Abstract
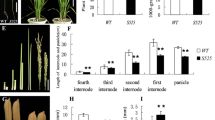
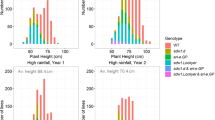
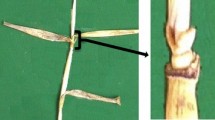
A review of research at the Scottish Crop Research Institute (SCRI) on the effects of semi-dwarfing genes on salt tolerance in barley is given. Work began in1993 with the fortuitous and unexpected result that the cultivar ‘Golden Promise’ showed considerable tolerance to salt. Golden Promise is a gamma-ray induced semi-dwarf mutant of the cultivar ‘Maythorpe’. The parent and mutant cultivars are presumed to be isogenic, but show significant differences in their responses to salt stress. The positive and pleiotropic effects of the mutant gene, commonly known as GPert were found to be effective in a number of genetic backgrounds. Earlier, in 1991 Frackowiak showed that the GPert mutation was allelic to the ari-e mutants in barley. The ari-emutants were salt tested and found to show the same positive responses to salt stress as Golden Promise. This supported the allelism tests, and consequently the GPert symbol was changed to ari-e.GP. The semi-dwarf mutant sdw1 (also known as denso) and the erectoides semi-dwarf mutant,ert-k 32 were also tested for their effects on tolerance to salt, but did not show any positive effects. Salt tolerance was therefore not a general phenomenon of semi-dwarf stature but specific to mutations at the Ari-e locus in these lines. Genetic markers (RAPDs, AFLPs and SSRs) have been used for fingerprinting, genetic mapping, and QTL analysis. The markers have helped 1) confirm the isogenic relationship between Maythorpe and Golden Promise, 2)clarify the confusion over the pedigree of Golden Promise, and 3) genetically map the ari-e.GPlocus and examine its pleiotropic effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amer, I.M. & H.N. El-Rassas, 1994. Utilization of gamma irradiation in barley breeding. Annals of Agricultural Science (Cairo) 39: 257–268.
Barua, U.M., K.J. Chalmers, W.T.B. Thomas, C.A. Hackett, V. Lea, P. Jack, B.P., Forster, R. Waugh & W. Powell, 1993. Molecular mapping of genes determining height, time to heading and growth habit in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Genome 36: 1080–1087.
Borg, G., 1959. Svalöf's original Pallas barley (Sv.04032), a new 2-row spring barley produced by X-ray treatment of Svalöf's Bonus barley. Sveriges Utsadesforenings Tidskrift 72–96.
Boulger, M.C., R.G. Sears & W.E. Kronsrad, 1981. An investigation of the association between dwarfing sources and gibberellic acid response in barley. In: Barley Genetics IV. Proceedings of the Fourth International Barley Genetics Symposium, Edinburgh, pp. 550–553.
Bouma, J., 1967. New variety of spring barley, 'Diamant' in Czechoslovakia. In: Induzierte Mutationen und ihre Nutzung, Erwin Baur Gedachtnisvorlesungen IV, 1966, Abh Dt AkadWiss Berl Akademie-Verlag, Berlin 2: 177–182.
Briggs, D.E., 1978. Barley Genetics. In: D.E. Briggs (Ed.), Barley, pp. 419–441. Chapman and Hall Ltd., London.
Epstein, E., J.D. Norlyn, D.W. Rush, R.W. Kingsbury & D.B. Kelley, 1980. Saline culture of crops: a genetic approach. Science 210: 399–404.
Farquhar, G.D. & R.A. Richards, 1984. Isotopic composition of plant carbon correlates with water-use efficiency of wheat genotypes. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology 11: 539–552.
Forster, B.P., H. Pakniyat, M. Macaulay, W. Matheson, M.S. Phillips, W.T.B. Thomas & W. Powell, 1994. Variation in the leaf sodium content of Hordeum vulgare (barley) cultivar Maythorpe and its derived mutant cv. Golden Promise. Heredity 73: 249–253.
Franckowiak, J.D., 1991. Allelism tests among selected semi-dwarf barleys. Barley Genetics Newsletter 21: 17–23.
Gustafsson, A., A. Hagberg, G. Persson & K. Wiklund, 1971. Induced mutations and barley improvement. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 41: 239–248.
Haahr, V. & D. von Wettstein, 1976. Studies on an induced high yielding dwarf mutant of spring barley. In: H. Gaul (Ed.), Barley Genetics III, Proceedings of the Third International Barley Genetics Symposium, 1975, pp. 215–218. Verlag Karl Thiemig, Munich, Germany.
Hanson, P.R., J.A. McVittie & J.L. Smalley, 1980. Seedling response to exogenous gibberellic acid in spring barley. Zeitschrift für Planzenzüchtung 84: 115–121.
Jacobsen, T. & R.M. Adams, 1968. Salt and silt in ancient Mesopotamian agriculture. Science 128: 1251–1258.
Kapala, A. & W. Rybinski, 1995. Variability of seed protein composition of hulless mutants of spring barely (Hordeum vulgare L.). Journal of Applied Genetics 36: 129–135.
Kucera, L., U. Lundqvist & A. Gustafsson, 1975. Induction of breviaristatum mutants in barley. Hereditas 80: 263–278.
Kumar, A., 1996. The adventures of the TY1-copia group of retrotransposons in plants. Trends in Genetics 12: 41–43.
Laurie, D.A., N. Pratchett, C. Romero, E. Simpson & J.W. Snape, 1993. Assignment of the denso dwarfing gene to the long arm of chromosome 3 (3H) by use of RFLP markers. Plant Breeding 111: 198–203.
Lundqvists, U., 1986. Barley mutants - diversity and genetics. In: G. Olsson (Ed.), Svalöf 1886-1986, Research and Results in Plant Breeding, pp. 85–88. Svalöf AB 268 00, Svalöv, Sweden.
Müller, H.J., 1927. Artificial transmutation of the gene. Science 66: 84–87.
Pakniyat, H., E. Baird, W.T.B. Thomas, P.D.S. Caligari, W. Powell & B.P. Forster, 1996. Effect of semi-dwarf mutants on salt tolerance in barley. In: A.E. Slinkard, G.J. Scoles & B.G. Rossnagel (Eds.), Proceedings of Fifth International Oat Conference & Seventh International Barley Genetics Symposium, Saskatoon 1996, pp. 660–661. University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon.
Pakniyat, H.J., 1996. Genetic studies on salt tolerance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). PhD thesis. The University of Reading, Reading, UK.
Pakniyat, H., L.L. Handley, W.T.B. Thomas, T. Connolly, M. Macaulay, P.D.S. Caligari & B.P. Forster, 1997a. Comparison of shoot dry weight, Na+ content and ? 13C values of ari-e and other semi-dwarf barley mutants under salt stress. Euphytica 94: 7–14.
Pakniyat, H.,W.T.B. Thomas, P.D.S. Caligari & B.P. Forster, 1997b. Comparison of salt tolerance of GPert and non-GPert barleys. Plant Breeding 116: 189–191.
Pearce, F., 1987. Banishing the salt of the earth. New Scientist 11: 53–56.
Persson, G., 1969. An attempt to find suitable genetic markers for dense ear loci in barley. Hereditas 62: 25–96.
Russell, J., J. Fuller, G. Young, W.T.B. Thomas, G. Taramino, M. Macaulay, R. Waugh & W. Powell, 1997. Discriminating between barley genotypes using microsatellite markers. Genome 40: 442–450.
SCOPE, 1978. Scientific Committee on Problems of Environment. In: E.B. Worthington (Ed.), Land Irrigation in Developing Countries, pp. 3–8. Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Sigburbjorsson, B. & A. Micke, 1969. Progress in mutation breeding. In: Induced Mutation in Plants. Proceedings of an International Symposium on: Nature, Induction and Utilization of Mutation in Plants. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, 1969, pp. 673–697.
Stadler, L.J., 1930. Some genetic effects of X-rays in plants. Journal of Heredity 21: 3–19.
Stoner, R., 1988. Engineering a solution to the problem of salt laden soils. New Scientist 3: 44–46.
Thomas, W.T.B., M.J.C. Asher, J.S. Swanston & C.E. Thomas, 1988. The transfer of resistance to powdery mildew from Hordeum spontaneum to the spring barley cv. Golden Promise. In: M.L. Jorna & L.A. Slootmaker (Eds.), Cereal Breeding Related to Integrated Cereal Production, Proc. EUCARPIA Conf., pp. 200–204. Pudoc, Wageningen.
Thomas, W.T.B., W. Powell & W. Wood, 1984. The chromosomal location of the dwarfing gene present in the spring barley variety Golden Promise. Heredity 53: 177–183.
Vos, P., R. Hogers, M. Bleeker, M. Reijans, T.V.D. Lee, M. Hornes, A. Frijters, J. Pot, J. Peleman, M. Kuiper & M. Zabeau, 1995. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Research 23: 4407–4414.
Wan, Y. & P.G. Lemaux, 1994. Generation of large numbers of independently transformed fertile barley plants. Plant Physiology 104: 37–48.
Zabeau, M. & P. Vos, 1993. Selective restriction fragment amplification: a general method for DNA fingerprinting. European Patent Application No: 92402629.7, Publication No: 0534858.
Zwar, J.A. & P.M. Chandler, 1995. α-Amylase production and leaf protein synthesis in a gibberellin-responsive dwarf mutant of 'Himalay' barley (Hordeum vulgare L.).Planta 197: 39–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forster, B.P. Mutation genetics of salt tolerance in barley: An assessment of Golden Promise and other semi-dwarf mutants. Euphytica 120, 317–328 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017592618298
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017592618298