Abstract
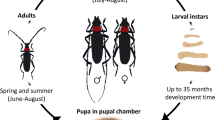
The herringbone leaf-mining fly, Ophiomyiacamarae Spencer, is a promising candidateagent for the biological control of the alieninvasive weed Lantana camara L. in SouthAfrica. During extensive host-specificity testsinvolving 39 test plant species from 12families, survival to adulthood was restrictedto L. camara, L. trifolia, and fourspecies of the closely-related genus Lippia (Verbenaceae) in no-choice tests. However, survival of the immature stages wassignificantly lower on L. trifolia andthe four Lippia species than on L.camara. In addition, O. camaraedisplayed very strong oviposition preferencefor L. camara during paired-choice tests.This narrow laboratory host range suggests thatO. camarae will not pose any risks tonon-target verbenaceous plants if released inSouth Africa. Permission to release O. camaraeinto South Africa was approved by the regulatoryauthorities in 2001.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baars, J-R. and S. Neser, 1999. Past and present initiatives on the biological control of Lantana camara (Verbenaceae) in South Africa. African Entomology, Memoir. 1: 21–33.
Balciunas, J.K., D.W. Burrows and M.F. Purcell, 1996. Comparison of the physiological and realized host-ranges of a biological control agent from Australia for the control of the aquatic weed, Hydrilla verticillata. Biological Control 7: 148–158.
Blossey, B., 1995. Impact of Galerucella pusilla and G. calmariensis (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on field populations of purple loosestrife (Lythrum salicaria). In: E.S Delfosse and R.R. Scott (eds), Proceedings of the VIII International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia. pp. 27–31.
Broughton, S., 2000. Review and evaluation of Lantana biocontrol programs. Biological Control 12: 272–286.
Cilliers, C.J. and S. Neser, 1991. Biological control of Lantana camara (Verbenaceae) in South Africa. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 37: 57–75.
Cullen, J. M., 1990. Current problems in host-specificity screening. In: E.S. Delfosse (ed), Proceedings of the VII International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, Istituto Sperimentale per la Patologia Vegetale, Rome, Italy, 1988. pp. 27–36.
Oosthuizen, M.J., 1964. Biological control of Lantana camara in Natal. Journal of the Entomological Society of Southern Africa 27: 3–16.
Palmer, W.A. and K.R. Pullen, 1995. The phytophagous arthropods associated with Lantana camara, L. hirsita, L. urticifolia and L. urticoides (Verbenaceae) in North America. Biological Control 5: 54–72.
Salvo, A. and G. Valladares, 1999. Parasitoid assemblage size and host ranges in a parasitoid (Hymenoptera)-agromyzid (Diptera) system from central Argentina. Bulletin of Entomological Research 89: 193–197.
Seawright, A.A., 1965. Toxicity of Lantana spp. in Queensland. Australian Veterinary Journal 48(1): 235–338.
Stegmaier, C.E., 1966. A leaf miner on Lantana in Florida, Ophiomyia camarae (Diptera: Agromyzidae). Florida Entomologist 49(3): 151–152.
Spencer, K.A., 1963. Synopsis of the Neotropical Agromyzidae (Diptera). Transactions of the Entomological Society of London 115: 291–389.
Taylor, E.E., 1989. A history of biological control of Lantana camara in New South Wales. Plant Protection Quarterly 4: 61–65.
Wapshere, A.J., 1974. A strategy for evaluating the safety of organisms for biological control of weeds. Annals of Applied Biology 77: 201–211.
Winder, J.A. and K.L.S. Harley, 1983. The phytophagous insects on Lantana in Brazil and their potential for biological control in Australia. Tropical Pest Management 29: 346–362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simelane, D. Biology and host range of Ophiomyia camarae, a biological control agent for Lantana camara in South Africa. BioControl 47, 575–585 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016541809545
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016541809545