Abstract
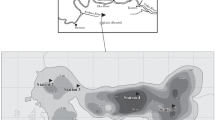
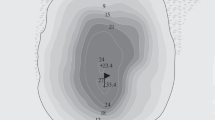
Results of an analysis of phytoplankton samples, collected between 1982 and 1995 from Srebarna Lake, a biosphere reserve, in north-eastern Bulgaria, are presented. The lake is polymictic, and strongly eutrophied. It has undergone an anthropogenically-forced succession. In 1994, a restoration of the lake was commenced when a canal connecting it to the Danube River was built.
Special attention is paid to the shifts in the qualitative composition of the phytoplankton (240 species), in the number of dominant species and assemblage structure, as well as to the changes in structural parameters and phytoplankton abundance during lake enrichment. The generalised changes involved a shift from a chlorococcal dominated-phytoplankton, rich in phytoplankton groups, to a chroococcal and oscillatoralean one, poor in algal groups. With recovery, from hypertrophy to eutrophy, more algal groups contributed to the phytoplankton, and dominance of chlorococcal genera resumed. An increase in total phytoplankton abundance with advancing eutrophication and a decrease during early oligotrophication were detected. The values of structural parameters were related to nutrient input and changed after restoration. However, the stages of phytoplankton development along the trophic gradient and back were not exactly reversed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Cobelas, M. & B. A. Jacobsen, 1992. Hypertrophic plankton: an overview. Freshwater Forum 2: 184–192.
Bailey-Watts, A. E., A. Kirika, L. May & D.H. Jones, 1990. Changes im phytoplankton over various timescales in a shallow, eutrophic loch: the Loch Leven experience with special reference to the influence of flushing rate. Freshwat. Biol. 23: 85–112.
Bales, M., B. Moss, G. Phillips, K. Irvine & J. Stansfield, 1993. The changing ecosystem of a shallow, brackish lake, Hickling Broad, Norfolk, U.K. II. Longterm trends in water chemistry and ecology and their implications for restoration of the lake. Freshwat. Biol. 29: 141–165.
Bjõrk, S., 1994. Overview. In M. Eiseltová (ed.), Restoration of Lake Ecosystems. A holistic approach. IWRB Publ. 32: 1–5.
Carlson, R. E., 1977. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22: 840–845.
Clasen, J.& H. Bernhardt, 1980. Shallow lakes and Reservoirs. Final report of the OECD regional project.Wat. res. Cent. Medmenham Marlow, Bucks, England, 289 pp.
Descy, J.–P., 1993. Ecology of the phytoplankton of the River Moselle: effects of disturbance on community structure and diversity. Hydrobiologia 249: 111–116.
Dokulil, M. & J. Padisák, 1994. Longterm compositional response of phytoplankton in a shallow turbid environment, Neusiedlersee, Austria/Hungary. Hydrobiologia 275–276: 125–137.
G. L. Tóth & J. Padisák, 1982. Kísérlet a Balaton Tihanyi térsége eutrofizálódásának több tényezös becslésére I. Bevesetö meggondol ások, módszerek, algológiciai mutatók. Bot. Közl. 69: 71–84.
Hamza, W., P. Pandolfi & M. I. Taticchi, 1995. Planktonic interactions and their role in describing the trophic status of a shallow lake in Central Italy (Lago Trasimeno). Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol. 53: 125–140.
Kalff, J. & R. Knoechel, 1978. Phytoplankton and their dynamics in oligotrophic and eutrophic lakes. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 9: 475– 495.
Kawabata, Z. & H. Kagawa, 1986. Succession of phytoplankton species in indoor reservoir models varying in sediment composition and water inlet site. Hydrobiologia 133: 31–38.
Kovachev, St., T. Michev, M. Stoyneva, V. Velev, G. Baeva & R. Bardova., 1996. Preliminary report on Srebarna monitoring. – Ministry of Environment, 56 pp (manuscript, in Bulgarian).
Michev, T., M. Stoyneva, V. Velev & N. Michov, 1993. Preliminary report on ecological study of Srebarna Lake, Ministry of Education, 62 pp (manuscript, in Bulgarian).
Moss, B., 1983. The Norfolk Broadland: Experiments in the restoration of a complex wetland. Biol. Rev. 58: 521–561.
Naidenov, V., 1965. Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Copepoden und Brachiopodenfauna der bulgarischen Donauueberschwemmungsgebiete. Bull. zool. Inst. (Sofia), XIX: 5–54 (in Bulgarian, German summ.).
Olrik, K., 1994. Phytoplankton – Ecology. Ministry of the Environment, Denmark, Danish Environmental Protection Agency, 183 pp.
Olrik, K. & A. Nauwerck, 1993. Stress and disturbance in the phytoplankton community of a shallow, hypertrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 249: 15–24.
Padisák, J., 1993a. Species composition, spatial distribution, and the seasonal and interannual dynamics of phytoplankton in brown-water lakes enclosed with reedbelts (Neusiedlersee/Ferto; Austria/ Hungary). BFB – Bericht 79: 13–29.
Padisák, J., 1993b. The influence of different disturbance frequences on the species richness, diversity and equitability of phytoplankton in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 249: 135–156.
Pearsall, W. H., 1932. Phytoplankton in the English Lakes. II. The composition of the phytoplankton in relation to dissolved substances. J. Ecol. 20: 241–262.
Radev, V. (ed.), 1993. Project ‘Recovery of the biosphere reserve Srebarna’. Waterengineering Ltd., Sofia, October 1993 (in Bulgarian).
Reynolds, C. S., 1984. The ecology of freshwater phytoplankton. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 384 pp.
Reynolds, C. S., 1987. The response of phytoplankton communities to changing lake environments and the response of phytoplankton. Freshwat. Biol. 23: 25–53.
Reynolds, C. S., 1993. Scales of disturbance and their role in plankton ecology. Hydrobiologia. 249: 157–171.
Reynolds, C. S., 1994. The long, the short and the stalled: on the attributes of phytoplankton selected by physical mixing in lakes and rivers. In J.–P. Descy, C. S. Reynolds & J. Padisák (eds), Phytoplankton in Turbid Environments: Rivers and Shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 289: 9–22.
Reynolds, C. S., 1996. Further remarks on phytoplankton ecology and trophic degree (manuscript), 7 pp.
Reynolds, C. S. & E. G. Bellinger, 1992. Pattern of abundance and dominance of the phytoplankton of Rostherne Mere, England: evidence from an 18 year data set. Aquat. Sci. 54: 11–36.
Reynolds, C. S., J.–P. Descy & J. Padisák, 1994. Are phytoplankton dynamics in rivers so different from those in shallow lakes? In J.–P. Descy, C. S. Reynolds & J. Padisák (eds), Phytoplankton in Turbid Environments: Rivers and Shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 289: 1–8.
Reynolds, C. S. & G. H. Jaworski, 1978. Enumeration of natural Microcystis population. Br. Phycol. J. 13: 269–277.
Rodhe, W., 1969. Crystallisation of eutrophication concepts in northern Europe. In G. A. Rochlich (ed.), Eutrophication: causes, consequences, correctives. Washington: 50–64.
Rojo, C. & M. Alvarez-Cobelas, 1993. Hypertrophic phytoplanktona and the Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis. Hydrobiologia 249: 43–57.
Rott, E., 1984. Phytoplankton as biological parameter for the trophic characterization of lakes. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 1078–1085.
Smith, V. H., 1990. Phytoplankton responses to eutrophication in inland waters. In I. Akatsuka (ed.), Introduction to Applied Phycology, SPB Acad. Publ., The Hague, The Netherlands: 231–249.
Sommer, U., 1993. The scientific bases of eutrophication management: reconcycling basic physiology and empirical biomass models. In R. de Bernardi, R. Pagnotta, A. Pugnetti (eds), Strategies for lake ecosystems beyond 2000. Mem. Ist. ital. Idrobiol. 52: 89–111.
Sommer, U., Z. M. Gliwicz, W. Lampert & A. Duncan, 1986. The PEG-model of seasonal succession of planctonic events in freshwaters. Arch. Hydrobiol. 106: 433–471.
Stoyneva, M., 1991. Algal flora of the River Danube (Bulgarian sector) and its adjacent water basins. Ph. D. Thesis, Sofia University, Sofia, 372 pp. (in Bulgarian, English abstr.).
Stoyneva, M. & St. Draganov, 1994. Algal flora of the River Danube (Bulgarian sector) and its adjoined water basins. IV. Contribution to the algal flora of some adjoined water basins. Ann. Univ. Sof. 84: 15–24.
Stoyneva, M. & T. Michev. Srebarna case: habitat changes as reflected by waterfowl. In J. Kerekes & S. Farago (eds), Proceed. SIL Workshop on Aquatic birds, Sopron, Hungary, 16–23 November, 1994 (in press).
Tilman, D., S. S. Kilham & P. Kilham, 1982. Phytoplankton community ecology: the role of limiting nutrients. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 13: 343–372.
Trifonova, I. S., 1989. Changes in community structure and productivity of phytoplankton as indicators of lake and reservoir eutrophication. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 33: 363– 371.
Trifonova, I. S., 1990. Ecology and succession of lake phytoplankton. Nauka, Leningrad, 184 (in Russian).
Vollenweider, R. A., 1989. Global problems of eutrophication and its control. In J. Salanki & S. Herodek (eds), Conservation and management of lakes, Akad. Kiadó, Budapest: 19–42.
Vollenweider, R. & J. Kerekes, 1982. Eutrophication of water: Monitoring, assessment and control. OECD, Paris, 154 pp.
Vörös, L. & P. N. Göde, 1993. Long term changes of phytoplankton in Lake Balaton (Hungary). Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 25: 682–686.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoyneva, M.P. Development of the phytoplankton of the shallow Srebarna Lake (north-eastern Bulgaria) across a trophic gradient. Hydrobiologia 369, 259–267 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017015825018
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017015825018