Abstract
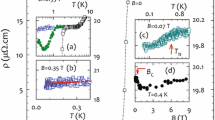
YbCu5−xAlx exhibits long range antiferromagnetic order for x>1.5 with TN rising up to 2 K for the composition YbCu3Al2. This development of antiferromagnetic order is due to a valence shift from the non-magnetic Yb 4f 14 ground state in YbCu5 to the magnetic 4f13 ground state in YbCu3Al2. At the critical concentration x=1.5 the system is in a state of magnetic instability, where typical non-Fermi-liquid (nFl)-properties are observed, e.g., a−log T contribution in C/T and a power law in ρ=ρ0+cTα with α<2. We have measured the specific heat and electrical resistance of YbCu3.5Al1.5 in various magnetic fields in order to clarify the nature of the non-Fermi- liquid behavior in this series. The specific heat divided by temperature in zero field can be described by a Self Consistent Renormalization (SCR)-model for a 3D antiferromagnet down to the lowest measured temperature and over more than a decade of temperature. The resistance data clearly deviate from the Fermi-liquid (Fl)-T2-behavior in zero magnetic field, whereas with increasing field, the range of the Fl-behavior enlarges. The derived SCR parameters indicate that the system is not exactly at the quantum critical point (QCP) and application of external magnetic field pushes the system further away from the QCP. A hyperscaling analysis of the specific heat data taken in various magnetic fields in the region where C/T is proportional to −log T points to collective effects responsible for the nFl-behavior in YbCu3.5Al1.5. The scaling disappears for T<240 mK which would point to a crossover from weakly interacting to non Gaussian strongly interacting spin fluctuations as the cause of the nFl-behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. Bauer, E. Gratz, L. Keller, P. Fischer, and A. Furrer, Physica B 186–188, 608 (1993).
E. Bauer, R. Hauser, L. Keller, P. Fischer, O. Trovarelli, J. G. Sereni, J. J. Rieger, and G. R. Stewart, Phys. Rev. B 56, 711 (1997).
E. Bauer, R. Hauser, A. Galatanu, H. Michor, G. Hilscher, J. G. Sereni, M. G. Berisso, P. Pedazzini, M. Galli, F. Mirabelli, and P. Bonville, Phys. Rev. B 60, 1238 (1999).
H. v. Loehneysen, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 8, 9689 (1996).
K. Heuser, Dissertation, Universität Augsburg 1999, Shaker Verlag ISBN 3–8265–6343–3.
F. M. Grosche, M. J. Steiner, P. Agrawal, I. R. Walker, D. M. Freye S. R. Julian, and G. G. Lonzarich, Physica B 281 & 282, 3 (2000).
E. Bauer, Adv. Phys. 40, 417 (1991).
E. Bauer, A. Galatanu, L. Naber, M. Galli, F. Mirabelli, C. Seuring, K. Heuser, E.-W. Scheidt, T. Schreiner, and G. R. Stewart, Physica B 281 & 282, 319 (2000).
C. Seuring, K. Heuser, E.-W. Scheidt, T. Schreiner, E. Bauer, and G. R. Stewart, Physica B 281 & 282, 374 (2000).
K. Heuser, E.-W. Scheidt, T. Schreiner, and G. R. Stewart, Phys. Rev. B 57, R4198 (1998).
E. Bauer, R. Hauser, E. Gratz, D. Gignoux, D. Schmitt, and J. G. Sereni, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 4, 7829 (1992).
R. Bachmann, F. J. DiSalvo Jr., T. H. Geballe, R. L. Greene, R. E. Howard, C. N. King, H. C. Kirsch, K. N. Lee, R. E. Schwall, H.-U. Thomas, and R. B. Zubeck, Rev. Sci. Instr. 43, 205 (1972).
T. Moriya and T. Takimoto, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 64, 960 (1995).
B. Andraka and A. M. Tsvelik, Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 2886 (1991).
O. Trovarelli, C. Geibel, S. Mederle, C. Langhammer, F. M. Grosche, P. Gegenwart, M. Lang, G. Sparn, and F. Steglich, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 626 (2000).
K. Heuser, E.-W. Scheidt, T. Schreiner, and G. R. Stewart, Phys. Rev. B 58, R15959 (1998).
J. S. Kim, J. Alwood, S. A. Getty, F. Sharifi, and G. R. Stewart, Phys. Rev. B 62 (2000).
A. M. Tsvelik and M. Reizer, Phys. Rev. B 48, 9887 (1993).
S. Korner, A. Weber, J. Hemberger, E. W. Scheidt, and G. R. Stewart, J. Low Temp. Phys. 121, 105 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seuring, C., Scheidt, EW., Bauer, E. et al. Investigation on the Nature of the Concentration-Induced Non-Fermi-Liquid Behavior in YbCu3.5Al1.5. Journal of Low Temperature Physics 123, 25–33 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017589213930
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017589213930