Abstract
Purpose. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of deflazacort after oral administration (30 mg) to healthy volunteers were determined and compared with those of 20 mg of methylprednisolone and 25 mg of prednisolone.
Methods. Methylprednisolone, prednisolone and the active metabolite of deflazacort, 21-desacetyldeflazacort, were measured in plasma using HPLC. For the assessment of pharmacodynamics, differential white blood cell counts were obtained over 24 hours. An integrated pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model was applied to link corticosteroid concentrations to the effect on lymphocytes and granulocytes.
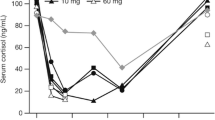
Results. Deflazacort is an inactive prodrug which is converted rapidly to the active metabolite 21-desacetyldeflazacort. Maximum concentrations of 21-desacetyldeflazacort averaged 116 ng/ml and were observed after 1.3 h. The average area under the curve was 280 ng/ml · h, and the terminal half-life was 1.3 h. 21-Desacetyldeflazacort was cleared significantly faster than both methylprednisolone and prednisolone. The PK-PD-model was suitable to describe time course and magnitude of the observed effects. The results were consistent with reported values for glucocorticoid receptor binding affinities for the investigated compounds.
Conclusions. Due to the short pharmacokinetic half-life of its active metabolite, pharmacodynamic effects of deflazacort are of shorter duration than those of methylprednisolone and prednisolone. The PK-PD model allows good prediction of pharmacodynamic effects based on pharmacokinetic and receptor binding data.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
P. Filipponi and A. Blass. Deflazacort: A new glucocorticoid. Drugs of Today 6: 329–334 (1987).
A. Assandri, G. Buniva, E. Martinelli, A. Perazzi, and L. Zerilli. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of deflazacort in the rat, dog, monkey and man. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 171: 9–23 (1984).
J. Q. Rose and W. J. Jusko. Corticosteroid analysis in biological fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 162: 273–280 (1979).
W. F. Ebling, S. J. Szefler, and W. J. Jusko. Analysis, prodrug conversion, reversible metabolism of methylprednisolone. Drug Metab. Disp. 13: 296–304 (1985).
S. J. Szefler, W. F. Ebling, J. W. Georgitits, and W. J. Jusko. Methylprednisolone versus prednisolone pharmacokinetics in relation to dose in adults. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 30: 323–329 (1986).
F. J. Frey. Kinetics and dynamics of prednisolone, Endocrine Reviews; 8: 453–473 (1987).
B. M. Frey, F. J. Frey, N. G. Holford, F. Lozada, L. Z. Benet. Prednisolone pharmacodynamics assessed by inhibition of the mixed lymphocyte reaction. Transplantation 6: 578–584 (1982).
L. E. Fisher, E. A. Ludwig, and W. J. Jusko. Pharmacoimmunodynamics of methylprednisolone: Trafficking of helper T lymphocytes. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 20: 319–331 (1992).
J. A. Wald, R. M. Law, E. A. Ludwig, R. R. Sloan, E. Middleton, W. J. Jusko. Evaluation of dose-related pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of prednisolone in man. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 20: 567–589 (1992).
H. Möllmann, P. Rohdewald, J. Barth, M. Verho, H. Derendorf. Kinetics of methylprednisolone and its hemisuccinate ester. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 37: 502–507 (1985).
J. Barth, M. Damoiseaux, H. Möllmann, K. H. Brandis, G. Hochhaus, and H. Derendorf. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of prednisolone after intravenous and oral administration. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 30: 317–324 (1992).
H. Möllmann, P. Rohdewald, J. Barth, M. Verho, and H. Derendorf. Pharmacokinetics and dose linearity testing of methylprednisolone phosphate. Biopharm. Drug Disp. 10: 453–464 (1989).
A. Tanner, F. Bochner, J. Caffin, J. Halliday, and L. Powell. Dose-dependent prednisolone kinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 24: 571–578 (1979).
F. Luzzani, and A. Glasser. Differential binding in vitro to glucocorticoid receptors of deflazacort and prednisolone. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 76: 427–430 (1981).
P. Rohdewald, H. Möllmann, K. M. Müller, and G. Hochhaus. Glucocorticoid receptors in the respiratory tract. In: Bochumer Treff 1984: Rezeptoren und nervöse Versorgung des bronchopulmonalen Systems, Verlag Gedon & Reuss, Munich, 1985, pp. 223–242.
H. Derendorf, H. Möllmann, M. Krieg, S. Tunn, C. Möllmann, J. Barth, and H. J. Röthig. Pharmacodynamics of methylprednisolone phosphate after single intravenous administration to healthy volunteers. Pharm. Res. 8: 263–268 (1991).
H. Derendorf, G. Hochhaus, H. Möllmann, J. Barth, M. Krieg, S. Tunn, and C. Möllmann. Receptor-based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis of corticosteroids. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 33: 115–123 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Möllmann, H., Hochhaus, G., Rohatagi, S. et al. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of Deflazacort in Comparison to Methylprednisolone and Prednisolone. Pharm Res 12, 1096–1100 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016287104656
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016287104656