Abstract
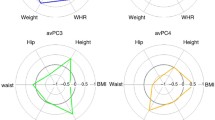
Using methods of mathematical statistics the relationships were determined between 31 anthropometric traits (ATs) and the frequency of the X-monosome cell clone in 53 patients with either 45,X-monosomy or mosaic forms (45,X/46,XX) of the Shereshevsky–Turner syndrome (STS). AT variations were studied in patients untreated with growth hormone and in 25 control fertile healthy women. In 29 patients, the degree of mosaicism was assessed by interphase FISH analysis using X-centromer-specific DNA probe hybridized to the cell nuclei of two types of tissues differing in embryonic origin (lymphocytes and oral epithelium, originating from meso- and ectoderm, respectively). The level of X-monosome mosaicism had a substantial effect on some AT, which depended similarly on the proportion of X-monosome cells in tissues of different embryonic origin. Statistically significant negative correlations were revealed between the size of X-monosome clone and 13 height–weight, longitudinal, and circumference traits, whereas positive correlations were characteristic of seven mostly width traits. Eleven ATs showed no correlation with the X-monosome cell clone. Discriminant analysis of all ATs, whose variations depended on the frequency of X-monosome cell clone, was found to be an essential tool for precise classification of both STS patients with different degree of mosaicism and healthy women. Based on these results, the set of ATs characteristic of the STS phenotype was identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Davidenkova, E.F., Verlinskaya, D.K., and Tysyachnyuk, S.F., Klinicheskie sindromy pri anomal'nykh polovykh khromosomakh (Clinical Syndromes Associated with Sex Chromosome Abnormalities), Leningrad: Meditsyna, 1973.
Nielsen, J. and Wohlert, M., Sex Chromosome Abnormalities Found among 34 910 Newborn Children: Results from a 13-Year Incidence Study in Aarhus, Denmark, Birth. Defects, 1990, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 209-223.
Bochkov, N.P., Zakharov, A.F., and Ivanov, V.I., Meditsinskaya genetika (Medical Genetics), Moscow: Meditsyna, 1984.
Hassold, T., Pettay, D., Robinson, A., and Uchida, I., Molecular Studies of Parental Origin and Mosaicism in 45,X Conceptuses, Hum. Genet., 1992, vol. 89, no. 6, pp. 647-652.
Ikeda, Y., Higurashi, M., Egi, S., et al., An Anthropometric Study of Girls with the Ullrich-Turner Syndrome, Am. J. Med. Genet., 1982, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 271-280.
Sarkar, R. and Marimuthu, K.M., Association between the Degree of Mosaicism and the Severity of Syndrome in Turner Mosaics and Klinefelter Mosaics, Clin. Genet., 1983, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 420-428.
Vignetti, P., Tarani, L., Cives, C., et al., A Clinical and Cytogenetic Study of 50 Women with Turner's Syndrome: Considerations of the Problem of Pregnancies in These Patients, Part 2, Minerva Pediatr., 1991, vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 295-304.
Suri, M., Kabra, M., Jain, U., et al., A Clinical and Cytogenetic Study of Turner Syndrome, Ind. Pediatr., 1995, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 433-442.
Flynn, M.T., Ekstrom, L., De Arce, M., et al., Prevalence of Renal Malformation in Turner Syndrome, Pediatr. Nephrol., 1996, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 498-500.
Mazzanti, L., Cacciari, E., Bergamaschi, R., et al., Pelvic Ultrasonography in Patients with Turner Syndrome: Age-Related Findings in Different Karyotypes, J. Pediatr., 1997, vol. 131, no. 1, pp. 135-140.
Avtandilov, G.G., Meditsinskaya morfometriya. Rukovodstvo (Medical Morphometry: A Manual), Moscow: Meditsyna, 1990.
Lichter, P. and Cremer, T., Chromosome Analysis by Non-Isotopic in situ Hybridization, Human Cytogenetics: A Practical Approach, Rooney, D.E. and Czepulkowski, B.H., Eds., New York: Oxford Univ. Press, 1992, vol. 1, pp. 157-192.
Lil'in, V.T., Trubnikov, V.I., and Vanyukov, M.M., Vvedenie v sovremennuyu farmakogenetiku (Introduction to Modern Pharmacogenetics), Moscow: Meditsyna, 1984.
Nazarenko, S.A., Timoshevskii, V.A., and Ostroverkhova, N.V., Interphase Analysis of X Aneuploidy in Various Tissues of Healthy Individuals by Fluorescent in situ Hybridization, Genetika (Moscow), 1997, vol. 33, no. 10, pp. 1426-1430.
Trubnikov, V.I. and Gindilis, V.M., Multidimensional Genetic Analysis of Anthropometric Traits: I. Genetic Correlation of Traits, Vopr. Antropol., 1980, no. 64, pp. 94-106.
Borovikov, V.P., Populyarnoe vvedenie v programmu STATISTICA (Accessible Introduction to the STATISTICA Program), Moscow: Komp'yuterPress, 1998.
Tyurin, Yu.N. and Makarov, A.A., Statisticheskii analiz dannykh na komp'yutere (Computer-Aided Statistical Data Analysis), Moscow: INFRA-M, 1998.
Partsch, C.J., Pankau, R., Sippell, W.G., and Tolksdorf, M., Normal Growth and Normalization of Hypergonadotropic Hypogonadism in Atypical Turner Syndrome (45,X/46,XX/47,XXX): Correlation of Body Height with Distribution of Cell Lines, Eur. J. Pediatr., 1994, vol. 153, no. 6, pp. 451-455.
Zhukovskii, M.A., Khrisanfova, E.N., Berzina, S.V., and Blagoveshchenskaya, T.A., Somatic Characterization of Children with Shereshevsky-Turner Syndrome, Pediatriya, 1973, no. 10, pp. 18-20.
Brook, C.G.D., Murset, G., Zachmann, M., and Prader, A., Growth in Children with 45,XO Turner's Syndrome, Arch. Disease Childhood, 1974, vol. 49, pp. 789-795.
Palmer, S.G. and Reichmann, A., Chromosomal and Clinical Finding in 110 Females with Turner Syndrome Hum. Genet., 1976, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 35-49.
Baron, R., Jose, A., Padron, D.R.S., and Arse, H.B., Antropometria en la disgenesia gonadal tumeriana, Gine-Dips, 1979, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 103-107.
Pelz, L., Timm, D., Eyermann, E., et al., Body Height in Turner's Syndrome, Clin. Genet., 1982, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 62-66.
Ranke, M.B., Pfluger, H., Rosendahl, W., et al., Turner Syndrome: Spontaneous Growth in 150 Cases and Reviewed Literature, Eur. J. Pediatr., 1983, vol. 141, no. 2, pp. 81-88.
Varella, J., Vinkka, H., and Alvesalo, L., The Phenotype of 45,X Females: An Anthropometric Quantification, Ann. Hum. Biol., 1984, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 53-66.
Lyon, A.J., Preece, M.A., and Grant, D.B., Growth Curve for Girls with Turner Syndrome, Arch. Disease Childhood, 1985, vol. 60, pp. 932-935.
Massa, G., Vanderschueren-Lodeweyckx, M., and Malvaux, P., Linear Growth in Patients with Turner Syndrome: Influence of Spontaneous Puberty and Parental Height, Eur. J. Pediatr., 1990, vol. 149, pp. 246-250.
Pelz, L., Sager, G., Hinkel, G.K., et al., Delayed Spontaneous Pubertal Growth Spurt in Girls with the Ullrich-Turner Syndrome, Am. J. Med. Genet., 1991, vol. 40, no. 4, pp. 401-405.
Haeusler, G., Schemper, M., Frisch, H., et al., Spontaneous Growth in Turner Syndrome: Evidence for a Minor Pubertal Growth Spurt, Eur. J. Pediatr., 1992, vol. 151, no. 4, pp. 283-287.
Haeusler, G. and Frisch, H., Methods for Evaluation of Growth in Turner's Syndrome: Critical Approach and Review of the Literature, Acta Paediatr., 1994, vol. 83, pp. 309-314.
Bernasconi, S., Larizza, D., Benso, L., et al., Turner's Syndrome in Italy: Familial Characteristics, Neonatal Date, Standards for Birth Weight and for Height and Weight from Infancy to Adulthood, Acta Paediatr., 1994, vol. 83, pp. 292-298.
Kaplowitz, P. and Webb, J., Diagnostic Evaluation of Short Children with Height 3 SD or More Below the Mean, Clin. Pediatr., 1994, vol. 33, no. 9, pp. 530-535.
Cabrol, S., Saab, C., Gourmelen, M., et al., Turner Syndrome: Spontaneous Growth of Stature, Weight Increase and Accelerated Bone Maturation, Arch. Pediatr., 1996, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 313-318.
Sempe, M., Hansson, B.C., and Limoni, C., Growth Curves in Untreated Ullrich–Turner Syndrome: French Reference Standard 1-22 Years, Eur. J. Pediatr., 1996, vol. 155, no. 10, pp. 862-869.
Gravholt, S.H. and Naeraa, R.W., Reference Values for Body Proportions and Body Composition in Adult Women with Ullrich-Turner Syndrome, Am. J. Med. Genet., 1997, vol. 72, pp. 403-408.
Nazarenko, S.A., Timoshevsky, V.A., and Sukhanova, N.N., High Frequency of Tissue-Specific Mosaicism in Turner Syndrome Patients, Clin. Genet., 1999, vol. 56, no. 1, pp. 59-65.
Rongen-Westerlaken, C., Rikken, B., Vastrick, P., et al., Body Proportions in Individuals with Turner Syndrome: The Dutch Growth Hormone Working Group, Eur. J. Pediatr., 1993, vol. 152, no. 10, pp. 813-817.
Papenhausen, P.R., Mueller, O.T., Bercu, V., et al., Cell Line Segregation in a 45,X/46,XY Mosaic Child with Asymmetric Leg Growth, Clin. Genet., 1991, vol. 40, no. 3, pp. 237-241.
Kaiser, C. and Abt, K., Recognizing Ullrich-Turner Syndrome by Discriminant Analysis of Craniofacial Structure, Am. J. Med. Genet., 1996, vol. 62, pp. 113-119.
Eggert, P., Pankau, R., and Oldigs, H.D., How Necessary Is a Chromosomal Analysis in Growth-Retarded Girls?, Clin. Genet., 1990, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 351-354.
Ross, J.L., Kushner, H., and Zinn, A.R., Discriminant Analysis of the Ullrich-Turner Syndrome Neurocognitive Profile, Am. J. Med. Genet., 1997, vol. 72, pp. 275-280.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazarenko, S.A., Sukhanova, N.N. The Effect of the X-Monosome Cell Clone Frequency on Anthropometric Variation in Patients with Shereshevsky–Turner Syndrome. Russian Journal of Genetics 37, 553–560 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016679001531
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016679001531