Abstract
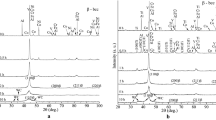
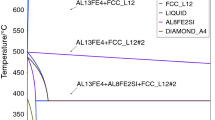
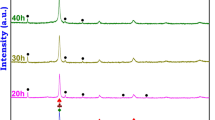
Microstructures and their stability in as-atomised Al-6.5Fe-1.5V and Al-6.5Fe-1.5V-1.7Si powders have been investigated using transmission electron microscopy (TEM) equipped with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDXS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) techniques. It was observed that microstructures of the as-atomised powder particles showed a close relationship with powder particle sizes. The as-atomised powders exhibited three types of microstructures, namely 'zone A', 'zone B' and 'zone C'. The 'zone A' type microstructure consisted of very fine and homogeneous distributed precipitates in the α-Al matrix. The 'zone B' microstructure represented the regions consisting of microcellular structures whereas the 'zone C' microstructure represented the regions consisting of coarse cellular structures and globular quasi-crystalline phase particles. Fine powder particles exhibited both 'zone A' and 'zone B' microstructures. The size of 'zone A' decreased with increasing powder particle sizes. The intercellular phases in 'zone B' of both Al-Fe-V and Al-Fe-V-Si were very fine, randomly oriented microquasi-crystalline icosahedral particles. Microstructures of coarse powder particles exhibited both 'zone B' and 'zone C'. The intercellular phases in 'zone C' of Al-Fe-V powders could be Al6Fe, whereas in Al-Fe-V-Si powders they were probably silicide phase. Formation of powder microstructures may be explained by the interactions between the growing α-Al fronts with the freely dispersed, primary phase particles or the solute micro-segregation. Studies using DSC techniques have revealed the microstructural stability of as-atomised powders. There were three DSC exotherms observed in the as-atomised Al-Fe-V powders. The 'zone A' was stable at elevated temperatures and the exotherm peak corresponding to the transformation reactions occurring in 'zone A' was at 360°C. The exotherm peak, which might correspond to the transformation of the globular clusters of microquasi-crystalline icosahedral phase to single-phase icosahedral particles, was at 450°C. The exotherm peak, which may correspond to the formation of Al13Fe4 and Al45(V, Fe)7 phases, was at 500°C. In the as-atomised Al-Fe-V-Si powders, only one exotherm was observed with a peak at 400°C. This exotherm may correspond to precipitation of silicide phase particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. J. Grant, J. Metals 35 (1983) 20.
W. Wang, D. Liu and N. J. Grant, Scripta Metall. 21 (1987) 1279.
H. Jones, Mater. Sci. Eng. 5(1) (1969/70) 1.
I. R Hughes and H. Jones,J. Mater. Sci. 11 (1976) 1781.
R. M. K. Young and T. W. Clyne, Scripta Metall. 15 (1981) 1211.
W. J. Boettinger, L. Bendersky and J. G. Early, Metall. Trans. A. 17A(1986)781.
W. J. Boettinger, L. A. Bendersky, R. J. Schaefer and F. S. Biancaniello, ibid. 19A (1988) 1101.
M. G. Chu and D. A. Granger, ibid. 21A (1990) 205.
P. Gilgien, A. Zryd and W. Kurz, Acta Metall. Mater. 43(9) (1995) 3477.
I. J. Polmear, M. J. Couper and M. J. Bannister, Mater. Forum. 12 (1988)54.
R. A. Dunlap and K. Dini, Can. J. Phys. 63 (1985) 1267.
R. M. K. Young and J. H. Tweed, Mater. Sci. Eng. A134 (1991) 1153.
J. L. Murray, A. J. McALLISTER, R. J. SCHAEFER, L. A. BENDERSKY, F. S. BIANCANIELLO and D. L. MOFFAT, Metall. Trans. A. 18A (1985) 385.
D. J. Skinner, V. R. V. Ramanan, M. S. Zedalis and N. J. Kim,Mater. Sci. Eng. 99 (1988) 407.
M. S. Zedalis, V. R. V. Ramanan and D. J. Skinner, in “Thermal Analysis in Metallurgy,” edited by R. D. Shull and A. Joshi (The Mineral, Metals & Materials Society, Pennsylvania,1992) p.279.
P. A. Bancel, P. A. Heiney, P. W. Stephens, A. I. Goldman and P. M. Horn, Phys. Rev. Lett. 54(22) (1985) 2422.
L. Bendersky,ibid. 55(14) (1985) 1461.
L. Bendersky, R. J. Schaefer, F. S. Biancaniello, W. J. Boettinger, M. J. Kaufman and D. Shechtman,Scripta Metall. 19 (1985) 909.
J. W. Cahn, D. Shechtman and D. Gratias,J. Mater. Res. 1(1) (1985)13.
V. Elser, Phys. Rev. B. 32(8) (1985) 4892.
R. J. Schaefer and L. Bendersky, Scripta Metall. 20 (1985) 745.
J. W. Zindel, P. Kurath and H. L. Fraser, in “High Strength Powder Metallurgy Aluminum Alloys II,” edited by G. J. Hildeman and M. J. Koczak (The Metallurgical Society, Pennsylvania, 1985) p.213.
M. Audier and P. Guyot,Phil. Mag. B. 53(1) (1986) L43.
R. D. Field, J. W. Zindel and H. L. Fraser, Scripta Metall. 20 (1986) 415.
F. Gillessen and D. M. Herlach, Mater. Sci. Eng. A134 (1991) 1220.
K. F. Kelton, Int. Mater. Rev. 38(3) (1993) 105.
C. M. Adam, V. R. V. Ramanan and D. J. Skinner, in “Undercooled Alloy Phases,” edited by E. W. Collings and C. C. Koch (The Metallurgical Society, Pennsylvania, 1987) p.59.
M. Gremaud, M. Carrard and W. Kurz, Acta Metall. Mater. 38(12) (1990) 2587.
M. Carrard, M. Gremaud and M. Pierantoni, Scripta Metall. Mater. 25 (1991) 925.
K. K. Fung, C. Y. Yang, Y. Q. Zhou, J. G. Zhao, W. S. Zhan and B. G. Shen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 56(19) (1986) 2060.
X. D. Zou, K. K. Fung and K. H. Kuo, Phys. Rev. B. 35(9) (1987) 4526.
K. H. Kuo, Mater. Sci. Forum. 22–24 (1987) 131.
D. H. Kim and B. Cantor, Phil. Mag. A. 69(1) (1994) 45.
P. S. Gilman and S. K. Das, in Proceedings of International Conference on PM Aerospace Materials (A Metal Powder Report Conference) Luzern, November 2–4, 1987 (MPR Publishing Services, Shrewsbury 1988) Vol. 27.1.
D. J. Skinner, in “Dispersion Strengthened Aluminum Alloys,” edited by Y.-W. Kim and W. M. Griffith (The Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 1988) p.181.
M. A. Rodriguez and D. J. Skinner, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 9 (1990) 1292.
N. J. Kim, Int. J. Rapid Solidification 6 (1991) 175.
V. R. V. Ramanan, D. J. Skinner and M. S. Zedalis, Mater. Sci. Eng. A134 (1991) 912.
W. J. Park, S. Ahn and N. J. Kim, ibid. A189 (1994) 291.
Y. L. Tang, S. K. Guan, D. S. Shao, N. F. Shen and H. Q. Hu, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 12(1993) 1749.
P. Gilman, Metals and Materials 6 (1990) 504.
R. J. Dashwood, Ph.D. thesis, University of London, 1990.
E. S. Humphreys, P. J. Warren and A. Cerezo, Mater. Sci. Eng. A250 (1998) 158.
R. Asthana, P. K. Rohatgi and S. N. Tewari, in “Microstructure Formation during Solidification of Metal Matrix Composites,” editing by P. K. Rohatgi (The Minerals, Metal & Materials Society, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1993) p.11.
D. Shangguan, S. Ahuja and D. M. Stefanescu, Metall. Trans. A. 23A (1992) 669.
(a)F. R. Juretzko, B. K. Dhindaw, D. M. Stefanescu, S. Sen and P. A. Curreri,Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 29A (1998) 1691; (b) D. M. STEFANESCU, F. R. JURETZKO, B. K. DHINDAW, A. CATALINA, S. SEN and P. A. CURRERI, ibid. 29A (1998) 1697.
L. A. Bendersky, A. J. McAlister and F. S. Biancaniello, ibid. 19A (1988) 2893.
Tongsri R, Ph.D thesis, University of London 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tongsri, R., Minay, E.J., Thackray, R.P. et al. Microstructures and their stability in rapidly solidified Al-Fe-(V, Si) alloy powders. Journal of Materials Science 36, 1845–1856 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017584131357
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017584131357