Abstract
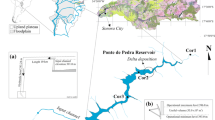
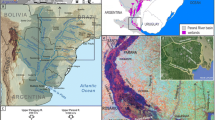
The regulation of the Jamari River advanced peak floods by 1–2 months and increased dry-season discharges from 60 to 200 m3 s−1, resulting in water levels approximately 1 m above those recorded before regulation. Daily variation in water level associated with fluctuations in electricity production by the dam propagated to the lower reaches of the tributary Candeias River. Dissolved oxygen (DO), temperature, pH, and conductivity measured over 1.5 years on three locations along the regulated and two free-flowing rivers indicated important alterations in the case of oxygen concentrations. DO levels shifted from saturated (7–8 mg l−1) during the flood season (when the spillways were open releasing epilimnetic water) to hypoxic (1.5–3 mg l−1) during the dry season (when the floodgates were closed and only hypolimnetic water used to run the turbines was feeding the river). Fluctuations in water level and variation in dissolved oxygen tended to be greater at the site closest to the dam, gradually attenuating downstream. Mitigation of the downstream effects of river regulation would require modifications in the operation of the dam.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcifa, M. S., C. G. Froehlich & S. M. F. Gianesella-Galvão, 1981. Circulation patterns and their influence on physicochemical and biological conditions in eight reservoirs in Southern Brazil. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 20: 1054–1059.
Bain, M. B., J. T. Finn & H. E. Booke, 1988. Streamflow regulation and fish community structure. Ecology 69: 382–392.
Baker, B. W. & G. L. Wright, 1978. The Murray valley: its hydrological regime and the effects of water development on the river. Proc. r. Soc. Vict. 90: 103–110.
Barrow, C. J., 1988. The impact of hydroelectric development on the Amazonian environment with particular reference to the Tucurui Project. J. Biogeogr. 15: 67–78.
Brasil, 1985. Diagnóstico dos recursos hídricos: Avaliação do regime hidrometereológico do noroeste do Brasil-Programa POLONOROESTE. Ministério das Minas e Energia, Departamento Nacional de Águas e Energia Elétrica, Brasília, DF, Brazil: 204 pp.
Cadman, J. D., 1989. Energy from the Amazon. Civ. Engng. 59(12): 54–57.
Cassidy, R. A. & P. E. Dunn, 1987. Water temperature control and areal oxygen consumption rates at a new reservoir, and the effects on the release water. In Craig, J. F. & J. B. Kemper (eds), Regulated Streams: Advances in Ecology. Plenum Press, New York: 339–351.
Craig, J. F. & J. B. Kemper, 1987. Regulated Streams: Advances in Ecology. Plenum Press, New York: 431 pp.
Dolan, R., A. Howard & A. Gallenson, 1974. Man's impact on the Colorado River in the Grand Canyon. Am. Sci. 62: 392–401.
ELETRONORTE, 1988. Estudos de impacto ambiental (EIA), v. 2 – Metodologia e diagnóstico ambiental. Report # SAM-70-2360-03. Brasília, DF, Brazil: 264 pp.
ELETRONORTE, 1990. Usina Hidroelétrica Samuel. Departamento de Comunicação Social – ELETRONORTE, Brasília, DF, Brazil: 28 pp.
ELETRONORTE, 1993. Estação Ecológica de Samuel, Rondônia, Brasil: Plano de manejo (versão preliminar). Departamento de Meio Ambiente – ELETRONORTE, Brasília, DF, Brazil: 40 pp.
ELETRONORTE, 1994. Precipitação pluviométrica (mm) e vazões máximas e mínimas. ERGS – ELETRONORTE, Porto Velho, Rondônia, Brazil: 1 pp.
ELETRONORTE/SONDOTÉCNICA, 1976. Relatório de reconhecimento do local da Usina de Samuel. Brasília, DF, Brazil: 14 pp.
ELETRONORTE/SONDOTÉCNICA, 1978. Relatório da campanha hidrosedimentométrica e climatológica. Report no. SAM-10-3177-RE, Brasília, DF, Brazil: 226 pp.
ELETRONORTE/SONDOTÉCNICA, 1989. Derivação das águas da bacia do Rio Candeias para a ampliação da geração na UHE Samuel, resumo do Estudo de pré-viabilidade. Report # SAM-75-1001 RE, Brasília, DF, Brazil: 80 pp.
Froehlich, C. G., M. S. Arcifa-Zago & M. A. J. de Carvalho, 1978. Temperature and oxygen stratification in Americana Reservoir, State of São Paulo, Brazil. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 20: 1710–1719.
Guy, P. R., 1980. River bank erosion in the mid-Zambezi valley, downstream of Lake Kariba. Biol. Conserv. 19: 199–212.
Imevbore, A. M. A., 1967. Hydrology and plankton of Eleiyele Reservoir, Ibadan, Nigeria. Hydrobiologia 30: 154–176.
Junk, W. J. & J. A. S. Nunes de Mello, 1987. Ipactos ecológicos das represas hidrelétricas na bacia Amazônica brasileira. In Kohlhepp, G. & A. Schrader (eds), Homem e Natureza na Amazônia. Tübinger Geographische Studien 95, Tübinger, Germany: 367–385.
King, R. D. & P. A. Tyler., 1982. Downstream effects of the Gordon River power development, South-west Tasmania. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 33: 431–442.
Kinsolving, A. D. & M. B. Bain, 1993. Fish assemblage recovery along a riverine disturbance gradient. Ecol. Applic. 3: 531–544.
Klammer, G., 1984. The relief of the extra-Andean Amazon Basin. In Sioli, H. (ed), The Amazon: Limnology and Landscape Ecology of a Mighty Tropical River and its Basin. Dr W. Junk Publishers, Dordecht: 47–83.
Lehmkuhl, D. M., 1972. Change in thermal regime as a cause of reduction of benthic fauna downstream of a reservoir. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 29: 1329–1332.
Mozeto, A. A., T. A. Stone, I. F. Brown & D. L. Skole, 1990. O uso do sistema geográfico de informação e de sensoriamento remoto na avaliaç7#x00E3;o do impacto ambiental na Estação Ecológica da UHE Samuel, Rondônia, Brasil. Interciencia 15: 265–271.
Petts, G. E., 1984. Impounded Rivers. John Wiley & Sons, New York: 326 pp.
Petts, G. E., 1990. Regulation of large rivers: Problems and possibilities for environmentally-sound river development in South America. Interciencia 15: 388–395.
Ribeiro, M. C. L. B., M. Petrere Jr. & A. F. Juras, 1995. Ecological integrity and fisheries ecology of the Araguaia-Tocantins river basin, Brazil. Regul. Riv. 11: 325–350.
Santos, U. M., M. N. G. Ribeiro & A. C. F. N. S. Tancredi, 1986/87. Estudo preliminar sobre a hidroquímica da bacia de JaciParaná (RO). Acta amaz. 16/17 Sup.: 143–150.
Sioli, H., 1984. The Amazon and its main affluents: hydrography, morphology of the river courses, and river types. In Sioli, H. (ed.), The Amazon: Limnology and Landscape Ecology of a Mighty Tropical River and its Basin. Dr W. Junk Publishers, Dordrecht: 127–165.
Skole, D. & C. Tucker, 1993. Tropical deforestation and habitat fragmentation in the Amazon: Satellite data from 1978 to 1988. Science 260: 1905–1910.
Sreenivasan, A., 1964. A hydrological study of a tropical impoundment, Bhavanisagar Reservoir, Madras State, India, for the years 1955–61. Hydrobiologia 24: 514–539.
Stone, T. A., I. F. Brown & G. M. Woodwell, 1991. Estimation, by remote sensing, of deforestation in central Rondônia, Brazil. For. Ecol. Manage. 38: 291–304.
Trotzky, H. W. & R. W. Gregory, 1974. The effects of water flow manipulation below a hydroelectric power dam on the bottom fauna of the upper Kennebec River, Maine. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 103: 318–324.
Tundisi, T. M., J. G. Tundisi, A. Saggio, A. L. Oliveira Neto & E. G. Sp#x00ED;ndola, 1991. Limnology of the Samuel Reservoir (Brazil, Rondônia) in the filling phase. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 24: 1482–1488.
Turner, R. M. & M. M. Karpiscak, 1980. Recent vegetation changes along the Colorado River between Glen Canyon dam and Lake Mead, Arizona. Prof. Pap. U.S. geol. Surv. no. 1132: 125 pp.
Vanicek, C. D., R. H. Kramer & D. R. Franklin, 1970. Distribution of Green River fishes in Utah and Colorado following closure of the Flamming Gorge dam. The Southwestern Naturalist 14: 297–315.
Walker, K. F., T. J. Hilmann & W. D. Williams, 1978. Effects of impoundments on rivers: An Australian case study. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 20: 1695–1701.
Ward, J. V. & J. A. Stanford, 1979. The Ecology of Regulated Streams. Plenum Press, New York: 398 pp.
Ward, J. V. & J. A. Stanford, 1987. The ecology of regulated streams: Past accomplishments and directions for future research. In Craig, J. F. & J. B. Kemper (eds), Regulated Streams: Advances in Ecology. Plenum Press, New York: 391–409.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viana, J.P. Physical and chemical post-dam alterations in the Jamari River, a hydroelectric-developed river of the Brazilian Amazon. Hydrobiologia 472, 235–247 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016389919574
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016389919574