Abstract
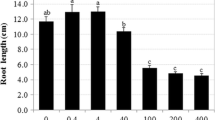
The effects of different concentrations (10−5 – 10−2 M) of copper sulfate on root growth, cell division and nucleoli in root tip cells of Zea mays L. were investigated. 10−5 M Cu stimulated root growth, but at higher concentrations (10−4 – 10−2 M) inhibited it. Cu had toxic effects on chromosomal morphology: c-mitosis, anaphase bridges, and chromosome stickiness were induced. Some nuclei had irregular shape and particles extruded from nucleoli to nuclei and finally from the nuclei into the cytoplasm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, K., Sharma, A., Talukder, G.: Copper toxicity in plant cellular systems.-Nucleus 30: 131–158, 1987.
Baker, D.E., Senft, J.P.: Coper.-In: Alloway, B.J. (ed.): Heavy Metals in Soils. Pp. 179–205. Blackie Academic & Professional, London 1995.
Burton, K.W., Morgan, E., Roig, A.: The influence of heavy metals upon the growth of Sitka-spruce in south Wales forests. I. Upper critical and foliar concentrations.-Plant Soil 73: 327–336, 1983.
Clijsters, H., Van Assche, F.: Inhibition of photosynthesis by heavy metals.-Photosynth. Res. 7: 31–40, 1985.
De Vos, C.H.R., Bookum, W.M.T., Vooijs, R., Schat, H., de Kok, L.J.: Effect of copper on fatty acid composition and peroxidation of lipids in the roots of copper tolerant and sensitive Silene cucubalus.-Plant Physiol. Biochem. 31: 151–158, 1993.
Eleftheriou, E.P., Karataglis, S.: Ultrastructural and morphological characteristics of cultivated wheat growing on copper-polluted fields.-Bot. Acta 102: 134–140, 1989.
Fernandes, J.C., Henriques, F.S.: Biochemical, physiological, and structural effects of excess copper in plants.-Bot. Rev. 57: 246–273, 1991.
Fiskesjö, G.: The Allium test as a standard in environmental monitoring.-Hereditas 102: 99–112, 1985.
Fiskesjö, G.: The Allium test-an alternative in environmental studies: the relative toxicity of metal ions.-Mutat. Res. 197: 243–260, 1988.
Iglesias, A.A., Andreo, C.S.: Inhibition of Zea mays phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase by copper and cadmium ion.-Photosynthetica 18: 134–138, 1984.
Jensén, P., Adalsteinsson, S.: Effects of copper on active and passive Rb+ influx in roots of winter wheat.-Physiol. Plant. 75: 195–200, 1989.
Kahle, H.: Response of roots of trees to heavy metals.-Environ. exp. Bot. 33: 99–119, 1993.
Klášterská, I., Natarajan, A.T., Ramel, C.: An interpretation of the origin of subchromatid aberrations and chromosome stickiness as a category of chromatid aberrations.-Hereditas 83: 153–162, 1976.
Lastra, O., Chueca, A., Gonzalez, C., Lachica, M., Gorge, J.L.: El cobre como nutriente de la planta.-An. Edafol. Angrobiol. 46: 1005–1020, 1987.
Levan, A.: Cytological reaction induced by inorganic salt solutions.-Nature 156: 751, 1945.
Li, M.X.: Introducing a good stain used for nuclei and chromosome.-Bull. Biol. 5: 53, 1982.
Li, M.X., Zhang, Z.P., Yuan, J.S., Pu, X.L.: An improved method for Ag-NOR staining and its application to plant chromosomes.-Chin. Bull. Bot. 7: 56–59, 1990.
Liu, D.H., Jiang, W.S.: Effects of Al3+ on the nucleolus of Allium cepa root-tip cells.-Hereditas 115: 213–219, 1991.
Liu, D.H., Jiang, W.S., Lu, C., Zhao, F.M.: Effects of copper sulfate on the nucleolus of Allium cepa root-tip cells.-Hereditas 120: 87–90, 1994.
Lolkema, P.C., Vooijs, R.: Copper tolerance in Silene cucubalus: subcellular distribution of copper and its effects on chloroplasts and plastocyanin synthesis.-Planta 167: 30–36, 1986.
Marschner, H.: Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. 2nd Edition.-Academic Press, London 1995.
McGill, M., Pathak, S., Hsu, T.C. Effects of ethidium bromide on mitosis and chromosomes: A possible material basis for chromosome stickiness.-Chromosoma 47: 157–164, 1974.
Ouzounidou, G.: Root growth and pigment composition in relationship to element uptake in Silene compacta plants treated with copper.-J. Plant Nutr. 17: 933–943, 1994a.
Ouzounidou, G.: Copper-induced changes on growth, metal content and photosynthetic function of Alyssum montanum.-Environ. exp. Bot. 34: 165–172, 1994b.
Ouzounidou, G., Eleftheriou, E., Karataglis, S.: Ecophysiological and ultrastructural effects of copper in Thlaspi ochroleucum, Cruciferae.-Can. J. Bot. 70: 947–957, 1992.
Ouzounidou, G., Čiamporová, M., Moustakas, M., Karataglis, S.: Responses of maize (Zea mays L.) plants to copper stress-I. Growth, mineral content and ultrastructure of roots.-Environ. exp. Bot. 35: 167–176, 1995.
Punz, W.F., Sieghardt, H.: The response of roots of herbaceous plant species to heavy metals.-Environ. exp. Bot. 33: 85–98, 1993.
Reboredo, F., Henriques, F.: Some observations on the leaf ultrastructure of Halimione portulacaides (L.) Aellen grown in a medium containing copper.-J. Plant Physiol. 137: 453–467, 1991.
Robson, A.D., Reuter, D.J.: Diagnosis of copper deficiency and toxicity.-In: Loneragen, J.F., Robson, A.D., Graham, R.D. (ed.): Copper in Soils and Plants. Pp. 287–312. Academic Press, New York-Sydney 1981.
Sanders, J.R., Adams, T.M., Christensen, B.T.: Extractability and bioavailability of zinc, cadmium and copper in three Danish soils sampled five years after application of sewage sludge.-J. Sci. Food Agr. 37: 1155–1164, 1986.
Stiborová, M., Doubravová, M., Březinová, A., Friedrich, A.: Effects of heavy metal ions on growth and biochemical characteristics of photosynthesis of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).-Photosynthetica 20: 418–425, 1986a.
Stiborová, M., Hromádková, R., Leblová, S.: Effects of ions of heavy metals on the photosynthetic characteristics of maize (Zea mays L.).-Biológia 41: 1221–1228, 1986b.
Strange, J., Macnair, M.: Evidence for a role for the cell membrane in copper tolerance of Mimulus guttatus Fischer ex DC.-New Phytol. 119: 383–388, 1991.
Tukendorf, A., Baszynski, T.: Partial purification and characterization of copper-binding protein from roots of Avena sativa grown on excess copper.-J. Plant Physiol. 120: 57–63, 1985.
Wainwright, S.J.; Woolhouse, H.W.: Some physiological aspects of copper and zinc tolerance in Agrostis tenuis Sibth: Cell elongation and membrane damage.-J. exp. Bot. 28: 1029–1036, 1977.
Wang, Y.H.: General Cell Biology.-Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishing House, Shanghai 1988.
Xu, Y.: Structure and funtion of calmodulin (I).-Biochem Biophys. 1: 22–27, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, W., Liu, D. & Liu, X. Effects of Copper on Root Growth, Cell Division, and Nucleolus of Zea Mays. Biologia Plantarum 44, 105–109 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017982607493
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017982607493