Abstract
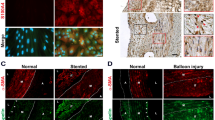
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase is a key enzyme mediating the cellular response to a variety of extracellular stimuli. In the present study, we performed immunohistochemical studies of the expression of the phosphorylated form of the kinase in 51 human aortas of various ages. The phosphorylated kinase immunoreactivity was strongly detected in vascular smooth muscle cells of the medial vessel layer of atherosclerotic lesions from adults. Immunoreactivity was also strongly detected in similar cells of the intima. On the other hand, immunoreactive phosphorylated kinase was only weakly detected in the medial vascular smooth muscle cells of non-atherosclerotic lesions from adults. We also investigated the expression of the phosphorylated kinase in infant aortas. In contrast to its weak immunoreactivity in adult non-atherosclerotic lesions, the kinase immunoreactivity was detected in high amounts in vascular smooth muscle cells of non-atherosclerotic lesions from infants. Thus, the abundant expression of the phosphorylated kinase in these cells in atherosclerotic lesions of adults and non-atherosclerotic lesions of infants suggests that the activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase may be an important element initiating the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells during atherogenesis and aortic development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler V, Fuchs SY, Kim J, Kraft A, King MP, Pelling J, Ronai Z (1995) Jun-NH2-terminal kinase activation mediated by UV-induced DNA lesions in melanoma and fibroblast cells. Cell Growth Differ 6:1437–1446.
Chan ED, Winston BW, Jarpe MB, Wynes MW (1997) Preferential activation of the p46 isoform of JNK/SAPK in mouse macrophages by TNF?. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 13169–13174.
Cobb MH, Goldsmith EJ (1995) How MAP kinases are regulated. J Biol Chem 270: 14843–14846.
Derijard B, Raingeaud J, Barrett T, Wu IH, Hab J, Ulevitch RJ, Davis RJ (1995) Independent human MAP kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science 267: 682–685.
Frostegard J, Ulfgren A-K, Nyberg P, Hedin U, Swedenborg J, Andersson U, Hansson GK (1999) Cytokine expression in advanced human atherosclerotic plaques: dominance of pro-inflammatory (Th1) and macrophage-stimulating cytokines. Atherosclerosis 145: 33–43.
Fuchs SY, Adler V, Pincus MR, Ronai Z (1998) MEKK1/JNK signaling stabilizes and activates p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 10541–10546.
Gupta S, Campbell D, Derijard B, Davis RJ (1995) Transcription factor ATF2 regulation by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science 267:389–393.
Hamada K, Takuwa N, Yokoyama K, Takuwa Y (1998) Stretch activates Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells through mechanisms involving autocrine ATP stimulation of purinoceptors. J Biol Chem 273: 6334–6340.
Hibi M, Lin A, Smeal T, Minden A, Karin M (1993) Identification of an oncoprotein-and UV-responsive protein kinases that bind and potentiate the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev 7: 2135–2148.
Hu Y, Cheng L, Hochleitner B-W, Xu Q (1997a) Activation of mitogenactivated protein kinases (ERK/JNK) and AP-1 transcription factor in rat carotid arteries after baloon injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17: 2808–2816.
Hu Y, Metzler B, Xu Q (1997b) Discordant activation of stress-activated protein kinases or c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinases in tissues of heat-stressed mice. J Biol Chem 272: 9113–9119.
Hu Y, Dietrich H, Metzler B, Wick G, Xu Q (2000) Hyperexpression and activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) in atherosclerotic lesions of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20: 18–26.
Lin A, Minden A, Martinetto H, Claret FX, Lange-Carter C, Mercurio F, Johnson GL, Karin M (1995) Identification of a dual specificity kinase that activates the Jun kinases and p38-Mpk2. Science 268: 286–290.
Mallat Z, Heymes C, Ohan J, Faggin E, Leseche G, Tedgui A (1999) Expression of interleukin-10 in advanced human atherosclerotic plaques. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19: 611–616.
Metzler B, Hu Y, Dietrich H, Xu Q (2000) Increased expression and activation of stress-activated protein kinases/c-Jun NH2-terminal protein kinases in atherosclerotic lesions coincide with p53. Am J Pathol 156:1875–1886. c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase in human aorta 171
Modur V, Zimmerman GA, Prescott SM, Mclntyre TM (1996) Endothelial cell inflammatory responses to tumor necrosis factor alpha. Ceramide-dependent and-independent mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. J Biol Chem 271: 13094–13102.
Nayler WG (1999) Review of preclinical data of calcium channel blockers and atherosclerosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 33: S7–S11.
Nishida E, Gotoh Y (1993) The MAP kinase cascade is essential for diverse signal transduction pathways. Trends Biochem Sci 18: 128–131.
Raingeaud J, Whitmarsh AJ, Barrett T, Derijard B, Davis RJ (1996) MKK3-and MKK6-regulated gene expression is mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol 16: 1247–1255.
Reusch HP, Chan G, Ives HE, Nemenoff RA (1997) Activation of JNK/SAPK and ERK by mechanical strain in vascular smooth muscle cells depends on extracellular matrix composition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 237: 239–244.
Rivard A, Andres V (2000) Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Histol Histopathol 15: 557–571.
Robinson MJ, Cobb MH (1997) Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9: 180–186.
Stary HC, Chandler AB, Glagov S, Guyton JR, Insull Jr W, Rosenfeld ME, Schaffer SA, Schwartz CJ, Wagner WD, Wissler RW (1994) A definition of initial, fatty streak, and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis. Circulation 89: 2462–2478.
Stary HC, Chandler AB, Dinsmore RE, Fuster V, Glagov S, Insull Jr W, Rosenfeld ME, Schwartz CJ, Wagner WD, Wissler RW (1995) A definition of advanced types of atherosclerotic lesions and a histological classification of atherosclerosis. Circulation 92: 1355–1374.
Su B, Karin M (1996) Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades and regulation of gene expression. Curr Opin Immunol 8: 402–411.
Treisman R (1996) Regulation of transcription by MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8: 205–215.
Waskiewicz AZ, Cooper JA (1995) Mitogen and stress response pathways: MAP kinase cascades and phosphatase regulation in mammals and yeast. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7: 798–805.
Whitmarsh AJ, Yang SH, Su MS, Sharrocks AD, Davis RJ (1997) Role of p38 and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases in the activation of ternary complex factors. Mol Cell Biol 17: 2360–2371.
Xu Q, Liu Y, Gorospe M, Udelsman R, Holbrook NK (1996) Acute hypertension activates mitogen-activated protein kinases in arterial wall. J Clin Invest 97: 508–514.
Yue TL, Ma XL, Gu JL, Ruffolo Jr RR, Feuerstein GZ (1998) Carvedilol inhibits activation of stress-activated protein kinase and reduces reperfusion injury in perfused rabbit heart. Eur J Pharmacol 345: 61–65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishio, H., Matsui, K., Tsuji, H. et al. Immunohistochemical Study of the Phosphorylated and Activated Form of c-Jun NH2-terminal Kinase in Human Aorta. Histochem J 33, 167–171 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017952310800
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017952310800