Abstract
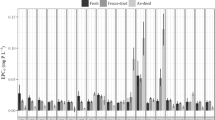
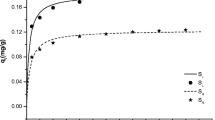
To understand the effects of drying on phosphorus sorption properties of wetland sediment, the acid ammonium oxalate and citrate-dithionite-bicarbonate (CDB) extractions were applied to sediments from seven shallow lakes near Perth, Western Australia. Air-drying generally led to a marked increase in oxalate- and CDB-extractable Fe, but not in extractable-Al which varied less than 2%. Air-drying also induced changes in equilibrium concentration, labile potential and sorption capacity of phosphorus in reflooded sediments. These were accompanied by changes in pH, turbidity, E440 and soluble Fe3+ in the water. The FeOx/FeCDB ratios of wet and air-dried sediments suggested an increase in iron crystallinity upon drying, correlated with the decrease in P-sorption capacity (R 2= 0.72, p < 0.05).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arenas, V. & G. De La Lanza, 1981. The effect of dried and cracked sediment on availability of phosphorus in a coastal lagoon. Estuaries 4: 206–212.
Bostöm, B., J. M. Andersen, S. Fleicher & M. Jansson, 1988. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediment–water interface. Hydrobiologia 170: 229–244.
Buller, A. J. & J. McManus, 1979. Sediment sampling and analysis. In Dyer, K. R. (ed.), Estuarine Hydrography and Sedimentation: A Handbook. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge: 87–131.
De Datta, S. K., 1964. Diss. Abstr. 25: 716.
De Groot, C. J. & A. Fabre, 1993. The impact of desiccation of a freshwater marsh (Garcines Nord, Camargue, France) on sediment–water–vegetation interactions. Part 3. The fractionation composition and the phosphate adsorption characteristics of the sediment. Hydrobiologia 252: 105–116.
Fabre, A., 1988. Experimental studies on some factors influencing phosphorus solubilization in connection with the drawdown of a reservoir. Hydrobiologia 159: 153–158.
Feldma, D. S. Jr., J. Gagnon, R. Hofmann & J. Simpson, 1987. StatView II, the Solution for Data Analysis and Presentation of Graphs. Abacus Concepts, Inc.
Forster, S. & G. Graf, 1992. Continuously measured changes in redox potential influenced by oxygen penetrating from burrows of Callianassa subterranean. Hydrobiologia 235–236: 527–532.
Håkanson, L. & M. Jansson, 1983. Principles of Lake Sedimentology. Springer-Verlag: Berlin Heidelberg: Germany.
Jackson, M. L., C. H. Lim & L. W. Zelazny, 1986. Oxides, hydroxides and alumininosilicates. In Klute, A. (ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part I. Physical and Mineralogical Methods – Agronomy Monograph 9. 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Inc. Soil Science Society of America, Inc. Madison, Wisconsin: 101–142.
Mclaughlin, I. R., J. C. Ryden & J. K. Syers, 1981. Sorption of inorganic phosphate by iron-and aluminium-containing components. J. Soil Sci. 32: 365–375.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for determination of phosphorus in natural waters. Anal. Chem. Acta 27: 31–36.
Qiu, S. & A. J. McComb, 1994. Effects of oxygen concentration on phosphorus release from reflooded, air-dried wetland sediments. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 45: 1319–1328.
Redshaw, E. J., C. F. Mason, C. R. Hayes & R. D. Roberts, 1990. Factors influencing phosphate exchange across the sediment – water interface of eutrophic reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 192: 223–245.
Rhoton, F. E., J. M. Bigham, L. D. Norton & N. E. Smeck, 1981. Contribution of magnetite to oxalate – extractable iron in soils and sediments from the Maumee River Basin of Ohio. Soil Sci. Soc. am. J. 45: 1981.
Richardson, C. J., 1985. Mechanisms Controlling phosphates retention capacity in Freshwater Wetland. Science 228: 1425–1427.
Ryan, J., D. Curtin & M. A. Cheema, 1985. Significance of iron oxides and calcium carbonate particle size in phosphorus sorption by calcareous soils. Soil Sci. Soc. am. J. 49: 75–77.
Schwertmann, U. 1988. Goethite and hematite formation in the presence of clay minerals and gibbsite at 25 °C, Soil Sci. Soc. am. J. 52: 289–291.
Twinch, A. J., 1987. Phosphate exchange characteristics of wet and dried sediment samples from a hypetrophic reservoir: implications for the measurements of sediment phosphorus status. Water Res. 21: 1225–1230.
Voutsinou–Taliadouri, F. & J. Satsmadjis, 1983. Metals in polluted sediments from the Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Mar. Poll. Bull. 14: 234–236.
William, J. D. H., K. S. John, S. S. Surendra & F. H. Robin, 1971. Levels of inorganic and total phosphorus in lake sediments as related to other sediments parameters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 5: 1113–1120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, S., McComb, A.J. Interrelations between iron extractability and phosphate sorption in reflooded air-dried sediments. Hydrobiologia 472, 39–44 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016317100164
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016317100164