Abstract
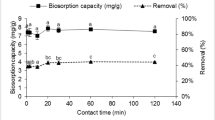
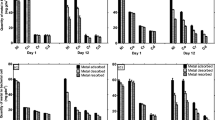
In order to clarify the binding states of copper in microbial cells, copper biosorption from aqueous systems using the chemically treated Micrococcus luteus IAM 1056 cells (hot water-treated, diluted NaOH-treated, chloroform–methanol-treated, and chloroform–methanol/concentrated KOH-treated cells) was examined. The intact cells of M. luteus adsorbed 527 μmol of copper per g cells, and its copper adsorption was very rapid and was affected by the solution pH. The chloroform–methanol/concentrated KOH-treated cells showed higher copper biosorption capacity than the intact and the other chemically treated cells. The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) parameters, g ∥ and |A ∥|, of Cu(II) ion in microbial cells indicate that Cu(II) ion in the intact and all the chemically treated cells have coordination environments with nitrogen and oxygen as donor atoms, being similar to those of type II proteins. The parameter g ∥ also indicated that the coupling between Cu(II) ion and the cell materials in the CHCl3–MeOH/concentrated KOH-treated cells is rather more stable than those between Cu(II) ion and the cell materials in the other treated cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abragam, A. & Pryce, H.M.L. 1951 Theory of the nuclear hyperfine structure of paramagnetic resonance spectra in crystals. Proceedings of the Royal Society A205, 135–153.
Brady, D. & Duncan, J.R. 1994 Bioaccumulation of metal cations by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 41, 149–154.
Beveridge, T.J. & Murray, R.G.E. 1980 Sites of metal deposition in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. Journal of Bacteriology 141, 876–887.
Chang, J.S., Law, R. & Chang, C.C. 1997 Biosorption of lead, copper, and cadmium by biomass of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PU21. Water Research 31, 1651–1658.
Cotoras, D., Viedema, P., Cifuentes, L. & Mestre, A. 1992 Sorption of metal ions by whole cells of Bacillus and Micrococcus. Environmental Technology 13, 551–559.
Gersmann, H.R. & Swalen, J.D. 1962 Electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of copper complexes. Journal of Chemical Physics 36, 3221–3233.
Huang, C. & Huang, C.P. 1996 Application of Aspergillus oryzae and Rhyzopus oryzae for Cu(II) removal. Water Research 30, 1985–1900.
Karna, R.R., Uma, L., Subramanian, G. & Mohan, P.M. 1999 Biosorption of toxic metal ions by alkali-treated biomass of a marine cyanobacterium, Phormidium valderianum BDU 30501. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 15, 729–732.
Kapoor, A., Viraraghaven, T. & Cullimore, D.R. 1999 Removal of heavy metals using fungus Aspergillus niger. Bioresource Technology 70, 95–104.
Macaskie, L.E. 1995 Copper tolerance, phosphatase activity and copper uptake by a heavy metal-accumulating Citrobacter species. Microbios 84, 137–153.
Martell, A.E. & Hancock, R.D. 1996 Metal Complexes in aqueous Solutions. Chapter 2, Plenum Press, New York and London. ISBN 0–306–45248–0.
Matheickal, J.T. & Yu, Q. 1999 Biosorption of lead(II) and copper(II) from aqueous solutions by pre-treated biomass of Australian marine algae. Bioresource Technology 69, 223–229.
Mattuschka, B., Straube, G. & Trevors, J.T. 1994 Silver, copper, lead and zinc accumulation by Pseudomonas stutzeri AG259 and Streptomyces albus: electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray studies. BioMetals 7, 201–208.
Nakajima, A., Horikoshi, T. & Sakaguchi, T. 1981 Studies on the accumulation of heavy metal elements in biological systems. XVII. Selective accumulation of heavy metal ions by Chlorella regularis. Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 12, 76–83.
Nakajima, A. & Sakaguchi, T. 1986 Selective accumulation of heavy metals by microorganisms. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 24, 59–64.
Peisach, J. & Blumberg, W.E. 1974 Structural implications derived from the analysis of electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of natural and artificial copper proteins. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 165, 691–708.
Philip, L., Iyengar, L. & Venkobachar, C. 1995 Biosorption of copper(II) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. International Journal of Environmental Pollution 5, 92–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakajima, A., Yasuda, M., Yokoyama, H. et al. Copper biosorption by chemically treated Micrococcus luteus cells. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 17, 343–347 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016638230043
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016638230043