Abstract
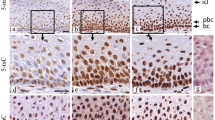
In general, the incidence of proliferating cells parallels that of carcinogenesis. We have investigated proliferating activity and phenotype expression in epithelial cells in normal tissue, mucinous metaplasia and ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Twenty-eight resected pancreases (15 cases of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and 13 cases of other diseases) were examined. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections were examined for proliferating cell activity using histone H3 mRNA in situ hybridization and immunostaining for Ki-67. In the normal pancreas, the labelling indices for proliferating cells were low and no generating zone was found. The following progressive increase was found in the labelling indices: normal ductal epithelium < mucinous metaplasia without papillary hyperplasia < mucinous metaplasia with papillary hyperplasia < ductal carcinoma. In the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas, the S-phase fraction, as defined by the ratio H3-mRNA-labelling index/Ki-67-labelling index, increased as the degree of differentiation decreased. Mucinous metaplasia with papillary hyperplasia showed organoid differentiation toward pyloric mucosa. If used in combination with other proliferative markers on paraffin-embedded tissue sections, histone H3 mRNA in situ hybridization could open broader perspectives on the biology of cell proliferation in the pancreatic ductal system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almoguera C, Shibata D, Forrester K, Martin J, Arnheim N, Perucho M (1988) Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell 53: 549–554.
Bravo R, Frank R, Blundell PA, Macdonald-Bravo H (1987) Cyclin/PCNAis the auxiliary protein of DNApolymerase delta. Nature 326: 515–517.
Butterworth BE, Goldsworthy TC (1991) The role of cell proliferation in multistage carcinogenesis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 198: 683–687.
Campani D, Boggi U, Cecchetti D, Esposito I, Ceccarelli F, D'Antonio L, De Negri F, Mosca F, Bevilacqua G, Fornaciari G (1999) p53 overexpression in lymph node metastases predicts clinical outcome in ductal pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 19: 26–32.
Chou MY, Chang AL, McBride J, Donoff B, Gallagher GT, Wong DT (1990) A rapid method to determine proliferation patterns of normal and malignant tissues by H3 mRNA in situ hybridization. Am J Pathol 136: 729–733.
Crocker J, Nar P. (1987) Nucleolar organizer regions in lymphomas. J Pathol 151: 111–118.
Cubilla AL, Fitzgerald PJ (1976) Morphological lesions associated with human primary invasive nonendocrine pancreas cancer. Cancer Res 36: 2690–2698.
Elsässer HP, Adler G, Kern H (1993) Replication and regeneration of the pancreas. In: Go VLW, DiMagno EP, Gardner JD, Lebenthal E, Reber HA, Scheele G, eds. The Pancreas, 2nd edn, New York: Raven Press, pp. 75–86.
Epstein WL, Maibach HI (1965) Cell renewal in human epidermis. Arch Dermatol 92: 462–468.
Gerdes J, Schwab U, Lemke H, Stein H (1983) Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer 31: 13–20.
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH, Schwab U, Stein H (1984) Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Imunol 133: 1710–1715.
Gown AM, Jiang JJ, Matles H, Skelly M, Goodpaster T, Cass L, Reshatof M, Spaulding D, Coltrera MD (1996) Validation of the S-phase speci-ficity of histone (H3) in situ hybridization in normal and malignant cells. J Histochem Cytochem 44: 221–226.
Handa K, Yamakawa M, Takeda H, Kimura S, Takahashi T (1999) Expression of cell cycle markers in colorectal carcinoma: superiority of cyclin A as an indicator of poor prognosis. Int J Cancer 84(3): 225–233.
Islam HK, Fujioka Y, Tomidokoro T, Sugiura H, Takahashi T, Kondo S, Katoh, H. (1999) Immunoshistochemical analysis of expression of molecular biologic factors in intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of pancreas – diagnostic and biologic significance. Hepato-Gastroenterology 46: 2599–2605.
Klöppel G, Bommer G, Ruckert K, Seifert G (1980) Intraductal proliferation in the pancreas and its relationship to human and experimental carcinogenesis. Virchows Arch [Pathol Anat] 387: 221–233.
Klöppel G, Solcia E, Longnecker DS, Capella C, Sobin LH (1996) World Health Organization International Histological Classification of Tumours, Histological typing of tumors of the exocrine pancreas, 2nd edn. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Konishi H, Steinbach G, Terry NHA, Lee JJ, Dubin JA, Glober GA, Fujita K, Spaulding D, Cass L, Hittelman WN (1996) Histone H3 mRNA in situ hydridization correlates with in vivo bromodeoxyuridine labelling of S-phase cells in rat colonic epithelium. Cancer Res 56: 434–437.
Kotelnikov V, Cass L, Coon JS, Spaulding D, Preisler HD (1997) Accuracy of histone H3 messenger RNA in situ hydridization of the assessment of cell proliferation in human tissues. Clin Cancer Res 3: 669–673.
Lipkin M, Sherlock P, Bell B (1964) Cell proliferation kinetics in the gastrointestinal tract of man. Gastroenterology 45: 405–417.
Louis DN (1994) The p53 gene and protein in human brain tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 53: 11–21.
Lu CD, Morita S, Ishibashi T, Hara H, Isozaki H, Tanigawa N (1999) Loss of p27Kip1 expression independently predicts poor prognosis for patients with resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 85: 1250–1260.
Lüttges J, Reinecke-Luthge A, Mollmann B, Menke MA, Clemens A, Klimpfinger M, Sipos B, Klöppel G (1999a) Duct changes and K-ras mutations in the disease-free pancreas: analysis of type, age relation and spatial distribution. Virchow Arch 435: 461–468.
Lüttges J, Schlehe B, Menke MA, Vogel I, Henne-Bruns D, Kloppel G (1999b) The K-ras mutation pattern in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma usually is identical to that in associated normal, hyperplastic, and metaplastic ductal epithelium. Cancer 85: 1703–1710.
Maeyama H, Furuwatari C, Ota H, Akamatsu T, Nakayama J, Katsuyama T (1997) Histone H3 messengerRNAin situ hybridization for identifying proliferating cells in formalin-fixed rat gastric mucosa. Histochem J 29: 867–873.
Matsuzawa K, Akamatsu T, Katsuyama T (1992) Mucin histochemistry of pancreatic duct cell carcinoma, with special reference to organoid differentiation simulating gastric pyloric mucosa.HumPathol 23: 925–933.
Merchenthaler I, Stankovics J, Gallyas F (1989) A highly sensitive one step method for silver intensification of the nickel-diaminobenzidine end-product of peroxidase reaction. J Histochem Cytochem 37: 1563–1565.
Morstyn G, Hsu SM, Kinsella T, Gratzner H, Russo A, Mitchell JB (1983) Bromodeoxyuridine in tumors and chromosomes detected with a monoclonal antibody. J Clin Invest 72: 1844–1850.
Murphy SA, Warren S (1954) Pancreatic duct hyperplasia and cancer. Gastroenterology 27: 629–640.
Nagao T, Ishida Y, Kondo Y (1996) Determination of S-phase cells by in situ hybridization for histone H3 mRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with histologic grade and other cell proliferative markers. Mod Pathol 9: 99–104.
Ota H, Katsuyama T, Ishii K, Nakayama J, Shiozawa T, Tsukahara Y (1991) A dual staining method for identifying mucins of different gastric mucous cells. Histochem J 23: 22–28.
Rautiainen E, Haapasalo H, Sallinen P, Rantala I, Helen P, Helin H (1998) HistonemRNAin situ hybridization in astrocytomas: a comparison with PCNA, MIB-1 and mitoses in paraffin-embedded material. Histopathology 32: 43–50.
Slater SD, Williamson RC, Foster CS (1998) Proliferation of parenchymal epithelial cells enhanced in chronic pancreatitis. J Pathol 186: 104–108.
Solcia E, Capella C, Klöppel G (1997) Atlas of tumor pathology Vol. 20 Tumors of the pancreas, 3rd edn. Washington DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
Stein GS, Sierra F, JL, Plumb MA, Marashi F, Carozzi N, Prokopp K, Baumbach L(1984) Organization and expression of human histone genes. In: Stein GS, Stein JL, Marzluff W, eds. Histone Gene: Structure, Organization and Regulation. Wiley, New York, pp.397–455.
Tada M, Omata M, Ohto M(1991) Clinical application of ras gene mutation for diagnosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 100: 233–238.
Terada T, Ohta T, Kitamura Y, Ashida K, Matsunaga Y(1998) Cell proliferative activity in intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms and invasive ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas: an immunohistochemical study. Arch Pathol Lab Med 122: 42–46.
Yanagisawa A, Ohtake K, Ohashi K, Hori M, Kitagawa T, Sugano H, Kato Y (1993) Frequent c-Ki-ras oncogene activation in mucous cell hyperplasia of pancreas suffering from chronic inflammation. Cancer Res 53: 953–956.
Vemuru RP, Aragona E, Gupta S (1992) Analysis of hepatocellular proliferation: study of archival liver tissue is facilitated by an endogenous marker of DNA replication. Hepatology 16: 968–973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arakura, N., Hayama, M., Honda, T. et al. Histone H3 MRNA in situ Hybridization for Identifying Proliferating Cells in Human Pancreas, with Special Reference to the Ductal System. Histochem J 33, 183–191 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017956412617
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017956412617