Abstract
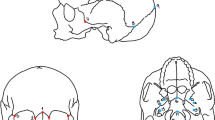
Fluctuating asymmetry (FA), the random differences between the left and right sides of a bilaterally symmetrical character, is often purported to be a sensitive measure of developmental instability particularly in populations exposed to environmental stressors. As the level of developmental instability increases, often too does the level of FA. In this study we tested the hypothesis that exposure of pregnant mice to low doses of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlordibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) would increase the level of FA in the mandibles of their offspring. We used ten landmark coordinates around the mandible to create a single size variable (centroid size) and 20 Procrustes shape variables. These were used to test for effects of dioxin on mandible size and shape and their asymmetries. We found no detectable effect of TCDD on levels of FA in either size or shape of the mandible, but TCDD did produce a significant decrease in mandible size, and a significant effect on the overall shape.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, B.D. and Birnbaum, L.S. (1990). TCDD-induced altered expression of growth factors may have a role in producing cleft palate and enhancing the incidence of clefts after coadministration of Retinoic Acid and TCDD. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 106, 418–32.
Abbott, B.D., Perdew, G.H. and Birnbaum, L.S. (1994). Ah receptor in embryonic mouse palate and effects of TCDD on receptor expression. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 126, 16–25.
Alaluusua, S., Lukinmaa, P., Pohjanvirta, R., Unkila, M. and Toumisto, J. (1993). Exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlordibenzopara-dioxin leads to defective dentin formation and pulpal perforation in rat incisor tooth. Toxicology 81, 1–13.
Auffray, J., Alibert, P., Renaud, S., Orth, A. and Bonhomme, F. (1996). Fluctuating asymmetry in Mus musculus subspecific hybridization: Traditional and Procrustes comparative approach. In L.F. Marcus, M. Corti, A. Loy, G.J.P. Naylor and D.E. Slice (eds) Advances in Morphometrics. New York: Plenum Press.
Badyaev, A.V., Foresman, K.M. and Fernandes, M.V. (2000). Rapid environmental change and developmental stability: Vegetation removal causes increased fluctuating asymmetry in free-living shrew populations. Ecology 81, 336–45.
Birnbaum, L.S. (1995). Developmental effects of dioxins. Environmental Health Perspectives 10(7), 89–94.
Bookstein, F.L. (1991). Morphometric Tools for Landmark Data: Geometry and Biology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Bryant, P.L., Clark, G.C., Probst, M.R. and Abbott, B.D. (1997). Effects of TCDD on Ah receptor, ARNT, EGF, and TGF-a expression in embryonic mouse urinary tract. Teratology 55, 326–37.
Clarke, G.M. (1995). Relationship between developmental stability and fitness: Application for conservation biology. Conservation Biology 9, 18–24.
Clarke, G.M. and Ridsdill-Smith, T.J. (1990). The effect of Avermectin B1 on developmental stability in the bush fly, Muscavetustissima, as measured by fluctuating asymmetry. Entomology Experimental and Applied 54, 265–9.
Couture, L.A., Abbot, B.D. and Birnbaum, L.S. (1990). A critical review of the developmental toxicity and teratogenicity of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin: Recent advances toward understanding the mechanism. Teratology 42, 619–27.
Dryden, I.L. and Mardia, K.V. (1998). Statistical Analysis of Shape. Chichester: Wiley.
Falconer, D.S. and Mackay, T.F.C. (1996). Introduction to Quantitati¨e Genetics. Essex: Longman.
Fitzgerald, C.T. Fernandez-Salguero, P., Gonzalez, F.J., Nebert, D.W. and Puga, A. (1996). Differential regulation of mouse Ah receptor gene expression in cell lines of different tissue origins. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 333, 170–8.
Geyer, H.J., Schramm, K-W., Scheunert, I., Schugart, K., Buters, J., Wurst, W., Greim, H., Kluge, F., Steinberg, C.E.W., Kettrup, A., Maddukar, B., Olson, J.R. and Gallo, M.A. (1997). Considerations on genetic and environmental factors that contribute to resistance or sensitivity of mammals including humans to toxicity of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and related compounds. Part 1: Genetic factors affecting the toxicity of TCDD. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 36, 213–30.
Gierthy, J.F., Lincoln, D.W., Gillespie, M.B., Seeger, J.I., Martinez, H.L., Dickerman, H.W. and Kumar, S.A. (1987). Suppression of estrogen-regulated extracellular plasminogen activator activity of MCF-7 cells by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Cancer Research 47, 6198–203.
Gierthy, J.F., Silkworth, J.B., Tassinari, M., Stein, G.S. and Lian, J.B. (1994). 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorolibenzo-p-dioxin inhibits differentiation of normal diploid rat osteoblasts in vitro. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 54, 231–8.
Graham, J.H., Emlen, J.M. and Freeman, D.C. (1993). Developmental stability and its applications in ecotoxicology. Ecotoxicology 2, 175–84.
Graham, J.H., Freeman, D.C. and Emlen, J.M. (1994). Antisymmetry, directional asymmetry, and dynamic morphogenesis. In T.A. Markow (ed) Developmental Instability: Origins and E¨olutionary Significance. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Graham, J.H., Roe, K.E. and West, T.B. (1993). Effects of lead and benzene on the developmental stability of Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicology 2, 185–95.
Gray, T.K., Flynn, T.C., Gray, K.M. and Nabell, L.M. (1987). 17 beta-estradiol acts directly on the clonal osteoblastic cell line UMR106. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science 84(17), 6267–71.
Harris, M., Zacharewski, T. and Safe, S. (1990). Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related compounds on the occupied nuclear estrogen receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cell. Cancer Research 50, 3579–84.
Kaufman, M.H. (1992). The Atlas of Mouse Development. San Diego: Academic Press.
Klingenberg, C.P. and McIntyre, G.S. (1998). Geometric morphometrics of developmental instability: Analyzing patterns of fluctuating asymmetry with procrustes methods. Evolution 52(5), 1363–75.
Leamy, L.J. (1984). Morphometric studies in inbred and hybrid house mice. V. Directional and fluctuating asymmetry. American Naturalist 123, 579–3.
Leamy, L.J., Doster, M.J. and Huet-Hudson, Y.M. (1999). Effects of methoxychlor on directional and fluctuating asymmetry of mandible characters in mice. Ecotoxicology 8, 63–71.
Leamy, L.J., Routman, E.J. and Cheverud, J.M. (1997). A search for quantitative trait loci affecting asymmetry of mandibular characters in mice. Evolution 51, 957–69.
Moore, J.A., Gupta, B.N., Zinkl, J.G. and Vos, J.G. (1973). Postnatal effects of maternal exposure to 2,3,7,8-Tetra-chlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Environmental Health Perspectives 5, 81–5.
Neubert, D., Zens, P., Rothenwallner, A. and Merker, H.J. (1973). A survey of the embryotoxic effects of TCDD in mammalian species. Environmental Health Perspectives 5, 67–79.
Palmer, A.R. (1994). Fluctuating asymmetry analyses: A primer. In T.A. Markow (ed) De¨elopmental Instability: Its Origins and E¨olutionary Implications. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Palmer, A.R. and Strobeck, C. (1992). Fluctuating asymmetry as a measure of developmental stability: Implications of non-normal distributions and power of statistical tests. Acta Zoologica Fennica 191, 57–72.
Pankakoski, E., Koivisto, I. and Hyvarinen H. (1992). Reduced developmental stability as an indicator of heavy metal pollution in the common shrew Sorex araneus. Acta Zoologica Fennica 191, 137–44.
Partanen, A., Alaluusua, S., Miettinen, P.J., Thesloff, I., Tuomisto, J., Pohjanvirta, R. and Lukinmaa, P. (1998). Epidermal growth factor receptor as a mediator of developmental toxicity of dioxin in mouse embryonic teeth. Laboratory Investigation 78(12), 1473–81.
Peters, J.M., Narotsky, M.G., Elizondo, G., Fernandez-Saluero, P.M., Gonzalez, F.J. and Abbott, B.D. (1999). Amelioration of the TCDD-induced teratogenesis in aryl hydrocarbon receptor AhR-null mice. Toxicological Science 47, 86–92.
Peterson. R.E., Theobald, H.M. and Kimmel, G.L. (1993). Developmental and reproductive toxicity of dioxins and related compounds: Cross-species comparisons. Critical Reviews in Toxicology 23(3), 283–335.
Siegel, M.I. and Doyle, W.J. (1975). Stress and fluctuating limb asymmetry in various species of rodents. Growth 39, 363–9.
Siegel, P., Siegel, M.I., Krimmer, E.C., Doyle, W.J. and Barry, III, H. (1977). Fluctuating dental asymmetry as an indicator of the stressful prenatal effects of D9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the laboratory rat. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 42, 339–44.
Slice, D.E., Bookstein, L.F. and Rohlf, F.J. (1996). A glossary for geometric morphometrics. In L.F. Marcus, M. Corti, A. Loy, G.J.P. Naylor and D.E. Slice (eds) Advances in Morphometrics. New York: Plenum Press.
Sokal, R.R. and Rohlf, J.F. (1995). Biometry, 3rd ed. San Francisco: Freeman.
Swaddle, J.P., Cuthill, I.C. and Witter, M.S. (1994). The analysis of fluctuating asymmetry. Animal Behavior 48, 986–9.
Turner, R.T., Colvard, D.S. and Spelsberg, T.C. (1990). Estrogen inhibition of periosteal bone formation in rat long bones: Down-regulation of gene expression for bone matrix proteins. Endocrinology 127(3), 1346–51.
Valentine, D.W., Soule, M.E. and Samallow, P. (1973). Asymmetry analysis in fishes: A possible statistical indicator of environmental stress. Fisheries Bulletin 71(2), 357–69.
Van Valen, L. (1962). A study of fluctuating asymmetry. Evolution 16, 125–42
Vanden Huevel, J.O. and Lucier. G. (1993). Environmental toxicology of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Environmental Health Perspectives 100, 189–200.
Waddington, C.H. (1942). Canalization of development and the inheritance of acquired characters. Nature 150, 563–5.
Woods, R.E., Sgro, C.M., Hercus, M.J. and Hoffmann, A.A. (1999). The association between fluctuating asymmetry, trait variability, trait heritability, and stress: A multiply replicated experiment on combined stresses in Drosophila melanogastor. Evolution 53, 493–505.
Zakharov, V.M. and Yablokov, A.V. (1990). Skull asymmetry in the Baltic Grey Seal: Effects of environmental pollution. Ambio 19(5), 266–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allen, D.E., Leamy, L.J. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin Affects Size and Shape, But Not Asymmetry, of Mandibles in Mice. Ecotoxicology 10, 167–176 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016693911300
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016693911300