Abstract
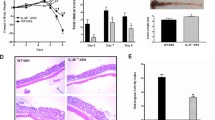
Mice deficient in interleukin-2 (IL-2−/−) develop inflammatory bowel disease resembling human ulcerative colitis. After death, macroscopic and microscopic scores were used to determine colonic inflammation. Both scores were significantly increased in the colon of IL-2 −/− mice as compared to wild types mice. The level of IL-1β 24-week-old was increased in IL-2 −/− mice produced by the colon as compared with IL-2 +/+ controls. However, the concentrations of IL-6 and IL-10 were not changed. The spleen weight of IL-2 −/− mice was significantly increased compared with IL-2 +/+ controls. We used immunochemical techniques in low-temperature paraffin-embedded spleen of IL-2 −/− mice to examine pathological changes of CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and CD11b+ cells. The tissue was successfully stained and was well preserved. The percentage CD4+ T cells was not significantly changed, while the percentage CD8+ T cells was significantly decreased in IL-2 −/− mice compared with IL-2 +/+ controls. On the other hand, the percentage CD11b+ cells was significantly increased in the spleen of IL-2 −/− mice compared with IL-2 +/+ controls. As well as the marked difference in CD8+ and CD11b+ cells in the spleen, the increased level of IL-1β in colonic tissue might indicate that cytotoxic T cells as well as macrophages are involved in the development and/or perpetuation of the inflammatory reactions in IL-2 −/− mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Sadlack B, Merz H, Schorle H, Schimpl A, Feller AC, Horak, I: Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell 75:253–261, 1993
Autenrieth IB, Bucheler N, Bohn E, Heinze G, Horak I: Cytokine mRNA expression in intestinal tissue of interleukin-2 deficient mice with bowel inflammation. Gut 41:793–800, 1997
Grabstein KH, Eisenman J, Shanebeck K, Rauch C, Srinivasan S, Fung V, Beers C, Richardson J, Schoenborn MA, Ahdieh M: Cloning of a T cell growth factor that interacts with the beta chain of the interleukin-2 receptor. Science 264:965–968, 1994
Reinecker HC, MacDermott RP, Mirau S, Dignass A, Podolsky DK: Intestinal epithelial cells both express and respond to interleukin 15. Gastroenterology 111:1706–1713, 1996
Paterson DJ, Jefferies WA, Green JR, Brandon MR, Corthesy P, Puklavec M, Williams AF: Antigens of activated rat T lymphocytes including a molecule of 50,000 Mr detected only on CD4 positive T blasts. Mol Immunol 24:1281–1290, 1987
van Ewijk W, van Soest PL, van den Engh GJ: Fluorescence analysis and anatomic distribution of mouse T lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies to the antigens Thy-1, Lyt-1, Lyt-2, and T-200. J Immunol 127:2594–2604, 1991
Ikebe M, Miyakawa K, Takahashi K, Ohbo K, Nakamura M, Sugamura K, Suda T, Yamamura K, Tomita K: Lymphohaematopoietic abnormalities and systemic lymphoproliferative disorder in interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain-deficient mice. Int J Exp Pathol 78:133–148, 1997
Meijssen MA, Brandwein SL, Reinecker HC, Bhan AK, Podolsky DK: Alteration of gene expression by intestinal epithelial cells precedes colitis in interleukin-2-deficient mice. Am J Physiol 274:G472–G479, 1998
Schorle H, Holtschke T, Hunig T, Schimpl A, Horak I: Development and function of T cells in mice rendered interleukin-2 deficient by gene targeting. Nature 352:621–624, 1991
Van Meeteren ME, Meijssen MAC, Zijlstra FJ: The effect of dexamethasone treatment on murine colitis. Scan J Gastroenterol 35:517–521, 2000
Dieleman LA, Ridwan BU, Tennyson GS, Beagley KW, Bucy RP, Elson CO: Dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis occurs in severe combined immodeficient mice. Gastroenterology 107:1643–1652, 1994
McLean IW, Nakane PK: Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 22:1077–1083, 1974
Gendelman HE, Moench TR, Narayan O, Griffin DE: Selection of a fixative for identifying T cell subsets, B cells, and macrophages in paraffin-embedded mouse spleen. J Immunol Methods 65:137–145, 1983
Whiteland JL, Nicholls SM, Shimeld C, Easty DL, Williams NA, Hill TJ: Immunohistochemical detection of T-cell subsets and other leukocytes in paraffin-embedded rat and mouse tissues with monoclonal antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem 43:313–320, 1995
Dentener MA, Bazil V, Von Asmuth EJU, Ceska M, Buurman WA: Involvement of CD14 in lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-I, IL-6 and IL-8 release by human monocytes and alveolar macrophages. J Immunol 150:2885–2891, 1993
Lord PCW, Wilmoth LMG, Mizel SB, McCall CE. Expression of interleukin-1α and β genes by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest 87:1312–1321, 1991
Wright SD, Ramos RA, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ, Mathison JC: CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 249:1431–1433, 1990
Fearns C, Kravchenko VV, Ulevitch RJ, Loskutoff DJ: Murine CD14 gene expression in vivo: Extramyeloid synthesis and regulation by lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med 181:857–866, 1995
McDonald SAC, Palmen MJHJ, Van Rees EP, MacDonald TT: Characterization of the mucosal cell-mediated immune response in IL-2 knockout mice before and after the onset of colitis. Immunology 91:73–80, 1997
Schultz M, Tonkonogy SL, Sellon RK, Veltkamp C, Godfrey VL, Kwon J, Genther WB, Balish E, Horak I, Sartor RB: IL-2-deficient mice raised under germfree conditions develop delayed mild focal intestinal inflammation. Am J Physiol 276:G1461–G1472, 1999
Cominelly F, Kam L: Inflammatory mediators of inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 9:534–543, 1993
Sartor RB: Cytokines in intestinal inflammation: Pathophysiological and clinical considerations. Gastroenterology 106:533–539, 1994
Isaacs KL, Sartor RB, Haskil S: Cytokine messenger RNA profiles in inflammatory bowel disease mucosa detected by polymerase chain reaction amplification. Gastroenterolgy 103:1587–1595, 1992
Smith KA: Interleukin-2. Curr Opin Immunol 4:271–276, 1992
Sugamura K, Asao H, Kondo M, Tanaka N, Ishii N, Nakamura M, Takeshita T: The common gamma-chain for multiple cytokine receptors. Adv Immunol 59:225–277, 1995
Smith KA: Interleukin-2: inception, impact, and implications. Science 240:1169–1176, 1988
Simpson SJ, Mizoguchi E, Allen D, Bhan AK, Terhorst C: Evidence that CD4+, but not CD8+ T cells are responsible for murine interleukin-2-deficient colitis. Eur J Immunol 25:2618–2625, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrelds, I., van Meeteren, M., Meijssen, M. et al. Interleukin-2-Deficient Mice: Effect on Cytokines and Inflammatory Cells in Chronic Colonic Disease. Dig Dis Sci 47, 503–510 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017995414697
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017995414697