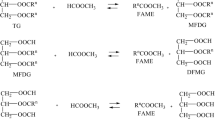
Abstract
The selection of a relative inexpensive and promising method of production of biofuel from renewable plant sources — rape oils — was substantiated. A mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty acid methyl esters (ROME) was obtained by esterification of rape oil. The percentage composition of methyl esters and the net heat value of the biofuel were found by chromatography of ROME. The physical properties of diesel fuel, ROME, and blends and the effect of these properties on injection, spraying, and mixing in the diesel cylinder were determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. N. Vyrubov, N. A. Ivashchenko, V. I. Ivin, et al., in: Internal Combustion Engines: Theory of Piston and Combined Engines [in Russian], A. S. Orlin and M. G. Kruglov (eds.), Mashinostroenie, Moscow (1983).
F. I. Abramchuk, A. P. Marchenko, N. F. Razleitsev, et al., in: Modern Diesels: Increased Fuel Economy and Prolonged Endurance [in Russian], A. F. Shekhovtsov (ed.), Tekhnika, Kiev (1992).
A. S. Lyshevskii, Fuel Spraying by Diesel Nozzles [in Russian], Mashgiz, Moscow (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchenko, A.P., Semenov, V.G. Alternative Biofuel From Rape Oil Derivatives. Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils 37, 183–185 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017976722355
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017976722355