Abstract
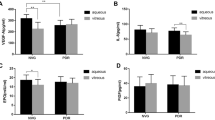
Purpose: To determine the association of prostaglandins E1 (PGE1), E2 (PGE2), and F2-alpha (PGF2-alpha) with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) in human vitreous. Methods: We collected human vitreous samples from eyes undergoing pars plana vitrectomy for proliferative diabetic retinopathy with vitreous hemorrhage (N=13) and for other reasons including macular gliosis and Stage IV idiopathic macular holes (N=7). Vitreal prostaglandins E1, E2, and F2-alpha were measured by radioimmunoassay. Results: Eyes with PDR had significantly lower vitreal levels of PGE1 (74.77 pg/ml +/− 15.70) compared to those without PDR (91.86 pg/ml +/− 13.36) (p=0.025) using t-test analysis. Eyes with PDR also had significantly lower levels of PGE2 (127.52 pg/ml +/− 70.52) compared to those eyes without PDR (194.43 pg/ml +/− 57.10) (p=0.045). In addition, eyes with PDR had significantly lower levels of PGF2-alpha (34.62 pg/ml +/− 11.56) compared to those eyes without PDR (51.43 pg/ml +/− 18.44) (p=0.021). Panretinal photocoagulation in diabetic eyes did not have an effect on vitreal concentrations of PGE1 (p=0.588), PGE2 (p=0.460) and PGF2-alpha (p=0.351), but sample size was too small. Conclusions: Diabetic eyes with PDR had significantly lower vitreal levels of PGE1, PGE2 and PGF2-alpha compared to controls consistent with decreased production of these prostaglandins by the endothelial cells of diabetic eyes. Laser treatment did not appear to have a significant effect on vitreal concentrations of these prostaglandins, but sample size was small. The lower concentration of these vasodilatory prostaglandins may reflect the vasculature's inability to produce these substances and the vasoconstrictive state of the end-stage diabetic eye with PDR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Futterman S, Kupfer C. The fatty acid composition of the retinal vasculature of normal and diabetic human eyes.Invest Ophthalmol1968:7(1):105-8.
Pieper G, Gross GJ. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes. In: Rubanui GM, ed. Cardiovascular significance of endothelium-derived vasoactive factors.Mount Kisco, New York: Futura Publishing Company, Inc,1991: pp 223-49.
Thomas MA, O'Grady GE, Swartz SL. Prostaglandin levels in human vitreous.Br J Ophthal1985; 69:275-9.
Naveh-Floman N, Weissman C, Belkin M. Arachidonic acid metabolism by rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes.Curr Eye Res1984;3(9):1135-9.
Naveh N, Belkin M, Ben-Chaim O. et al. Prostanoids in the vitreous of diabetic and nondiabetic human eyes with retinal detachment.Ophthalmic Res; 1990;22:3-11.
Stjernschantz J, Nilsson SFE, Astin M. Vasodynamic and angiogenic effects of eicosanoids in the eye. In:The Ocular Effects of Prostaglandins and Other Eicosanoids. Alan R. Liss, Inc, 1989; 155-70.
Whitelocke RAF, Eakins KE. Vascular changes in the anterior uvea of the rabbit produced by prostaglandins.Arch Ophthalmol1973; 89:495-99.
Pournaras C, Tsacopoulos M, Chapuis PH. Studies on the role of prostaglandins in the regulation of retinal blood flow.Exp Eye Res1978;26:687-97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Douros, S., Phillips, B.A., Nadel, A. et al. Human vitreal prostaglandin levels and proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Doc Ophthalmol 103, 27–34 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017557600233
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017557600233