Abstract
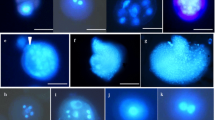
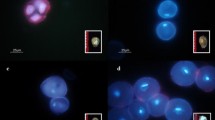
Anther culture of two wide hybrids (Diplotaxis erucoides × Brassica campestris) × B. juncea and (D. berthautii × B. campestris) × B. juncea, their CMS lines and the parent species elicited a range of responses highlighting the importance of the genotype. Androgenesis was expressed in cultured anthers of CMS (D. erucoides) B. juncea (22.8%), in restored pollen fertile plants of this CMS line (1.66%), and in the parent, B. juncea cv Pusa Bold (13.02%). AgNO3 was essential for androgenic response in the CMS lines, and it markedly increased the frequency of androgenesis in the cultivated species. Multiple crops of microspore embryos were obtained from responsive anthers of CMS plants in anther recultures. As high as92% microspore embryos of the CMS line germinated on basal B5medium and formed normal plantlets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal, P.K. & S.S. Bhojwani, 1993. Enhanced pollen grain embryogenesis and plant regeneration in anther cultures of Brassica juncea cv. PR-45. Euphytica 70: 191–196.
Bajaj, Y.P.S., 1983. In vitro production of haploids. In: D.A. Evans, W.R. Sharp, P.V. Ammirato & Y. Yamada (Eds.), Handbook of Plant Cell Culture, Vol I, pp. 228–287. Macmilan Publishing Co., New York.
Bicar, E.H. & N.L. Darvey, 1997. Development of the components of a cytoplasmic male sterility hybrid system in rye through anther culture. Euphytica 97: 151–160.
Biddington, N.L., H.T. Robinson & J.R. Lynn, 1993. ABA promotion of ethylene production in anther culture of Brussels sprouts (Brassica oleracea var. gemmifera) and its relevance to embryogenesis. Physiol Plant 88: 577–582.
Choung, P.V., K.P. Pauls & W.D. Beversdorf, 1988. High frequency embryogenesis in male sterile plants of Brassica napus through microspore culture. Can J Bot 66: 1676–1680.
Chunling, L., 1992. Agricultural Biotechnology. In: C.B. You & Z.C. Chen (Eds.), China Science and Technology Press, Beijing.
De Buyser, J., Y. Henry, R. Lonnet, R. Hertzog & A. Hespel, 1987. 'Florin': A doubled haploid wheat variety developed by the anther culture method. Plant Breed 98: 53–56.
Foroughi-Wehr, B. & G. Wenzel, 1989. Androgenetic haploid production. IPTAC Newslett 58: 11–18.
Gamborg, O.L., R.A. Miller & L. Ojima, 1968. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50: 151–158.
George, L. & P.S. Rao, 1982. In vitro induction of pollen embryos and plantlets in Brassica juncea. Plant Sci Lett 26: 111–116.
Heberle-Bors, E., 1982. In vitro pollen embryogenesis in Nicotiana tabacum L. and its relation to pollen sterility, sex balance, and floral induction of the pollen donor plants. Planta 156: 396–401.
Heberle-Bors, E., 1985. In vitro haploid formation from pollen: a critical review. Theor Appl Genet 71: 361–374.
Heberle-Bors, E. & W. Odenbach, 1985. In vitro pollen embryogenesis and cytoplasmic male sterilty in Triticum aestivum. Z Pflanzenzoücht 95: 14–22.
Heslop-Harrison, J. & Y. Heslop-Harrison, 1970. Evaluation of pollen viability by enzymatically induced fluorescence; intracelluler hydrolysis of fluorescein diacetate. Stain Tech 45: 115–120.
Hu, H., T.Y. His, C.C. Tseng, T.W. Ouyang & C.K. Ching, 1978. Frontiers of plant tissue culture. In: T.A. Thorpe (Ed.), International Association of Plant Tissue Culture, Calgary.
Huang, P.H., M.H. Lan & P.S. Chen, 1978. Selection and breeding of Ou-Hwa No.1 and No.2 and its performance. In: Proc Symp on Anther Culture, pp. 248–249. Science Press, Beijing (cmin Chinese).
Katiyar, R.K., 1994. Embryogenesis in isolated microspore cultures of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.). Plant Tissue Cult 4: 117–121.
Kaul, M.L.H., 1988. Male Sterility in Higher Plants. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Keller, W.A., 1984. Anther culture of Brassica. In: I.K. Vasil (Ed.), Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants, Vol 1, pp. 307–318. Academic Press, London.
Keller, W.A. & K.C. Armstrong, 1977. Embryogenesis and plant regeneration in Brassica napus through anther cultures. Can J Bot 55: 1383–1388.
Keller, W.A., K.C. Armstrong & I.A. de la Roche, 1982. the production and utilization of microspore-derived haploids in Brassica crops. In: K.L. Giles & S.K. Sen (Eds.), Plant Cell Culture in Crop Improvement, pp. 169–183. Plenum Publ Co, New York.
Keller, W.A., P.G. Arnison & B.K. Cardy, 1987. Haploids from gametophytic cells - recent developments and future prospects. In: C.E. Green, D.A. Somers, W.P. Hackett & D.D. Biesboer (Eds.), Plant Cell Tissue and Cell Culture, pp. 233–241. Allan R Liss, New York.
Khush, G.S. & S.S. Virmani, 1996. Haploids in Plant Breeding. In: S.M. Jain, S.K. Sopory & R.E. Veilleux (Eds.), In Vitro Haploid Production in Higher Plants, Vol I, pp 11–33. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, Boston, London.
Maheshwari, S.C., A.K. Tyagi, K. Malhotra & S.K. Sopory, 1980. Induction of haploidy from pollen grains in angiosperms: the current status. Theor Appl Genet 58: 193–206.
Malik, M., P. Vyas, N.S. Rangaswamy & K.R. Shivanna, 1999. Development of two new cytoplasmic male-sterile lines in Brassica juncea through wide hybridization. Plant Breed 118: 75–78.
Matzinger, D.F. & L.G. Burk, 1984. Cytoplasmic modification by anther culture in Nicotiana tabacum L. Journal of Heredity 75: 167–170.
Nakamura, A., T. Yamada, M. Oka, Y. Tatemichi, K. Egushi, T. Ayabe & K. Kobayashi, 1975. Studies on the haploid method of breeding by anther culture in tobacco. V. Breeding of wild fluecured variety F211 by haploid method. Bull Iwata Tobacco Exp Station 7: 29–39.
Nitsch, J.P., 1969. Experimental androgenesis in Nicotiana. Phytomorphology 19: 389–404.
Palmer, C.E. & W.A. Keller, 1997. Pollen embryos. In: K.R. Shivanna & V.K. Sawney (Eds.), Pollen Biotechnology for Crop Production and Improvement, pp. 392–422. Cambridge University Press. 203
Palmer, C.E., W.A. Keller & P.G. Arnison, 1996a. Experimental haploidy in Brassica species. In: S.M. Jain, S.K. Sopory & R.E. Veilleux (Eds.), In Vitro Haploid Production in Higher Plants, Vol 3, pp. 143–172. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, Boston, London.
Palmer, C.E., W.A. Keller & P.G. Arnison, 1996b. Utilization of Brassica haploids. In: S.M. Jain, S.K. Sopory & R.E. Veilleux (Eds.), In Vitro Haploid Production in Higher Plants, Vol 3, pp. 173–192. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, Boston, London.
Prabhudesai, V. & S. Bhaskaran, 1993. A continuous culture system of direct somatic embryogenesis in microspore-derived embryos of Brassica juncea. Plant Cell Rep 12: 289–292.
Prakash, S., P.B. Kirti & V.L. Chopra, 1995. Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) systems other than Ogu and Polima in Brassica - Current status. Proc Internatl Rapeseed Cong Cambridge UK, pp. 44–48.
Rao, G.U., V. Batra-Sarup, S. Prakash & K.R. Shivanna, 1994. Development of a new cytoplasmic male sterile system in Brassica juncea through wide hybridization. Plant Breed 112: 171–174.
Rao, P.S. & P. Suprasanna, 1996. Methods to double haploid chromosome numbers. In: S.M. Jain, S.K. Sopory & R.E. Veilleux (Eds.), In Vitro Haploid Production in Higher Plants, Vol 1, pp. 317–339. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, Boston, London.
Sharma, K.K. & S.S. Bhojwani, 1985. Microspore embryogenesis in anther cultures of two Indian cultivars of Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 4: 235–239.
Shen, L.Y. & R.E. Veilleux, 1995. Yield of embryos from sequential anther culture. American Potato Journal 72: 689–700.
Sopory, S.K. & M. Munshi, 1996. Anther culture. In: S.M. Jain, edS.K. Sopory & R.E. Veilleux (Eds.), In Vitro Haploid Production in Higher Plants, Vol I, pp. 145–176. Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, Boston, London.
Tsuchiya, K., 1993. Development of new rice varieties Hirohikari and Hirohonami, using haploid method of breeding by anther culture. In: K. Oono (Ed.), Plant Tissue Culture and Gene Manipulation for Breeding and Formation of Phytochemicals, pp. 191–196. Sato Press Mito, Japan.
Vyas, P., S. Prakash & K.R. Shivanna, 1995. Production of wide hybrids and backcross progenies between Diplotaxis erucoides and crop brassicas. Theor Appl Genet 90: 549–553.
Yadav, R.C., N.R. Yadav, P.R. Kumar & D.R. Sharma, 1988. Differential androgenic response in Brassica juncea (L.) Czern and Coss. Cruciferae Newslett 13: 76.
Zhensheng, L., 1992. Agricultural Biotechnology. In: C.B. You & Z.L. Chen (Eds.). China Science and Technology Press, Beijing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, M.R., Rangaswamy, N. & Shivanna, K. Induction of microspore embryos in a CMS line of Brassica juncea and formation of the androgenic plantlets. Euphytica 120, 195–203 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017502113066
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017502113066