Abstract
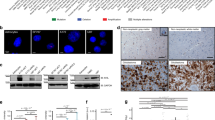
Hyaluronan binding to its cellular receptors CD44 and ICAM-1 appears to enhance the malignant behavior of tumors, including astrocytomas. RHAMM/IHABP, another hyaluronan receptor, has been identified in breast carcinoma cells, but its presence in astrocytomas is yet undetermined. Herein, we report that a monoclonal antibody against plectin (a cytoskeletal protein linker) recognizes on Western blots of U-373 MG glioblastoma cells, a 300-kDa band corresponding to plectin and two bands of 86 and 70 kDa. cDNA cloning and Northern blotting reveals that these two bands represent isoforms of RHAMM/IHABP. Sequence comparisons suggest that the plectin monoclonal antibody recognizes RHAMM/IHABP because this protein and plectin share short peptide sequences of similar primary and secondary structure. Western blotting demonstrates that most human astrocytoma tissues and cell lines express the 86- and 70-kDa isoforms of RHAMM/IHABP. Interestingly, the 70-kDa variant is undetectable in normal brain tissues and in primary cultures of astrocytes suggesting that its expression is tumor-specific. Transfection experiments with epitope-tagged RHAMM/IHABP cDNA established that RHAMM/IHABP associates with microtubules in astrocytoma cells, while in normal astrocytes it either co-localizes with microtubules or has a diffuse cytoplasmic distribution. This suggests that RHAMM/IHABP has the capacity to bind to microtubules in normal and transformed astrocytes, and that neoplasia may favor this association.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee JY, Spicer AP: Hyaluronan: a multifunctional, megadalton, stealth molecule. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12: 581–586, 2000
Baltuch GH, de Tribolet N, Van Meir EG: Expression of the CD44 adhesion molecule in tumours of the central and peripheral nervous system. J Neuro-Oncol 26: 191–198, 1995
Gingras MC, Roussel E, Bruner JM, Branch CD, Moser RP: Comparison of cell adhesion molecule expression between glioblastoma multiforme and autologous normal brain tissue. J Neuroimmunol 57: 143–153, 1995
Kuppner MC, Van Meir E, Gauthier T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N: Differential expression of the CD44 molecule in human brain tumours. Int J Cancer 50: 572–577, 1992
Maenpaa A, Kovanen PE, Paetau A, Jaaskelainen J, Timonen T: Lymphocyte adhesion molecule ligands and extracellular matrix proteins in gliomas and normal brain: expression of VCAM-1 in gliomas. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 94: 216–225, 1997
Vitolo D, Paradiso P, Uccini S, Ruco LP, Baroni CD: Expression of adhesion molecules and extracellular matrix proteins in glioblastomas: relation to angiogenesis and spread. Histopathology 28: 521–528, 1996
Delpech B, Maingonnat C, Girard N, Chauzy C, Maunoury R, Olivier A, Tayot J, Creissard P: Hyaluronan and hyaluronectin in the extracellular matrix of human brain tumour stroma. Eur J Cancer 29A: 1012–1017, 1993
Steck PA, Moser RP, Bruner JM, Liang L, Freidman AN, Hwang TL, Yung WK: Altered expression and distribution of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in human gliomas. Cancer Res 49: 2096–2103, 1989
Koochekpour S, Pilkington GJ, Merzak A: Hyaluronic acid/CD44H interaction induces cell detachment and stimulates migration and invasion of human glioma cells in vitro. Int J Cancer 63: 450–454, 1995
Radotra B, McCormick D: CD44 is involved in migration but not spreading of astrocytoma cells in vitro. Anticancer Res 17: 945–949, 1997
Radotra B, McCormick D: Glioma invasion in vitro is mediated by CD44–hyaluronan interactions. J Pathol 181: 434–438, 1997
Wiranowska M, Tresser N, Saporta S: The effect of interferon and anti-CD44 antibody on mouse glioma invasiveness in vitro. Anticancer Res 18: 3331–3338, 1998
Gunia S, Hussein S, Radu DL, Putz KM, Breyer R, Hecker H, Samii M, Walter GF, Stan AC: CD44s-targeted treatment with monoclonal antibody blocks intracerebral invasion and growth of 9L gliosarcoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 17: 221–230, 1999
Breyer R, Hussein S, Radu DL, Putz KM, Gunia S, Hecker H, Samii M, Walter GF, Stan AC: Disruption of intracerebral progression of C6 rat glioblastoma by in vivo treatment with anti-CD44 monoclonal antibody. J Neurosurg 92: 140–149, 2000
Hardwick C, Hoare K, Owens R, Hohn HP, Hook M, Moore D, Cripps V, Austen L, Nance DM, Turley EA: Molecular cloning of a novel hyaluronan receptor that mediates tumor cell motility. J Cell Biol 117: 1343–1350, 1992
Entwistle J, Zhang S, Yang B, Wong C, Li Q, Hall CL, Mowat M, Greenberg AH, Turley EA: Characterization of the murine gene encoding the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM. Gene 1995 163: 233–238, 1995
Turley EA: Hyaluronan and cell locomotion. Cancer Rev Metast 11: 21–30, 1992
Hofmann M, Fieber C, Assmann V, Gottlicher M, Sleeman J, Plug R, Howells N, von Stein O, Ponta H, Herrlich P: Identification of IHABP, a 95 kDa intracellular hyaluronate binding protein. J Cell Sci 111: 1673–1684, 1998
Assmann V, Jenkinson D, Marshall JF, Hart IR: The intracellular hyaluronan receptor RHAMM/IHABP interacts with microtubules and actin filaments. J Cell Sci 112: 3943–3954, 1999
Assmann V, Marshall JF, Fieber C, Hofmann M, Hart IR: The human hyaluronan receptor RHAMM is expressed as an intracellular protein in breast cancer cells. J Cell Sci 111: 1685–1694, 1998
Hall CL, Yang B, Yang X, Zhang S, Turley M, Samuel S, Lange LA, Wang C, Curpen GD, Savani RC, Greenberg AH, Turley EA: Overexpression of the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM is transforming and is also required for H-ras transformation. Cell 82: 19–26, 1995
McCarthy KD, de Vellis J: Preparation of separate astroglial and oligodendroglial cell cultures from rat cerebral tissue. J Cell Biol 85: 890–902, 1980
Kleihues P, Burger PC, Scheithauer BW: The new WHO classification of brain tumors. Brain Pathol 3: 255–268, 1993
Yang HY, Lieska N, Goldman AE, Goldman RD: A300,000–mol-wt intermediate filament-associated protein in baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. J Cell Biol 100: 620–631, 1985
Avrameas S, Ternynck T: The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry 6: 53–66, 1969
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC: Measurement of proteins using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150: 76–85, 1985
Sultana S, Zhou R, Sadagopan MS, Skalli O: Effects of growth factors and basement membrane proteins on the phenotype of U-373MGglioblastoma cells as determined by the expression of intermediate filament proteins. Am J Pathol 153: 1157–1168, 1998
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685, 1974
Towbin M, Staehelin Y, Gordon J: Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from acrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 4350–4354, 1979
Johnstone A, Thorpe R: Immunochemistry in Practice, 3rd edn, Blackwell Science, Oxford, 1996
Olmsted JB: Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogenous protein samples. J Biol Chem 256: 11955–11957, 1981
Lieska N, Yang HY, Goldman RD: Purification of the 300K intermediate filament-associated protein and its in vitro recombination with intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol 101: 802–813, 1985
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning, a Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989
D'alessio JM, Bebee R, Hartley JL, Noon MC, Polayes M: Lambda Zip Lox: automatic subcloning of cDNA. Focus 14: 76–79, 1992
Young RA, Davis RW: Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 1194–1198, 1985
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467, 1997
Zhou R, Skalli O: TGF-α differentially regulates GFAP, vimentin and nestin gene expression in U-373MG glioblastoma cells. Correlation with cell shape and motility. Exp Cell Res 254: 269–278, 2000
Wiche G: Role of plectin in cytoskeleton organization and dynamics. J Cell Sci 111: 2477–2486, 1998
Errante LD, Wiche G, Shaw G: Distribution of plectin, an intermediate filament-associated protein, in the adult rat central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 37: 515–528, 1994
Foisner R, Bohn W, Mannweiler K, Wiche G: Distribution and ultrastructure of plectin arrays in subclones of rat glioma C6 cells differing in intermediate filament protein (vimentin) expression. J Struct Biol 115: 304–317, 1995
Lie AA, Schroder R, Blumcke I, Magin TM, Wiestler OD, Elger CE: Plectin in the human central nervous system: predominant expression at pia/glia and endothelia/glia interfaces. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 96: 215–221, 1998
Clubb BH, Chou YH, Herrmann H, Svitkina TM, Borisy GG, Goldman RD: The 300–kDa intermediate filament-associated protein (IFAP300) is a hamster plectin ortholog. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273: 183–187, 2000
Weitzer G, Wiche G: Plectin from bovine lenses. Chemical properties, structural analysis and initial identification of interaction partners. Eur J Biochem 169: 41–52, 1987
Wang C, Entwistle J, Hou G, Turley EA: The characterization of a human RHAMM cDNA: conservation of the hyaluronan-binding domains. Gene 174: 299–306, 1996
Liu CG, Maercker C, Castanon MJ, Hauptmann R, Wiche G: Human plectin: organization of the gene, sequence analysis, and chromosome localization (8q24). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: 4278–4283, 1996
Spicer AP, Roller ML, Camper SA, McPherson JD, Wasmuth JJ, Hakim S, Wang C, Turley EA, McDonald JA: The human and mouse receptors for hyaluronan-mediated motility, RHAMM, genes (HMMR) map to human chromosome 5q33.2–qter and mouse chromosome 11. Genomics 30: 115–117, 1995
Wechsler-Reya R, Scott MP: The developmental biology of brain tumors. Annu Rev Neurosci 24: 385–428, 2001
Hall CL, Wang C, Lange LA, Turley EA: Hyaluronan and the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM promote focal adhesion turnover and transient tyrosine kinase activity. J Cell Biol 126: 575–588, 1994
Shouthern JA, Young DF, Heaney F, Baumgartner W, Randall RE: Identification of an epitope on the P and V proteins of simian virus 5 that distinguishes between two isolates with different biological characteristics. J Gen Virol 72: 1551–1557, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, R., Wu, X. & Skalli, O. The Hyaluronan Receptor RHAMM/IHABP in Astrocytoma Cells: Expression of a Tumor-specific Variant and Association with Microtubules. J Neurooncol 59, 15–26 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016373015569
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016373015569