Abstract
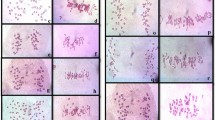
Cytology and gene expression of an amphiploid between Aegilops tauschiiL., native to China, and Secale silvestre L. were studied to reveal the genomic interaction between the donor species. High frequencies of aneuploids were observed in the progenies of the amphiploid, indicating its cytological instability. Feulgen staining and Giemsa-C banding showed that only the nucleolar organizing region from chromosome 5D of Ae. tauschii existed in the amphiploid (2n = 28). The nucleolus of S. silvestre was not observed. Endosperm storage protein electrophoresis indicated most gliadin and glutenin genes from both parents were expressed in the endosperm of the amphiploid. When inoculated by wheat stripe rust and powdery mildew isolates,the amphiploid did not express the resistance from its Secale parent,suggesting the presence of disease resistance suppressor(s) in the D genome of Ae. tauschii as well as nucleolar organizer suppressors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard, S. & M. Bernard, 1987. Creating new forms of 4x, 6x and 8x primary triticaleassociating both complete R and D genomes. Theor Appl Genet 74: 55–59.
Cabrera, A., Y. Dominguez, D. Rubiales, J. Ballesteros & A. Martin, 1996. Tetraploid triticale from Aegilops squarrosa L. Secale ssp. In: H. Gudes-Pinto, N. Darvey & V.P. Carnide (Eds.), Triticale: Today and Tomorrow, pp. 179–182. Kluwer Academic Publishers, the Netherlands.
Cook, R.J., 1987. The classification of wheat cultivars using a standard referenceelectrophoresis method. J Nat Agric Bot 17: 273–281.
Friebe, B., Y Mukai & B.S. Gill, 1992. C-banding polymorphisms in several accessions of Triticum tauschii (Aegilops squarrosa). Genome 35: 192–199.
Gill, B.S., W. Raupp, H.C. Sharama, L.E. Browder, J.H. Hatxhett, T.L. Harvey, J.G. Moseman & J.G. Waines,1986. Restance in Aegilops squarrosa to wheat leaf rust, wheat powdery mildew, greenbug and Hessian Fly. Plant Dis 70: 553–556.
Gustafson, J.P. & R.B. Flavell, 1996. Control of nucleolar expression in triticale. In:H. Gudes-Pinto, N. Darvey & V.P. Carnide (Eds.), Triticale: Today and Tomorrow, pp. 119–125. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands.
Jiang, H.R. & X.X. Kong, 1991. A new species in Triticale. J SichuanAgric Univ 9: 334–337.
Jiang, J., B. Friebe & B.S. Gill, 1994. Recent advances in alien gene transfer inwheat. Euphytica 73: 199–212.
Krolow, K.D., 1970. Untersuchungen über die Kreuzbarkeit zwischenWeizen und Roggen. Z Pflanzenzücht 64: 44–72.
Krolow, K.D., 1973. 4x-triticale production and use intriticale breeding. In: E.R. Sears & L.M.S. Sears (Eds.), Proc. 4th Intern Wheat Genet Symp, pp. 237–243. Columbia, Missouri, USA.
Krolow, K.D., 1983. New aspects for the use of 4x-triticaie (2n = 28) in triticale development. In:S. Sakamoto (Ed.), Proc. 6th Intern Wheat Genet Symp, pp. 903–907. Kyoto, Japan.
Lacadena, J.R.,M.C. Cermeno, J. Orellana & J.L. Santos, 1984. Evidence for wheat-rye nucleolar competition (amphiplasty) in triticale by silver-staining procedure. Theor Appl Genet 67: 207–213.
Lagudah, E.S. & G.M. Halloran,1988. Phylogenetic relationships of Triticum tauschii the D genome donor to hexaploid wheat. 1. Variation in HMW subunits of glutenin and gliadin. Theor Appl Genet 75: 592–598.
Lan, X.J., D.C. Liu & Z.R. Wang, 1997.Inheritance in synthetic hexaploid wheat ‘RSP’ of sprouting tolerance derived from Aegilops tauschii Cosson. Euphytica 95: 321–323.
Liu, D.C., C. Yen & J.L. Yang, 1997. C-banding analysis of D genome chromosome inChinese landraces of Triticum tauschii Cosson and Triticum aestivum L. cv. Chinese Spring. Wheat Inf Serv 84: 33–38.
Lukaszewski, A.J. & J.P. Gustafson, 1987. Cytogenetics of Triticale. In: J. Janick (Ed.), Plant BreedingReview, vol 5, pp. 41–93. Van Nostrand Rainhold Company, New York.
Lutz, J.E., S.L.K. Hasm, P. Limpert & F.J. Zeller, 1994. Powdery mildew resistance in Aegilops tauschii Coss and synthetic hexaploid wheat. Genet Res Crop Evol 41: 151–158.
Ma, H., R.P. Singh & A. Mujeeb-Kazi, 1995. Suppression/ expression ofresistance to stripe rust in synthetic hexaploid wheat (Triticum turgidum x T. tauschii). Euphytica 83: 87–93.
Ng, P.K.W. & W. Bushuk, 1987. Glutenin of Marquis wheat as a reference for estimating molecular weights ofglutenin subunits by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Cereal Chem 64: 324–327.
Payne, P.I. & G.J. Lawrence, 1983. Catalogue of alleles for the complex gene loci, Glu-A1, Glu-B1 and Glu-D1,which code for high molecular weight subunits of glutenin in hexaploid wheat. Cereal Res Comm 11: 29–35.
Ren, Z.L. & H.Q. Zhang, 1995. An improved C-banding technique for plants. J Sichuan Agric Univ 13:1–5.
Sekiguchi, S., J. Ono & T. Taira, 1993. Detection of HMW glutenin genes by DNA hybridization andbreadmaking quality of amphiploid synthesized between Aegilops squarossa and Secale cereale. Wheat Inf Serv 79: 77–79.
Shewry, P.R., S. Parmar, N. Fulrath & D.D. Kasarda, 1986. Chromosomal locations of the structural genes forsecalins in wild perennial rye (Secale montanum Guss.) and cultivated rye (S. cereale L.) determined by two dimensional electrophoresis. Can J Genet Cytol 28: 76–83.
Yen, C., J.L. Yang, X.D. Liu & L.R. Li, 1983. Thedistribution of Aegilops tauschii Cosson in China and with reference to the origin of the Chinese common wheat. In: S. Sakamoto (Ed.), Proc 6th Intern Wheat Genet Symp, pp. 55–58. Kyoto, Japan.
Zeller, F.J., U. Stephan & J. Lutz, 1993. Chromosomal location of powdery mildew resistance genes in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). 1. Mlk and other alleles in the Pm3 locus. Euphytica 68: 223–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zu-Jun, Y., Guang-Rong, L., Hua-Ren, J. et al. Expression of nucleolus, endosperm storage proteins and disease resistance in an amphiploid between Aegilops tauschii and Secale silvestre . Euphytica 119, 317–321 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017591519520
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017591519520