, R. E. and Fudge, R. J. P.: 1984, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 41, 682.
Bodaly, R. A., Rudd, J. W. M., Fudge, R. J. P and Kelly, C. A.: 1993, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 50, 980.
Boudou, A., Georgescauld, D. and Desmazes, J. P.: 1983, Aquatic Toxicology, John Wiley and Sons, New York, New York, p. 117.
Cabana, G., Tremblay, A., Kalff, J. and Rasmussen, J.: 1994, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 51, 381.
Driscoll, C. T., Yan, C., Schofield, C. L., Munson, R. and Holsapple, J.: 1994, Environ. Sci. Technol. 28, 136A.
Harris, R. C. and Snodgrass, W. J.: 1993, Water Poll. Res. J. Canada 28, 217.
Hendzel, M. and Jamieson, D. M.: 1976, Anal. Chem. 48, 926.
Hewett, S. W. and Johnson, B. L.: 1992, Fish Bioenergetics Model 2. University of Wisconsin Sea Grant Institute WIS-SG-91- 250.
Hintelmann, H., Welbourn, P. M. and Evans, R. D.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 80, 1031.
Horvat, M., Bloom, N. S. and Liang, L.: 1993, Anal. Chem. Acta 281, 135.
Jensen, S. and Jernelöv, A.: 1969, Nature 223, 753.
Jernelöv, A. and Lann, H.: 1971, Oikos 22, 403.
Johnels, A., Tyler, G. and Westermark, T.: 1979, Ambio 8, 160.
Kidd, K. A., Hesslein, R. H., Fudge, R. J. P., Hallard, K. A.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 80, 1011.
Malley, D. F., Stewart, A. R. and Hall, B. D.: 1996, Environ. Tox. Chem. 15, 928.
Parks, J.W., Sutton, J. A., Hollinger, J. D. and Russell, D. D.: 1987, Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2, 181.
Phillips, G. R. and Buhler, D. R.: 1978, Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 107, 853.
Rodgers, D. W.: 1994, Mercury Pollution: Integration and Synthesis, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, p. 427.
Rodgers, D. W. and Beamish, F. W. H.: 1981, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 38, 1309.
Rodgers, D. W. and Beamish, F. W. H.: 1983, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 40, 824.
Rudd, J. W. M., Furutani, A. and Turner, M. A.: 1980, Appl. Environ. Micro. 40, 777.
Spry, D. J. and Wiener, J. G.: 1991, Environ. Pollut. 71, 243.
St. Louis, V., Rudd, J. W. M., Kelly, C. A., Beaty, K. G., Bloom, N. S. and Flett, R. J.: 1994, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 51, 1065.
Stainton, M. P., Capel, M. J. and Armstrong, F. A. J.: 1977, Fish. Mar. Serv. Misc. Spec. Publ. 2, 180.
Watras, C. J., Bloom, N. S., Hudson, R. J. M., Gherini, S., Munson, R., Claas, S. A., Morrison, K. A.
Hurley, J., Wiener, J. G., Fitzgerald, W. F., Mason, R., Vandal, G., Powell, D., Rada, R., Rislov, L., Winfrey, M., Elder, J., Krabbenhoft, D., Andren, A. W., Babiarz, C., Porcella, D. B. and Huckabee, J. W.: 1994, Mercury Pollution: Integration and Synthesis, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, p. 153.
Winfrey, M. R. and Rudd, J. W. M.: 1990, Environ. Tox. Chem. 9, 853.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hall, B.D., Bodaly, R.A., Fudge, R.J.P. et al. Food as the Dominant Pathway of Methylmercury Uptake by Fish. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 100, 13–24 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018071406537
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018071406537