Abstract
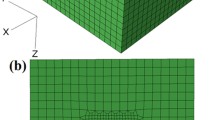
Vickers indentation of 6061-T6 aluminum was modeled using a three-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA) program. Two different work hardening behaviors were assumed. The results were compared with actual indentations using both a static microindenter and a load and depth recording microindenter. The hardness and plastic flow behavior showed excellent agreement, validating the FEA model, and implying that the work hardening of the aluminum decreases past a compressive strain of 0.09. The unloading results were analyzed using Sneddon's solution for the indentation of an elastic half-space by a rigid axisymmetric indenter. The results confirm the validity of applying Sneddon's solution in this case, implying that Bolshakov and Pharr's corrections of Sneddon's solution (which were determined for a conical indenter) are not directly applicable tothe Vickers indenter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Tabor, “Hardness of Metals” (Chapman & Hall, London, 1951).
R. Hill, “The Mathematical Theory of Plasticity” (Clarendon Press, Oxford,1950).
W. Hirst and M. G. J. W. Howse, Proc. Roy. Soc.A311 (1969) 429.
K. L. Johnson. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 18 (1970) 115.
A. E. Giannakopoulos, P. L. Larsson and R. Vestergaard, Int. J. Solids Str.31 (1994) 2679.
K. Zeng, E. SÖderlund, A. E. Giannakopoulos and D. J. Rowcliffe, Acta Mater.44 (1996) 1127.
I. N. Sneddon, Int. J. Engng. Sci.3 (1965).
R. B. King, Int. J. Solids Str.23 (1987) 1657.
G. M. Pharr, W. C. Oliver and F. R. Brotzen, J. Mater. Res.7 (1992) 613.
H. Li, A. Ghosh, Y. H. Han and R. C. Bradt, ibid. 8 (1993) 1028.
C. J. Maiden and S. J. Green, J. App. Mech.88 (1966) 496.
W. Mason, P. F. Johnson and J. R. Varner, J. Mater. Res. 7 (1992) 3112.
A. K. Varshneya, in Proceedings of the 4th Brazilian Symposiun on Glasses and Related Materials, Ouro Preto, Brazil, November 1999, J. Non-Cryst. Sol. 273 (2000)1.
A. Bolshakov and G. M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res.13 (1998) 1049.
Idem., Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 436 (1997) 189.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strange, D.J., Varshneya, A.K. Finite element simulation of microindentation on aluminum. Journal of Materials Science 36, 1943–1949 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017550008584
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017550008584