Abstract
Purpose. The pulmonary pharmacokinetics and bioactivity of E. coli derived recombinant consensus interferon (CIFN) and a modified lactose-conjugated consensus interferon (LacCIFN) were evaluated in animals.
Methods. Estimated doses of 20 and 100 µg/kg of the interferons were administered to anesthetized rats by aerosol via ultrasonic nebulizer as well as intravenous injection. Rats also received nominal doses of 50 and 200 µg/kg via intratracheal instillation (IT). Hamsters were treated with interferon via various routes including IT. The effectiveness of treatment was assessed by the resistance to development of hind leg paralysis following infection with encephalomyocarditis virus.
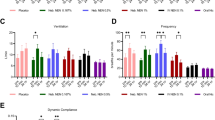
Results. Significant amounts of CIFN and LacCIFN were found in rat plasma after aerosol administration. Peak plasma levels occurred ≈25–30 minutes with estimated bioavailabilities approaching 70%. Absorption of CIFN was rate limiting and plasma levels were detectable 12 hr post-dose. The CIFN at IT doses as low as 5 µg/kg was effective at reducing paralysis in hamsters but protection was variable and doses of up to 100 µg/kg were not 100% effective.
Conclusions. Despite the incomplete protection, the results demonstrate the feasibility of treating systemic viral infections with interferon administered directly to the lungs.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. L. Klein, T. D. Bartley, P. H. Lai, and H. S. Lu. Structural characterization of recombinant consensus interferon-alpha. J. Chromatogr. 454: 205–215, 1988.
M. L. Klein, T. D. Bartley, J. M. Davis, D. W. Whiteley, and H. S. Lu. Isolation and structural characterization of three isoforms of recombinant consensus alpha interferon. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 276: 531–537, 1990.
V. Bocci, G. P. Pessina, A. Pacini, L. Paulesu, M. Muscettola, and K. E. Mogensen. Pulmonary catabolism of interferons: alveolar absorption of 125I-labeled human interferon alpha is accompanied by partial loss of biological activity. Antiviral Res. 4: 211–220, 1984.
V. Kinnula, K. Mattson, and K. Cantell. Pharmacokinetics and toxicity of inhaled human interferon-alpha in patients with lung cancer. J. Interferon Res. 9: 419–423, 1989.
J. S. Patton, P. Trinchero, and R. M. Platz. Bioavailability of pulmonary delivery peptides and proteins: α-interferon, calcitonins and parathyroid hormone. J. Con. Rel. 28: 79–85, 1994.
B. W. Altrock, K. D. Fagin, H. R. Hockman, E. N. Fish, L. Goldstein, D. Chang, K. Duker, and N. Stebbing. Antiviral and antitumor effects of a human interferon analog, IFN-αCon1, assessed in hamsters. J. Interferon Res. 6: 405–415, 1986.
J. L. Liu, B. Peterson, K. L. Whitcomb, M. Woodward, C. Ransone, K. Pippo, D. C. Collins, and A. D. Habberfield. Liver-targeted recombinant consensus interferon. J. Biol. Chem. In review, 1995.
R. W. Niven, A. Y. Ip, C. Ransome, H. Silvers, and T. Arakawa. Stability of recombinant consensus interferon (rCon-IFN) to air-jet and ultrasonic nebulization. J. Pharm. Sci. 84: 1210–1214, 1995.
R. W. Niven, K. L. Whitcomb, O. B. Kinstler, A. Y. Ip, and L. Shaner. The pulmonary absorption of aerosolized and intratracheally instilled rhG-CSF and monoPEGylated rhG-CSF. Pharm. Res. 12: 1143–1349, 1995.
R. W. Niven, F. D. Lott, and J. M. Cribbs. Pulmonary absorption of recombinant methionyl human granulocyte colony stimulating factor (r-huG-CSF) after intratracheal instillation to the hamster. Pharm. Res. 10: 1604–10, 1993.
R. W. Niven, F. D. Lott, A. Y. Ip, and J. M. Cribbs. Pulmonary delivery of powders and solutions containing granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rhG-CSF) to the rabbit. Pharm. Res. 11: 1101–1109, 1993.
R. W. Niven, K. L. Whitcomb, L. Shaner, L. D. Ralph, A. D. Habberfield, and J. V. Wilson. Pulmonary absorption of polyethylene glycolated recombinant human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (PEG rhG-CSF). J. Con. Rel. 32: 177–189, 1994.
S. Kobayashi, S. Kondo, and K. Juni. Study on pulmonary delivery of salmon calcitonin in rats: effects of protease inhibitors and absorption enhancers. Pharm. Res. 11: 1239–1243, 1994.
P. Colthorpe, S. J. Farr, I. J. Smith, D. Wyatt, and G. Taylor. The influence of regional deposition on the pharmacokinetics of pulmonary-delivered human growth-hormone in rabbits. Pharm. Res. 12: 356–359, 1995.
P. Colthorpe, S. J. Farr, G. Taylor, I. J. Smith, and D. Wyatt. The pharmacokinetics of pulmonary-delivered insulin: a comparison of intratracheal and aerosol administration to the rabbit. Pharm. Res. 9: 764–768, 1992.
K. G. Rice, O. A. Weisz, T. Barthel, R. T. Lee, and Y. C. Lee. Defined geometry of binding between triantennary glycopeptide and the asialoglycoprotein receptor of rat heptocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 18429–18434, 1990.
J. D. Brain, D. E. Knudson, S. P. Sorokin, and M. A. Davis. Pulmonary distribution of particles given by intratracheal instillation or by aerosol inhalation. Environ. Res. 11: 13–33, 1976.
J. O. Ford, R. F. Dodson, and M. G. Williams, Jr. An ultrastructural study of the blood/air barrier in the guinea-pig. Tissue Cell 16: 53–63, 1984.
O. S. Atwal, L. Viel, and K. J. Minhas. An uptake of cationized ferritin by alveolar type I cells in airway-instilled goat lung: distribution of anionic sites on the epithelial surface. J. Submicrosc. Cytol. Pathol. 22: 425–432, 1990.
J. Gil, D. A. Silage, and J. M. McNiff. Distribution of vesicles in cells of air-blood barrier in the rabbit. J. Appl. Physiol. 50: 334–340, 1981.
M. C. Williams. Endocytosis in alveolar type II cells: effect of charge and size of tracers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 6054–6058, 1984.
B. T. Peterson, and K. D. Dickerson. Concentration of aerosolized 99mTc-albumin in the pulmonary lymph of anesthetized sheep. J. Appl. Physiol. 68: 1233–1240, 1990.
P. Maasilta, M. Halme, K. Mattson, and K. Cantell. Pharmacokinetics of inhaled recombinant and natural alpha interferon [letter]. Lancet 337: 371, 1991.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niven, R.W., Whitcomb, K.L., Woodward, M. et al. Systemic Absorption and Activity of Recombinant Consensus Interferons After Intratracheal Instillation and Aerosol Administration. Pharm Res 12, 1889–1895 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016279503631
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016279503631