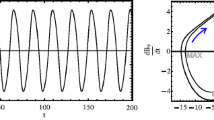Abstract
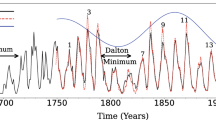
The aim of this paper is to investigate the dynamical nature of the complexity observed in the time evolution of the sunspot number. We report a detailed analysis of the sunspot number time series, and use the daily records to build the phase space of the underlying dynamical system. The observed features of the phase space prompted us to describe the global behavior of the solar cycle in terms of a noise-driven relaxation oscillator. We find the equations whose solutions best fit the observed series, which adequately describe the shape of the peaks and the oscillations of the system. The system of equations obtained from this fitting procedure is shown to be equivalent to a truncation of the dynamo equations. A linear transformation maps the phase space of these equations into the phase space reconstructed from the observations. The irregularities of the solar cycle were modeled through the introduction of a stochastic parameter in the equations to simulate the randomness arising in the process of eruption of magnetic flow to the solar surface. The mean values and deviations obtained for the periods, rise times and peak values, are in good agreement with the values obtained from the sunspot time series.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock, H. W.: 1961, Astrophys. J. 133, 572.
Barnes, J. A., Sargent III, H. H., Tryon, P. V.: 1980, in R. O. Pepin, J. A. Eddy, and R. B. Merrill (eds.), Proc. Conf. Ancient Sun., Pergamon Press, New York, p. 159.
Blackman, E. G. and Field, G. B.: 1999, Astrophys. J. 521, 597.
Bracewell, R. N.: 1953, Nature 133, 512.
Caligari, P., Moreno-Insertis, F., and Schüssler, M.: 1995, Astrophys. J. 441, 886.
Carbonell, M., Oliver, R., and Ballester, J. L.: 1994, Astron. Astrophys. 290, 983.
Charbonneau, P. and MacGregor, K. B.: 1996, Astrophys. J. 473, L59.
Choudhuri, A. R.: 1992, Astron. Astrophys. 253, 277.
Dikpati, M. and Charbonneau, P.: 1999, Astrophys. J. 518, 508.
Ferriz-Mas, A., Schmitt, D., and Schüssler, M.: 1994, Astron. Astrophys. 289, 949.
Foukal, P.: 1990, Solar Astrophysics, John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Galloway, D. J. and Weiss, N. O.: 1981, Astrophys. J. 243, 945.
Gilmore, R.: 1998, Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, 1455.
Gilmore, R., Vilaseca, R., Corbalan, R., and Roldan, E.: 1997, Phys. Rev. E55, 2479.
Gouesbet, G.: 1991, Phys. Rev. A43, 5321.
Hoyng, P.: 1993, Astron. Astrophys. 272, 321.
Javaraiah, J. and Komm, R.: 1993, Solar Phys. 184, 41.
Jones, C. A., 1982, in A. M. Soward (ed.), Stellar and Planetary Magnetism, Gordon and Breach, New York.
Knobloch, E. and Landsberg, A. S.: 1995, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 278, 294.
Knobloch, E., Tobias, S. M., and Weiss, N. O.: 1998, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 297, 1pp123.
Krause, F. and Rädler, K.-H.: 1980, Mean Field Magnetohydrodynamics and Dynamo Theory, Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Kuzanyan, K., Bao, S., and Zhang, H.: 1999, Solar Phys. 191, 231.
Leighton, R. B.: 1969, Astrophys. J. 156,1.
Mancho, A., Duarte, A., and Mindlin, G. B.: 1996, Phys. Letts. A221, 181.
Mindlin, G. B. and Solari, H.:1995, Phys. Rev. E54, 1497.
Mindlin, G. B., Merener, N., and Boyd, P. T.: 1998, Europhys. Lett. 42, 31.
Mininni, P. D., Gómez, D. O., and Mindlin, G. B.: 2000, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 5476.
Moss, D., Brandenburg, A., Tavakol, R., and Tuominen, I.: 1992, Astron. Astrophys. 265, 843.
Ossendrijver, A. J. H. and Hoyng, P.: 1996, Astron. Astrophys. 313, 31.
Paluš, M. and Novotná, D.: 1999, Phys.Rev.Lett. 83, 3406.
Platt, N., Spiegel, E. A., and Tresser, C.: 1993, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 73, 147.
Parker, E. N.: 1955, Astrophys. J. 122, 293.
Parker, E. N.: 1979, Cosmical Magnetic Fields, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Parker, E. N.: 1987, Astrophys. J. 312, 868.
Press, W. H., Flannery, B. P., Teukolsky, S. A., and Vetterling, W. T.: 1986, Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Priest, E. R.: 1984, Solar Magnetohydrodynamics, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Holland.
Salakhutdinova, I. I.: 1998, Solar Phys. 181, 221.
Schmalz, S. and Stix, M.: 1991, Astron. Astrophys. 245, 654.
Schwabe, H.: 1843, Astron. Nachr. 20, 495.
Spiegel, E. A. and Wolf, A.: 1987, in J. R. Buchler and H. Eichhorn (eds.), Chaotic Phenomena in Astrophysics, Vol. 497, New York Academy of Sciences, New York, p. 55.
Tobias, S. M, Weiss, N. O., and Kirk, V.: 1995, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 273, 1150.
Weiss, N. O., Cattaneo, F., and Jones, C. A.: 1984, Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 30, 305.
Withbroe, H.: 1989, The Solar Activity Cycle: History and Predictions, Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Preprint Series, No. 2852.
Yoshimura, H.: 1975, Astrophys. J. 29, 467.
Zeldovich, Ya. B. and Ruzmaikin, A. A.: 1990, Magnetic Fields in Astrophysics, Gordon and Breach, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mininni, P.D., Gomez, D.O. & Mindlin, G.B. Simple Model of a Stochastically Excited Solar Dynamo. Sol Phys 201, 203–223 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017515709106
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017515709106