Abstract
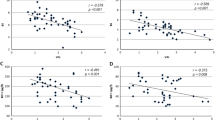
Objective: In this study we test the hypothesis of a nonlinear relationship of IGF-I with indices of body fat such as body mass index (BMI), insulin, and leptin. Methods: The controls used in three case–control cancer studies nested in the Northern Sweden Health and Disease Cohort, were combined for this analysis. Measurements of plasma IGF-I, IGFBP-3, insulin, and leptin were available for 445 men and 391 women. Results: In both men and women we found the highest mean IGF-I levels in subjects with BMI between 24 and 26. IGF-I concentrations decreased toward BMI ≤ 20 and BMI > 30 in men; however, the results for women did not reach statistical significance. The molar ratio of IGF-I/IGFBP-3 showed a similar profile to that of IGF-I, although much less pronounced. The observed peak mean IGF-I levels in the second quintiles of insulin and leptin in men supported these findings. No significant variation of mean IGF-I levels across quintiles of insulin and leptin were observed in women. Conclusions: The results of this study provide evidence that IGF-I plasma concentrations vary substantially over a wide range of body weight and that the relationship is nonlinear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Colditz GA, et al. (1998) Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of breast cancer. Lancet 351: 1393-1396.
Peyrat JP, Bonneterre J, Hecquet B, et al. (1993) Plasma insulinlike growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentrations in human breast cancer. Eur J Cancer 29A: 492-497.
Kaaks R, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A, et al. (2000) Serum Cpeptide, insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-binding proteins, and colorectal cancer risk in women. J Natl Cancer Inst 92: 1592-1600.
Ma J, Pollak MN, Giovannucci E, et al. (1999) Prospective study of colorectal cancer risk in men and plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3. J Natl Cancer Inst 91: 620-625.
Stattin P, Bylund A, Rinaldi S, et al. (2000) Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I, insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. J Natl Cancer Inst 92: 1910-1917.
Chan JM, Stampfer MJ, Giovannucci E, et al. (1998) Plasma insulin-like growth factor-I and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Science 279: 563-566.
Clemmons DR, Underwood LE (1991) Nutritional regulation of IGF-I and IGF binding proteins. Annu Rev Nutr 11: 393-412.
Kaaks R, Lukanova A (2001) Energy balance and cancer: the role of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I. Proc Nutr Soc 60: 91-106.
Argente J, Caballo N, Barrios V, et al. (1997) Multiple endocrine abnormalities of the growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor axis in patients with anorexia nervosa: effect of short-and long-term weight recuperation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82: 2084-2092.
Hill KK, Hill DB, McClain MP, Humphries LL, McClain CJ (1993) Serum insulin-like growth factor-I concentrations in the recovery of patients with anorexia nervosa. J Am Coll Nutr 12: 475-478.
Counts DR, Gwirtsman H, Carlsson LM, Lesem M, Cutler GB (1992) The effect of anorexia nervosa and refeeding on growth hormone-binding protein, the insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), and the IGF-binding proteins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 75: 762-767.
Forbes GB, Brown MR, Welle SL, Underwood LE (1989) Hormonal response to overfeeding. Am J Clin Nutr 49: 608-611.
Thissen JP, Ketelslegers JM, Underwood LE (1994) Nutritional regulation of the insulin-like growth factors. Endocrinol Rev 15: 80-101.
Yamamoto H, Kato Y (1993) Relationship between plasma insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) levels and body mass index (BMI) in adults. Endocrinol J 40: 41-45.
Copeland KC, Colletti RB, Devlin JT, McAuliffe TL (1990) The relationship between insulin-like growth factor-I, adiposity, and aging. Metabolism 39: 584-587.
Marin P, Kvist H, Lindstedt G, Sjostrom L, Bjorntorp P (1993) Low concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I in abdominal obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 17: 83-89.
Palmqvist R, Hallmans G, Rinaldi S, et al. (2001) Plasma IGF-I, IGF-binding protein-3 and risk of colorectal cancer: a prospective study in northern Sweden. Gut (In press).
Kaaks R, Lundin E, Manjer J, et al. (2001) Prospective study of IGF-I, IGF-binding proteins and breast cancer risk, in Northern and Southern Sweden. Cancer Causes Control (In press).
SAS Institute (1990). SAS/STATR User's Guide Version 6. SAS Manual 4[6]. Cary, NC: SAS Institute.
Ayabe T, Tsutsumi O, Sakai H, et al. (1997) Increased circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and decreased circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 in postmenopausal women with endometrial cancer. Endocrinol J 44: 419-424.
Yu H, Spitz MR, Mistry J, Gu J, Hong WK, Wu X (1999) Plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and lung cancer risk: a case-control analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst 91: 151-156.
Toniolo P, Bruning PF, Akhmedkhanov A, et al. (2000) Serum insulin-like growth factor-I and breast cancer. Int J Cancer 88: 828-832.
Anonymous (2001) Weight Control and Physical Activity. Lyon: IARC.
Stattin P, Soderberg S, Hallmans G, et al. (2001) Leptin is associated with increased prostate cancer risk: a nested case-referent study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 1341-1345.
Lukanova A, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A, et al. (2001) A crosssectional study of IGF-I determinants in women. Eur J Cancer Prev 10: 443-452.
Deurenberg P, Weststrate JA, Seidell JC (1991) Body mass index as a measure of body fatness: age-and sex-specific prediction formulas. Br J Nutr 65: 105-114.
Lonnqvist F, Thome A, Nilsell K, Hoffstedt J, Arner P (1995) A pathogenic role of visceral fat beta 3-adrenoceptors in obesity. J Clin Invest 95: 1109-1116.
Marin P, Andersson B, Ottosson M, et al. (1992) The morphology and metabolism of intraabdominal adipose tissue in men. Metabolism 41: 1242-1248. Relationship of IGF-I with indices of adiposity 515
Kissebah AH, Vydelingum N, Murray R, et al. (1982) Relation of body fat distribution to metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 54: 254-260.
Evans DJ, Hoffmann RG, Kalkhoff RK, Kissebah AH (1984) Relationship of body fat topography to insulin sensitivity and metabolic profiles in premenopausal women. Metabolism 33: 68-75.
Kirschner MA, Samojlik E, Drejka M, Szmal E, Schneider G, Ertel N (1990) Androgen-estrogen metabolism in women with upper body versus lower body obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 70: 473-479.
Kaye SA, Folsom AR, Soler JT, Prineas RJ, Potter JD (1991) Associations of body mass and fat distribution with sex hormone concentrations in postmenopausal women. Int J Epidemiol 20: 151-156.
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocrinol Rev 16: 3-34.
Baxter RC, Turtle JR (1978) Regulation of hepatic growth hormone receptors by insulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 84: 350-357.
Tollet P, Enberg B, Mode A (1990) Growth hormone (GH) regulation of cytochrome P-450IIC12, insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), and GH receptor messenger RNA expression in primary rat hepatocytes: a hormonal interplay with insulin, IGF-I, and thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol 4: 1934-1942.
Baumann G, Mercado M (1993) Growth hormone-binding proteins in plasma. Nutrition 9: 546-553.
Bereket A, Lang CH, Blethen SL, Ng LC, Wilson TA (1996) Insulin treatment normalizes reduced free insulin-like growth factor-I concentrations in diabetic children. Clin Endocrinol Oxf 45: 321-326.
Argente J, Caballo N, Barrios V, et al. (1997) Disturbances in the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis in children and adolescents with different eating disorders. Horm Res 48 (Suppl. 4).
Bereket A, Lang CH, Wilson TA (1999) Alterations in the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res 31: 172-181.
Kelley KM, Oh Y, Gargosky SE, et al. (1996) Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBPs) and their regulatory dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 28: 619-637.
Nam SY, Lee EJ, Kim KR, et al. (1997) Effect of obesity on total and free insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, and their relationship to IGF-binding protein (BP)-1, IGFBP-2, IGFBP-3, insulin, and growth hormone. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 21: 355-359.
Wabitsch M, Blum WF, Muche R, et al. (1996) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins before and after weight loss and their associations with hormonal and metabolic parameters in obese adolescent girls. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 20: 1073-1080.
Nyomba BL, Berard L, Murphy LJ (1997) Free insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in healthy subjects: relationship with IGF-binding proteins and insulin sensitivity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82: 2177-2181.
Frystyk J, Vestbo E, Skjaerbaek C, Mogensen CE, Orskov H (1995) Free insulin-like growth factors in human obesity. Metabolism 44: 37-44.
Tannenbaum GS, Guyda HJ, Posner BI (1983) Insulin-like growth factors: a role in growth hormone negative feedback and body weight regulation via brain. Science 220: 77-79.
Chapman IM, Hartman ML, Pieper KS, et al. (1998) Recovery of growth hormone release from suppression by exogenous insulinlike growth factor I (IGF-I): evidence for a suppressive action of free rather than bound IGF-I. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83: 2836-2842.
Maccario M, Grottoli S, Aimaretti G, et al. (1998) IGF-I levels in different conditions of low somatotrope secretion in adulthood: obesity in comparison with GH deficiency. Panminerva Med 40: 98-102.
Pombo M, Pombo CM, Astorga R, et al. (1999) Regulation of growth hormone secretion by signals produced by the adipose tissue. J Endocrinol Invest 22: 22-26.
Casanueva FF, Dieguez C (1998) Interaction between body composition, leptin and growth hormone status. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab 12: 297-314.
Casanueva FF, Villanueva L, Dieguez C, et al. (1987) Free fatty acids block growth hormone (GH) releasing hormone-stimulated GH secretion in man directly at the pituitary. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 65: 634-642.
Scacchi M, Pincelli AI, Cavagnini F (1999) Growth hormone in obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 23: 260-271.
Seck T, Englaro P, Blum WF, et al. (1998) Leptin concentrations in serum from a randomly recruited sample of 50-to 80-year-old men and women: positive association with plasma insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF-binding protein-3 in lean, but not in obese, individuals. Eur J Endocrinol 138: 70-75.
WHO Expert Committee (1995) Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Geneva: WHO; WHO Technical Report Series no. 854. 516 A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lukanova, A., Söderberg, S., Stattin, P. et al. Nonlinear relationship of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-I/IGF-binding protein-3 ratio with indices of adiposity and plasma insulin concentrations (Sweden). Cancer Causes Control 13, 509–516 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016392129279
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016392129279